| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 肩部肿块-上海市骨与软组织肿瘤读片2013(2-2)同济大学东方医院提供
| 性别 | 男 | 年龄 | 56岁 | 临床诊断 | 左肩部占位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般病史 | 发现左肩部肿块3年,逐渐增大 | ||||
| 标本名称 | 左肩部肿块 | ||||
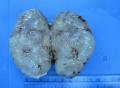
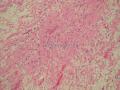
| 大体所见 | 肿块大小10cmX7.5XcmX5cm,切面灰白色,部分灰黄,质嫩,粘滑感。 | ||||
-
本帖最后由 海上明月 于 2013-09-13 17:55:24 编辑

- 王军臣
相关帖子
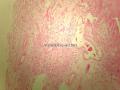
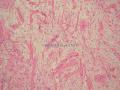
1)乏脂肪细胞变异亚型的梭形细胞脂肪瘤的病理诊断具有挑战性,形态学是最重要的依据,也需要把握相似类型肿瘤形态学谱和免疫表型谱的鉴别。
2)梭形细胞脂肪瘤(Spindle cell lipomas,SCL)多发生在年长男性人群,其发生的经典部位躯干上部/颈部,肿瘤位于皮下。肿瘤边界清晰,有包膜。
3)在梭形细胞脂肪瘤的变异形态中,有一种是极少有成熟脂肪细胞,甚至是完全没有成熟脂肪细胞的,即:乏脂肪细胞性SCL("fat-free" SCL,ff SCL)。
4)ff SCL是及其少见的,楼上文献收集300个机构的仅仅只有4例ff SCL。一般体积较小(mean, 2.0 cm)。但本例较大,可能与生长时间较长有关。
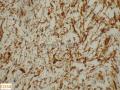
5)ff SCL 除了缺乏成熟的脂肪细胞外,其主要构成成分是CD34阳性梭形细胞,以及索条状/羽毛状老化胶原、粘液样基质和血管。
6)提示的特别重要的形态学特征包括:淡然的梭形细胞,几乎是以平行的阵列的形式,间杂索条状/羽毛状的老化胶原,基质呈粘液样。在ff SCL表达CD34是呈弥漫性阳性的。
7)诊断ff SCL的主要困难是由于缺乏脂肪细胞。易误诊为神经鞘瘤、、低级别纤维粘液肉瘤等等。需要综合评价和鉴别诊断。

- 王军臣
Am
J Dermatopathol. 2007 Oct;29(5):437-42.
Diagnostically challenging spindle cell lipomas: a report of
34 "low-fat" and "fat-free" variants.
Source
Department of Anatomic Pathology,
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH 44195, USA. billins@ccf.org
Abstract
Spindle cell
lipomas (SCL) classically occur as subcutaneous masses in the upper trunk/neck
of older men and are composed of mature fat, CD34-positive spindled cells,
ropey collagen, myxoid matrix, and blood vessels. A number of variants have
been reported, including SCL with pseudoangiomatous change, composite SCL
hibernoma, and composite SCL/pleomorphic lipoma. A review of over 300
consultation cases diagnosed as SCL revealed 34 cases in which fat was
noted to be present in <5% of the tumor (n = 30) or absent (n = 4). These
cases posed diagnostic difficulties because of the dearth of fat; we
propose the terms "low-fat" and "fat-free" SCL for these
variants. The tumors presented in older men (mean, 56 years; ratio of males to
females, 11:1) and presented as small (mean, 2.0 cm) circumscribed dermal or
subcutaneous masses of the head/neck (n = 18), back (n = 7), shoulder (n = 5),
leg (n = 2), arm (n = 1), or unknown location (n = 1). In the majority,
referring pathologists considered benign diagnoses, usually benign nerve sheath
tumors, but in four cases low-grade sarcoma was considered. In only three cases
was SCL considered. The tumors were composed of aggregates of CD34-positive,
bland spindled cellsarranged in characteristic parallel arrays, admixed
with ropey collagen and myxoid matrix. Isolated clusters or single adipocytes were
present in 30 cases; four were devoid of fat. CD34 was diffusely positive
(10/11). A high index of suspicion based on clinical context and identification
of other typical features of SCL are key features to the diagnosis of low-fat and fat-free
SCL.

- 王军臣