| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
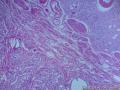
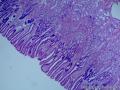
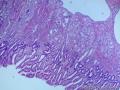
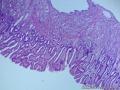
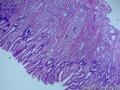
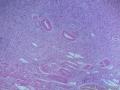
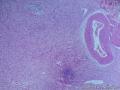
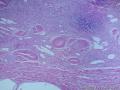
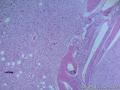
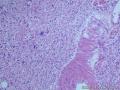
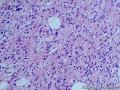
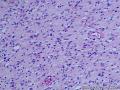
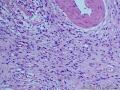
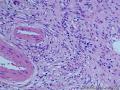
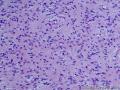
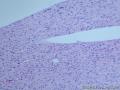
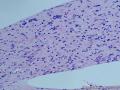
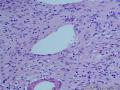
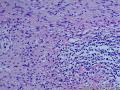
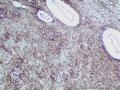
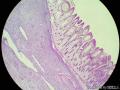
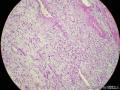
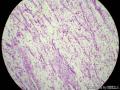
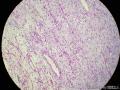
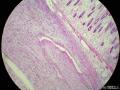
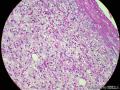
- 胃粘膜下肿块,炎性纤维性息肉?
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:867
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
| 性别 | 男 | 年龄 | 68 | 临床诊断 | 间质瘤 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般病史 | 胃粘膜下肿块 | ||||
| 标本名称 | 胃部分切除标本 | ||||
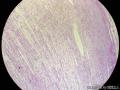
| 大体所见 | 粘膜下肿块2*1.8cm,界清,灰白色 | ||||
相关帖子
-
本帖最后由 kint123 于 2013-10-21 21:02:58 编辑
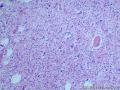
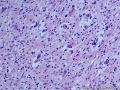
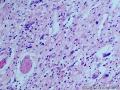
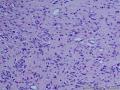
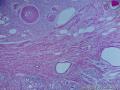
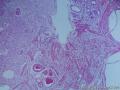
个人认为还是诊断炎性纤维性息肉合适一些
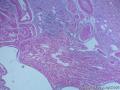
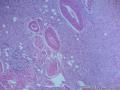
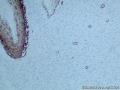
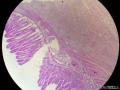
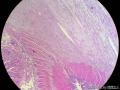
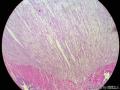
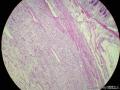
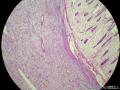
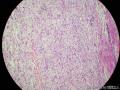
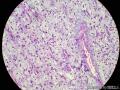
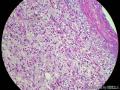
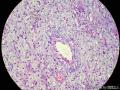
囊性扩张的腺体,畸形的血管,围绕血管的排列方式,散在的嗜酸性粒细胞,间质的异型细胞等,都更类似于息肉,而不是GIST
一些人诊断GIST可能是因为CD34阳性,但炎性纤维性息肉表达vimentin, CD34, calponin,不表达CD117
附上一点说明:引自《Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract, and Pancreas,
INFLAMMATORY FIBROID POLYP
Clinical Features
Inflammatory fibroid polyps are mesenchymal proliferations composed of a mixture of stromal spindle cells, small blood vessels, and inflammatory cells, particularly eosinophils.[190–192] They may occur anywhere in the GI tract but are most common in the stomach and small intestine. In the stomach, inflammatory fibroid polyps usually occur in the sixth decade of life. Recent studies have reported a disproportionately large number of gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps in female patients.[193], [194] Some have suggested an infectious etiology for inflammatory fibroid polyps.[191], [192] However, no causative agent has ever been identified[195]; thus, most observers currently consider inflammatory fibroid polyps to be a form of reactive pseudotumor. When small, these tumors may be discovered incidentally at endoscopy. However, large lesions may cause obstructive symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. In some cases, inflammatory fibroid polyps may contain a long stalk; these may prolapse through the pyloric sphincter and cause obstruction.[196] Some studies suggest that inflammatory fibroid polyps are more common among patients with atrophic gastritis and pernicious anemia.
Pathologic Features
Inflammatory fibroid polyps are typically small, wellcircumscribed, submucosally based, sessile lesions that may show ulceration of the overlying mucosa. Their median size is 1.5cm, and, although most lesions are smaller than 3cm in diameter, polyps that measure as large as 5cm in diameter have been reported. In the stomach, they most commonly arise in the antrum, immediately proximal to, or overlying, the pyloric sphincter.
Microscopically, inflammatory fibroid polyps are submucosal tumors and often show an abrupt demarcation at the level of the muscularis propria. Mucosal involvement is common with gastric lesions. However, unlike small intestinal lesions, involvement of the muscularis propria is unusual in gastric polyps. Extension of the tumor into the mucosa causes separation of gastric glands, which results in a disordered and atrophic appearance. Inflammatory fibroid polyps are composed of a loose mixture of spindle-shaped, plump, cytologically bland stromal cells, inflammatory cells, and small, thin-walled blood vessels in an edematous or myxoid background (Fig. 17-21). In the stomach, stromal cells often proliferate in a concentric fashion around small and medium-sized blood vessels.[197], [198] Mitotic figures are rare but may occasionally be present in deeper portions of the lesion. Atypical mitoses are never present. Eosinophils are a prominent inflammatory component and may also encircle vessels. Larger lesions may show collagen deposition and smooth muscle proliferation, or even giant cell formation.
Immunohistochemically, stromal cells have been reported to be positive for vimentin, CD34, fascin, CD35, cyclin D1, and calponin.[194,197–201] A smaller proportion are also positive for smooth muscle actin, HHF-35, KP-1, and Mac-387.[194,197–201] In contrast to stromal tumors of the GI tract, stromal cells in inflammatory fibroid polyps are negative for CD117 (c-kit).[194], [197] Although the histogenesis of inflammatory fibroid polyps remains controversial, a possible origin in dendritic cells or CD34-positive perivascular cells has been proposed.[194], [201] Differentiating between inflammatory fibroid polyps and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors is discussed next.

