| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
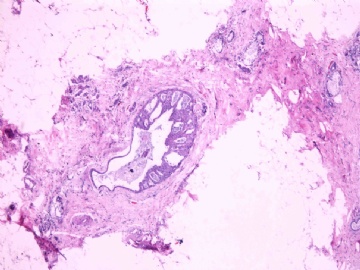
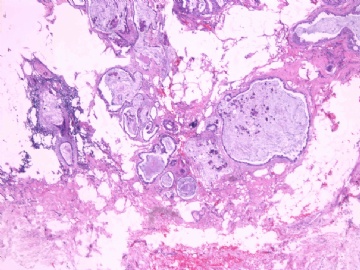
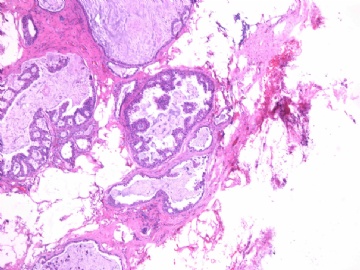
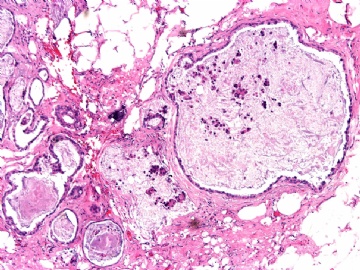
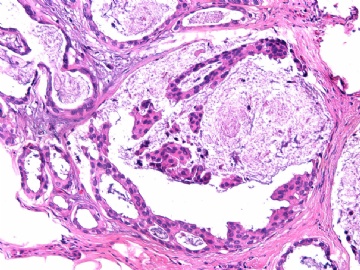
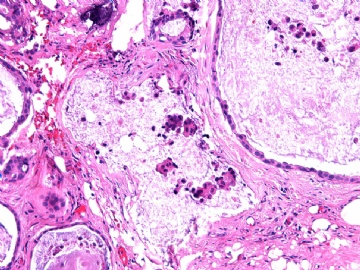
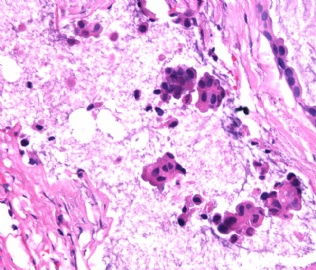
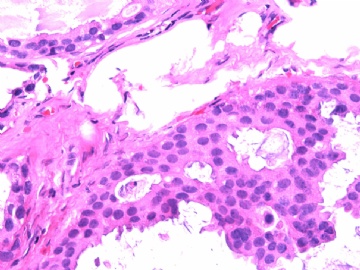
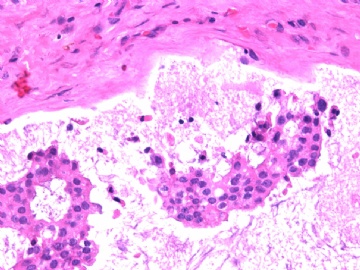
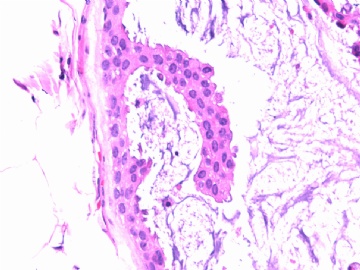
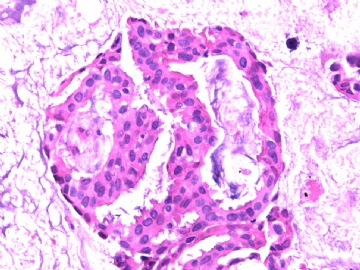
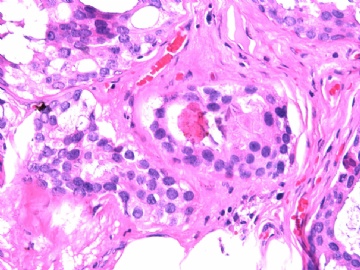
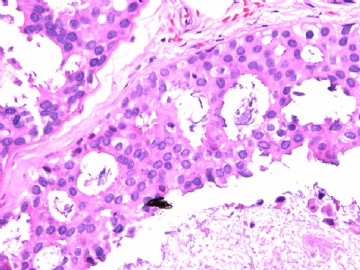
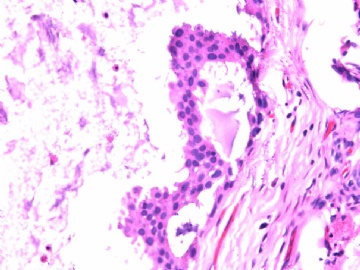
- B2865女性/62岁。 右乳腺肿块 0.8cm, 诊断?(IHC10-8-28)
-
wangjh1985 离线
- 帖子:2
- 粉蓝豆:1
- 经验:2
- 注册时间:2009-11-17
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-09-02 12:09:00 编辑
试着翻译20楼赵老师的帖子:
导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞的表型变化:生物学和诊断意义
摘要
最近,分子研究表明导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞不同于正常乳腺组织的肌上皮细胞。这样的变化可能会影响导管原位癌向浸润性乳腺癌的进展。本研究旨在进一步观察导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞的表型变化。对101例导管原位癌的(56例伴有浸润性乳腺癌,45例不伴有)石蜡切片进行7项肌上皮细胞标记物的免疫染色:SMA、SMMHC、钙结合蛋白、P63、CK5/6、CD10和P75。在每个病例中,将每种标记物在导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞的染色分布和强度与相同切片中围绕在正常导管小叶结构的肌上皮细胞的染色分布和强度进行比较。85例(84.2%)病例中,与正常的肌上皮细胞相比,导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞中,一种或多种肌上皮细胞标记物表达下降。各种标记物表达下降的比例为:SMMHC为76.5%,CD10为34.0%,CK5/6为30.2%,钙结合蛋白为17.4%,P63为12.6%,P75为4.2%,SMA为1%。SMMHC在高级别导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞中表达下降程度比非高级别导管原位癌的大(84.8%vs61.5%,p=0.01)。我们推断:导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞显示的免疫表型不同于正常正常乳腺导管小叶的肌上皮细胞。它的生物学意义还有待进一步研究。然而,这些结果提示:肌上皮细胞标记物在导管原位癌相关的肌上皮细胞中的敏感性较正常的肌上皮细胞中的低。因此在选择区别原位癌和浸润性乳腺癌的肌上皮细胞标记物时需要慎重考虑。
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-09-02 21:42:00 编辑
看来这也是一例有争议的肿瘤。
一般来讲,黏液外溢是在导管内的压力大于导管的张力时,导管才会破裂,黏液溢出,此时囊性扩张的导管上皮一般是低柱状或扁平的(因受压)。
在乳腺黏液囊肿性肿瘤中,鉴别黏液“良性”外溢和黏液癌的一个标准是看黏液内是否存在上皮细胞簇,如有就诊断为黏液癌。因为,黏液癌的定义就是癌细胞漂浮在细胞外黏液中。Dr.Abin 对“漂浮上皮巢”的生物学活性做了详细的解读,提出了理论上的鉴别点,扩展了我们的思路。
此病例我们的诊断意见倾向是“导管原位癌伴导管内黏液和微灶黏液癌”,并不一定准确,仅供参考。
谢谢各位老师的诊断意见和宝贵经验,通过交流使我收获很大, 我想这才是最重要的。
谢谢各位!

- xljin8
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-09-01 23:21:00 编辑
Am J Surg Pathol. 2009 Feb;33(2):227-32.
