| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 2013年第24期(总第76期)——右乳肿块(已点评)
| 性别 | 女 | 年龄 | 62 | 临床诊断 | 右乳腺癌 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般病史 | 发现右乳肿块伴触痛一周 | ||||
| 标本名称 | 右乳肿块会诊切片和蜡块各一 | ||||
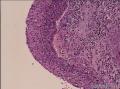
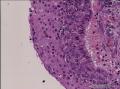
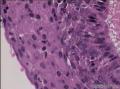
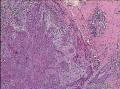
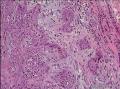
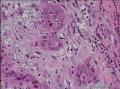
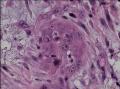
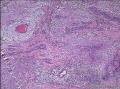
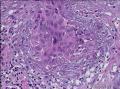
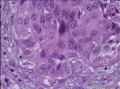
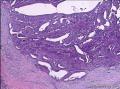
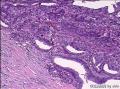
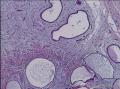
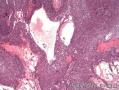
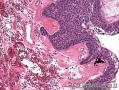
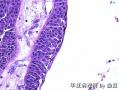
| 大体所见 | 不详 据家属介绍,术中切除一块,约大拇指大小。 因病史和大体不详,描述镜下所见:HE切片一张,中央见一囊性区,约0.8*0.6cm。浸润灶围绕囊壁一圈,浸润厚度约1-3mm,即,整个浸润区大约1.1*0.9cm。切片周围见周围型乳头状瘤和囊肿病。慢性炎症背景。 图1-4 囊壁上皮; 图5 囊壁与周围; 图6-9 周围的一个视野; 图10-13 周围的另一视野; 图14-15 乳头状瘤; 图16 囊肿病。 | ||||
点评专家:姜惠峰(71楼 链接:>>点击查看<< )
获奖名单:djdnx(4楼 链接:>>点击查看<< )
-
本帖最后由 草原 于 2014-02-09 18:11:03 编辑

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
vitamin-xbl 离线
- 帖子:383
- 粉蓝豆:0
- 经验:431
- 注册时间:2007-04-03
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
langmang1127 离线
- 帖子:1
- 粉蓝豆:21
- 经验:4
- 注册时间:2010-11-11
- 加关注 | 发消息
右侧乳腺xx部位,镜下呈复合性病变改变,可见内壁鳞状上皮被覆的囊壁样结构区(少量中性粒浸润)(乳头部位?),周边区似有萎缩和化生的乳腺小叶样结构,周围可见慢性炎反应,亦可见导管增生区(可见导管扩张、乳头状瘤样增生、局部似ADH);部分区域可见不规则形具并其周边组织(肌上皮或乳腺间质细胞)粘液样变,细胞体积大(20-30um),胞浆红染宽阔,胞核圆形或椭圆形大或不规则形、大小不一,核膜厚、核仁明显,似有核分裂像(不典型),核浆比例 >1/2,鳞皮或肌上皮或汗腺?
