| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B1820乳房不典型血管瘤( cqz-20)
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
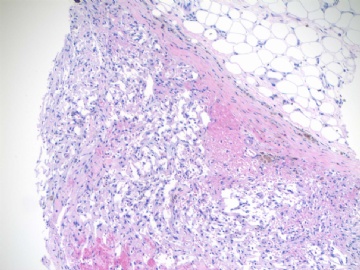
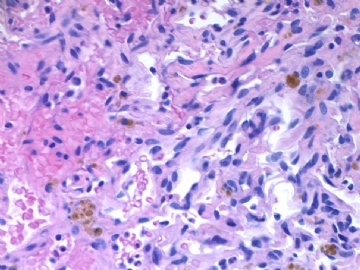
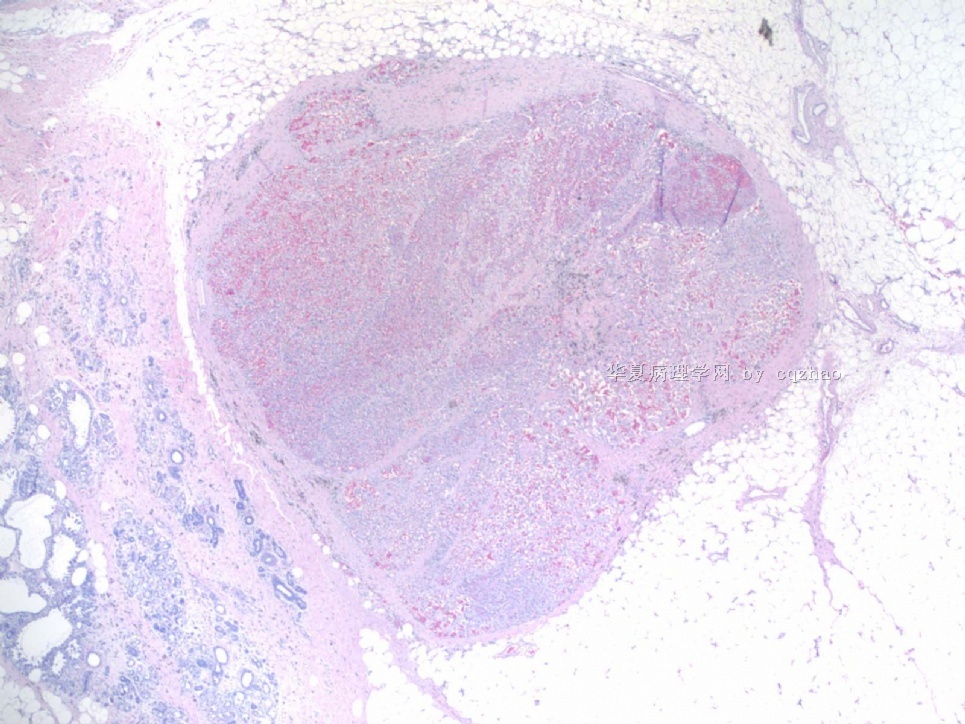
About 50 y/f breast core bx.
Immaging showed a 0.7x0.5 cm demarcated abnormal area.