Phenotypic alterations in ductal carcinoma in situ-associated myoepithelial cells: biologic and diagnostic implications.
Hilson JB, Schnitt SJ, Collins LC.
Department of Pathology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02215, USA.
Abstract
Recent molecular studies have indicated that ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)-associated myoepithelial cells (MECs) show differences from MECs in normal breast tissue. Such alterations may influence the progression of DCIS to invasive cancer. The purpose of this study was to investigate further phenotypic alterations in DCIS-associated MECs. Paraffin sections of 101 cases of DCIS (56 without and 45 with associated invasive carcinoma) were immunostained for 7 MEC markers: smooth muscle actin, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (SMMHC), calponin, p63, cytokeratin (CK) 5/6, CD10, and p75. In each case, the distribution and intensity of staining for each marker in DCIS-associated MECs was compared with that in MECs surrounding normal ductal-lobular structures on the same slide. In 85 cases (84.2%), DCIS-associated MECs showed decreased expression of one or more MEC markers when compared with normal MECs. The proportion of cases that showed reduced expression was 76.5% for SMMHC, 34.0% for CD10, 30.2% for CK5/6, 17.4% for calponin, 12.6% for p63, 4.2% for p75, and 1% for smooth muscle actin. Reduced MEC expression of SMMHC was significantly more frequent in high grade than in non-high-grade DCIS (84.8% vs. 61.5% of cases, P=0.01). We conclude that DCIS-associated MECs show immunophenotypic differences from MECs surrounding normal mammary ductal-lobular structures. The biologic significance of this remains to be determined. However, these results indicate that the sensitivity of some MEC markers is lower in DCIS-associated MECs than in normal MECs. This observation should be taken into consideration when selecting MEC markers to help distinguish in situ from invasive breast carcinomas.
All questions are very in details.
I thibk it is DCIS case.
如果是DCIS,导管因机械因素造成破裂后,癌细胞进入间质,这种情况是否存在象浸润性癌一样的转移危险. The risk will be different with true stromal invasion.
breast ductal epithelial cells (benign or malignant) can be positive for P63. I remember that some papers report it even though I cannot find the paper now.