- The More We See, The Less We Know!
-
xiaofeng1008 离线
- 帖子:783
- 粉蓝豆:33
- 经验:824
- 注册时间:2013-07-24
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
lantian0508 离线
- 帖子:1250
- 粉蓝豆:42
- 经验:1495
- 注册时间:2007-08-01
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
zyyzwangjin 离线
- 帖子:1220
- 粉蓝豆:262
- 经验:1873
- 注册时间:2013-08-19
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:867
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
没有查到很权威的文章,目前我认为炎性纤维性息肉的诊断标准、来源和定义还不是很清楚;
1、美国外科病理学等权威杂志没有相关的文献,只有1993年的一篇影响因子高的文章,但当时好像还没有CD117和CD34抗体,文献题名:Inflammatory fibroid polyp of the stomach. A special reference to an immunohistochemical profile of 42 cases. Am J Surg Pathol,1993。其中,或许就有GIST
2、2013年有篇文献,认为胆囊的炎性纤维性息肉也有血小板衍生因子的突变,提示和GIST有者某种密切的联系,文献题名:Inflammatory fibroid polyp of the gallbladder bearing a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha mutation. Arch Pathol Lab Med,2013。
3、综上所述,炎性纤维息肉可能和GIST有着形态学上的重叠,需要更多的研究。
4、个人意见,仅供参考!

- 你所浪费的今天,是昨天死去的人渴望的明天。你所拥有的现在,是明天的你回不去的昨天。
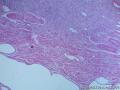
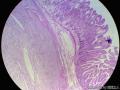
科室内找到一例结肠的炎性纤维性息肉,拍了图传上来!
总结其特点如下:
1、胃肠道的炎性纤维性息肉,因为是息肉,所以是凸向腔内的;
2、炎症的细胞相对较为丰富;
3、没有看到GIST常见的栅栏样的结构,有厚壁的大血管;
4、间质内有粘液变性;
形态上和胃肠道间质瘤还是不太一样的,并不难区别。楼主的这例,我考虑在没有看到切片的基础上,还是要考虑炎性纤维性息肉的可能。
大家看看我的这一例,也诊断GIST吗?

- 你所浪费的今天,是昨天死去的人渴望的明天。你所拥有的现在,是明天的你回不去的昨天。