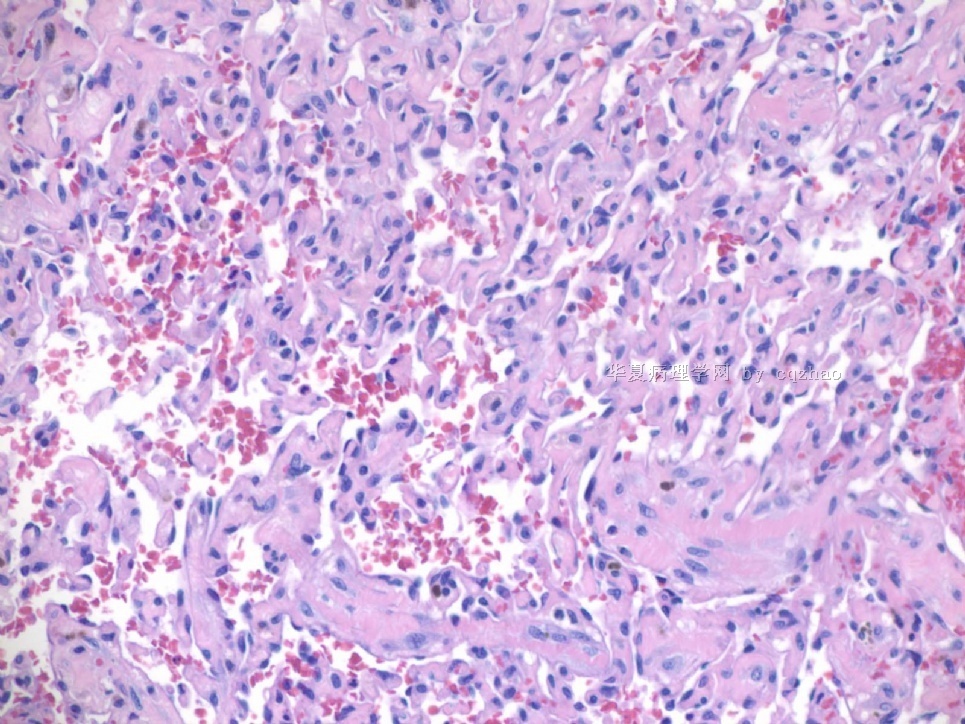
F1,100x, demostrating the margins
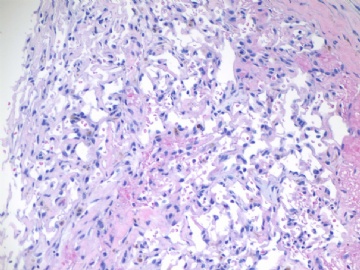
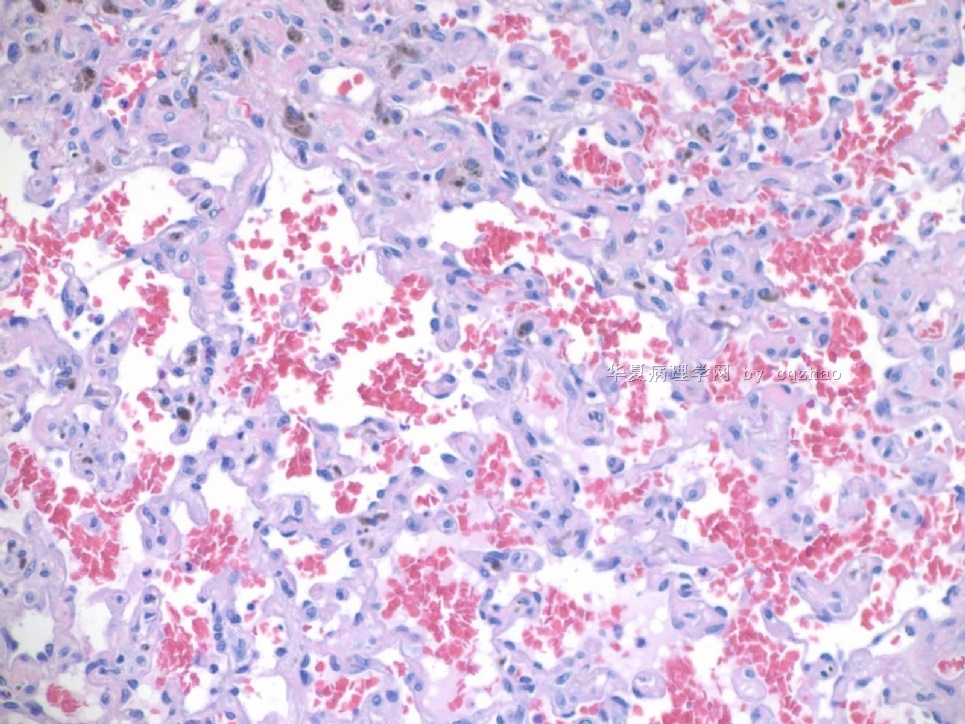
