| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
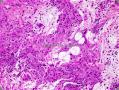
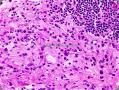
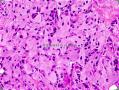
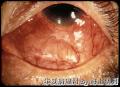
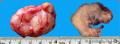
- B1424双眼肿块-上海市骨与软组织读片2013(9)复旦大学附属肿瘤医院提供
| 性别 | 男 | 年龄 | 45岁 | 临床诊断 | 双眼肿胀待查 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般病史 | 双眼凸出、眼眶肿胀、眼睑外翻,病程5年。病变起初累犯右眼,因心脏病延误治疗,病变蔓延至左眼。视力尚好。 | ||||
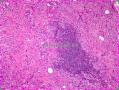
| 标本名称 | 肿块活检 | ||||
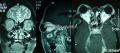
| 大体所见 | 见影像学 | ||||
-
本帖最后由 海上明月 于 2013-09-03 14:32:31 编辑

- 王军臣
相关帖子
-
本帖最后由 jcw62 于 2013-08-16 09:22:30 编辑
发生在结外的Rosai-Dorfman disease (Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy):
一、General
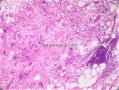
二、Micro description
Large histiocytic cells, frequently spindled, with less conspicuous emperipolesis than nodal lesions; fibroinflammatory component 。
三、Positive stains:
S100,CD68,lysozyme 。
-
本帖最后由 海上明月 于 2013-08-06 09:27:39 编辑
发生在后眼部的病例,要当心颅脑中枢内原发Rosai-Dorfman 病沿着视神经侵入眼部。
Subconjunctival masses associated with central nervous system rosai-dorfman disease.
Source
Department of Ophthalmology, Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, Miami, FL, USA. kcavuoto@med.miami.edu
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To describe a case of subconjunctival masses with multiple intracranial masses diagnosed as Rosai-Dorfman disease by biopsy.
METHODS:
Case report.
RESULTS:
A 25-year-old white man presented with bilateral subconjunctival masses, left optic nerve pallor, and posterior segment changes suggestive of regressed choroidal disease. Systemic evaluation was instituted including blood testing, neuroimaging, brain biopsy, and biopsy of the left subconjunctival mass. Pathologic analysis of the brain and subconjunctival mass biopsies revealed Rosai-Dorfman disease.
CONCLUSIONS:
The authors present a case of extensive extranodal involvement of Rosai-Dorfman of the eye and the central nervous system.

- 王军臣
-
本帖最后由 海上明月 于 2013-08-06 09:24:13 编辑
Rosai-dorfman with bilateral involvement of lacrimal sac as extranodal disease.
Source
Guru Nanak Eye Centre, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India. drskamal@gmail.com
Abstract
A 45 year old female presented with painless swelling over the inner side of both eyes since one year. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed well defined lesions in the bilateral lacrimal sac area with extension along the naso-lacrimal duct. Systemic work up showed polyclonal hyperglobulinemia, raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and anemia. The patient also had subcutaneous swelling in thoracic area over back. The histopathology of the bilateral excised tumor and fine needle aspiration cytology of thoracic swelling was consistent with features of Rosai-Dorfman syndrome.
下列发生在眼窝
Orbital and adnexal Rosai-Dorfman disease.
PURPOSE:
To report the clinico-radiological findings, clinical course, and treatment outcomes in five patients with orbital and adnexal Rosai-Dorfman (R-D) disease.
METHODS:
Analysis of case records of patients with Rosai-Dorfman disease seen at four orbital units between January 2000 and December 2006.
RESULTS:
Five patients (3 Caucasian males, 1 Hispanic female, and 1 African female), mean age 41.1 years, (range 18 months to 75 years) with orbital or adnexal Rosai-Dorfman disease were seen during the study period. Four of the patients had orbital involvement and one had eyelid involvement. Presenting features were proptosis (4 patients), diplopia (1 patient), epiphora (1 patient), and eyelid thickening (1 patient). Three of the patients with orbital involvement also had adjacent paranasal sinus involvement, and the nasolacrimal duct was involved in one patient. The patient with eyelid involvement had evidence of cutaneous R-D disease elsewhere in the body. The follow-up period (since initial diagnosis of R-D disease) ranged from 1 month to 15 years, and 2 of the patients had a history of recurrent growth despite treatment. Surgical debulking was employed in 2 patients with good results.
CONCLUSIONS:
Orbital and adnexal Rosai-Dorfman disease is a condition with protean manifestations that may show indolent but unremitting growth despite treatment. The disease may remain extranodal and localized for many years. Adjacent paranasal sinus involvement is commonly seen in conjunction with orbital disease, simulating midline destructive lesions. Surgical debulking gives good results in patients with functional or significant cosmetic problems.

- 王军臣