诊断:(右侧乳腺xx部位?)1、内壁被覆鳞状上皮的囊肿形成(导管扩张鳞化?表皮囊肿?)并周围组织慢性炎;2、乳腺导管内乳头状瘤并乳腺导管扩张症,局部导管上皮增生ADH;3、部分区域可见中度异型性的上皮样细胞团,鳞皮或肌上皮或汗腺来源可能,考虑为乳腺化生性癌,建议做免疫组化进一步确定。
疑虑:未见典型的乳腺小叶结构,但也隐约可见分叶状结构,上皮细胞团周边有粘液样基质的组织分割,如果是癌是原位病变还是浸润性改变?具诊断意义的异型性组织的细胞学尚比较温和,容易过度诊断。病人病变局灶,如果是,假如切除完全,是否提示一个好的预后?有可能有癌的先入为主思想,期待答案。
边学习边看啊,不成熟,请批评
总体不规则鳞状上皮样浸润细胞团的表达为,P63:外周细胞强弥漫核阳性(++),中央区细胞不规则散在阳性(+);Calponin:周边细胞部分(+);3、CK5/6(+);CK7:部分细胞(+++);CAM 5.2:部分细胞(+++);Ki-67:密集阳性区>65%。
可能是三个鉴别诊断:1、原发于乳腺的鳞癌;2、原发于乳腺的腺鳞癌;3、乳腺的化生性癌-鳞癌(应当有乳腺的导管癌成份)。本例的组化结果你中有我,我中有你。结合组织切片:倾向于乳腺表皮囊肿基础上的原发的鳞癌,部分区域可见腺鳞癌成份。
免疫组化结果:
1、 P63(基底细胞及乳腺、汗腺等肌上皮细胞标记物):
a. “囊壁鳞状上皮样组织基底层样、副基底层样细胞及外层细胞:全层弥漫阳性或;基底层样、副基底层样细胞阳性(++),外层细胞部分阴性(-)(似腺上皮组织)”
b. 不规则鳞状上皮样细胞浸润灶:外周细胞强弥漫核阳性(++),中央区细胞不规则散在阳性(+)。
2、 Calponin(肌上皮及腔基底细胞以及恶性肌上皮及多形性腺瘤标记物:
a. 囊壁(-),
b. 增生导管肌上皮(+)。
c.不规则鳞状上皮样细胞浸润灶:周边细胞部分(+)
3、CK5/6(Cornea Breast myoepithelial cells Mesothelium Adult nail unit Basal layer of: prostate, skin, urothelium,spermatogenic cells, and salivary glands Esophagus Epidermal and epithelial glands Oral mucosa Stomach,Benign Usual ductal hyperplasia[1] Adrenal cortical adenoma[2] Malignant Adrenal cortical carcinoma[2]Lung (adenocarcinoma[3] and squamous)标记物High molecular weight cytokeratin. Good basal cell marker.
a.囊壁基底层样区(+),
b.不规则浸润细胞团(+)
4、CK7:不规则巢团状浸润细胞团部分细胞(+++)
(Often used with CK7 to determine the origin of a carcinoma:
§ Typically CK7+/CK20+ carcinomas:
§ Pancreatic origin
§ Ovarian origin (mucinous)
§ Bile duct origin (extrahepatic, including gallbladder)
§ Typically CK7+/CK20- carcinomas:
§ Breast origin
§ Lung origin
§ Bile duct origin (intrahepatic)
§ Endocervical/Endometrial origin
§ Thyroid origin
§ Typically CK7-/CK20+ carcinomas:
§
§ Typically CK7-/CK20- carcinomas:
§ Prostate origin
§ Adrenal cortex origin
§ Can be used to differentiate urothelial carcinoma in situ (cells below the umbrella cells are CK20+) from non-neoplastic urothelium (only the superficial umbrella cells are CK20+ [seen in normal urothelium])[3]
|
Renal cell carcinoma (papillary, chromophobe) |
|
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma and a subset of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma |
|
Carcinomas of the breast, thyroid, salivary glands, endometrium |
|
Mesothelioma |
|
A subset of gastric carcinomas |
|
A subset of esophageal carcinomas |
§
5、CAM 5.2:
§ Low molecular weight cytokeratin.
a、 不规则巢团状细胞部分细胞(+++)
b、 乳腺导管上皮(+++)
6、Ki-67:不规则巢团状细胞团(密集阳性区)>65%
Expression of p63 in primary cutaneous adnexal neoplasms and adenocarcinoma metastatic to the skin
Doina Ivan, A Hafeez Diwan and Victor G Prieto
Modern Pathology (2005) 18, 137–142, advance online publication, 24 September 2004; doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800263
Figure 1.
Next figure|Figure and tables index
Immunohistochemical staining for p63 reveals strong and diffuse nuclear reactivity in the basaloid cells of trichoepitheliomas (a) and eccrine poromas (b). The myoepithelial cells of the ductal structures of the syringomas expressed p63; the inner layer of cuboidal epithelium did not (c). Also, strong p63 positivity was identified in the outer cells of the basaloid nodules of the eccrine spiradenomas (d).
Figure 2.Next figure|Previous figure|Figure and tables index