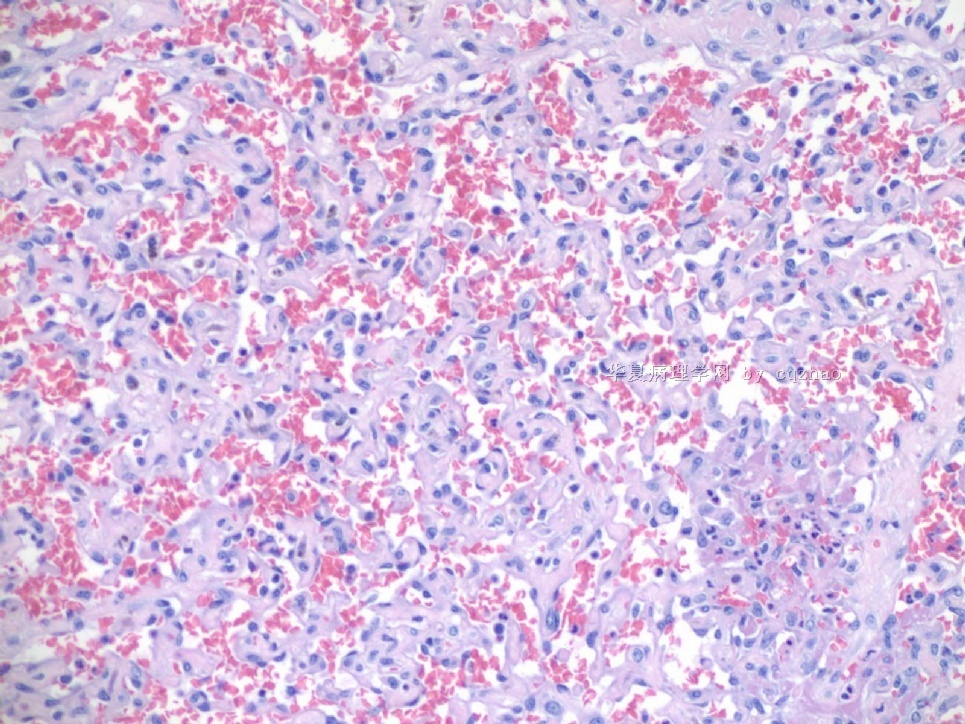
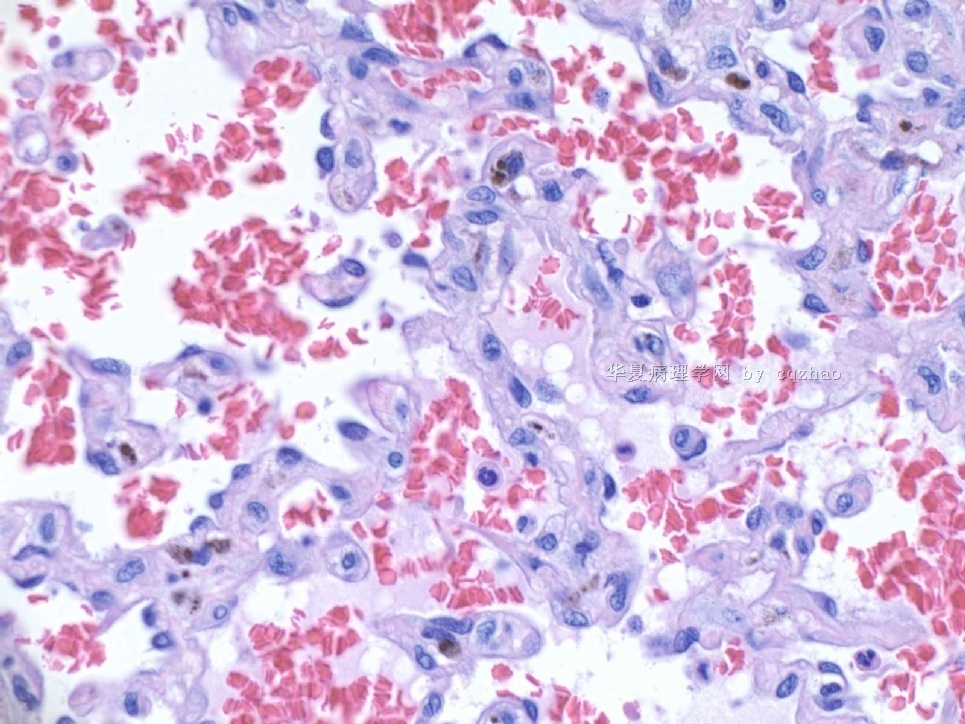
F2-3 200x
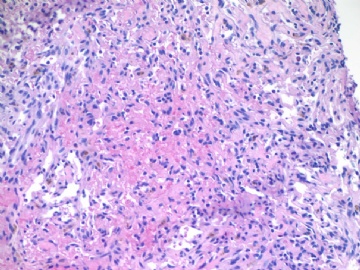
