| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
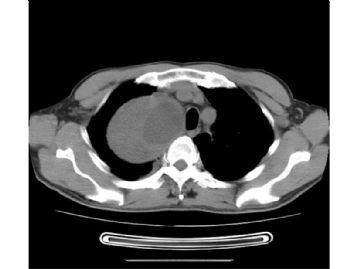
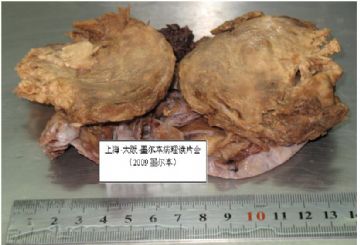
- 右上纵膈肿块(中-日-澳2009墨尔本病理读片会病例1)
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-01-21 01:13:00 编辑
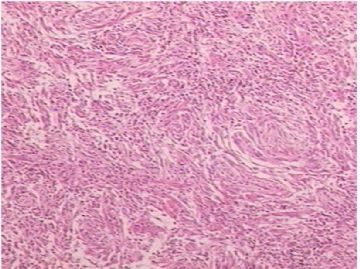
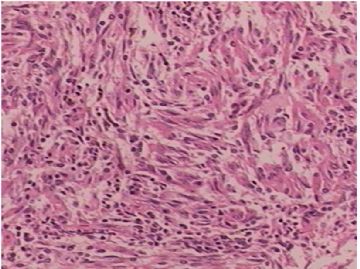
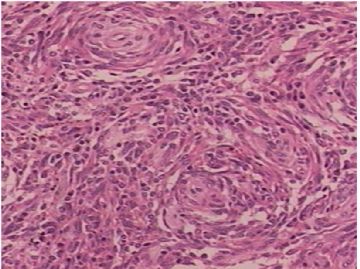
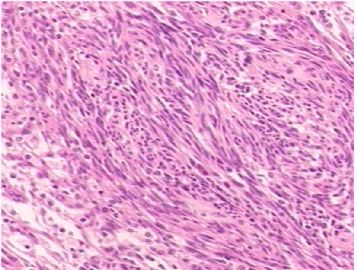
异位脑膜瘤可见于鼻腔、鼻窦、中耳、颈部、皮肤、骨内(尤其是颅骨与颜面部),甚至罕见于纵膈、肺和血管内。有报道在神经鞘膜的同时发生异位脑膜瘤(ectopic meningioma)。
注意要与神经鞘膜瘤(及其神经束膜瘤,S-100一般为阴性)、纤维组织细胞瘤、树突细胞肿瘤、A型胸腺瘤、促纤维增生恶性黑色素瘤和SFT等良恶性肿瘤鉴别。
需注意核分裂计数和肿瘤性坏死以及肿瘤周围浸润情况,以除外恶性。IHC标记可资辅助鉴别诊断。
本例的大体标本和影像显示有局部囊性变和出血。有文献报道,异位脑膜瘤可以因囊变而出血为首发症状。

- 王军臣
J Neurooncol. 1996 Sep;29(3):217-21.
Pathology of meningiomas.
University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Division of Pathology (Neuropathology), Houston, USA.
Because meningiomas arise from arachnoid cells present in the meninges, they can occur in any location where meninges or ectopic meninges exist, such as the nasal cavity, the paranasal sinuses, the middle ear, and even the mediastinum. Although the tumors may range in appearance from epithelial to mesenchymal, they are characterized by a uniform distribution of cells with shapes ranging from polygonal epithelial-like to spindled and fusiform. Historically, classification of meningiomas has been based upon cell shapes, cell patterns, cell products, or stroma, implying clinicopathologic differences among the types. Numerous observations have shown that certain conditions may indicate a predisposition for developing meningiomas, prompting extensive studies of meningiomas using cytogenetic techniques. Meningiomas are common neoplasms arising from the central nervous system meninges. They are important because of the morbidity they produce. Their critical intracranial and intraspinal locations make diagnosis and surgical removal difficult.

- 王军臣