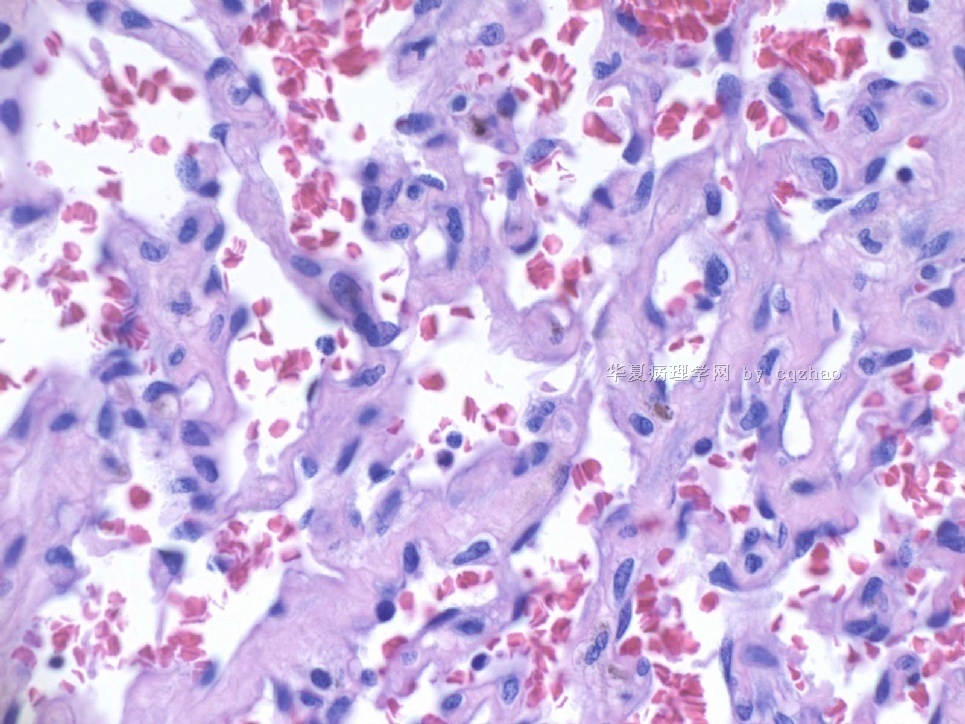
F4-5 400x
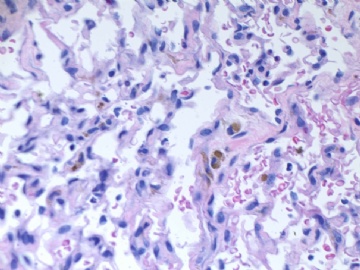
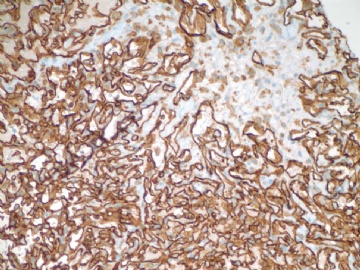
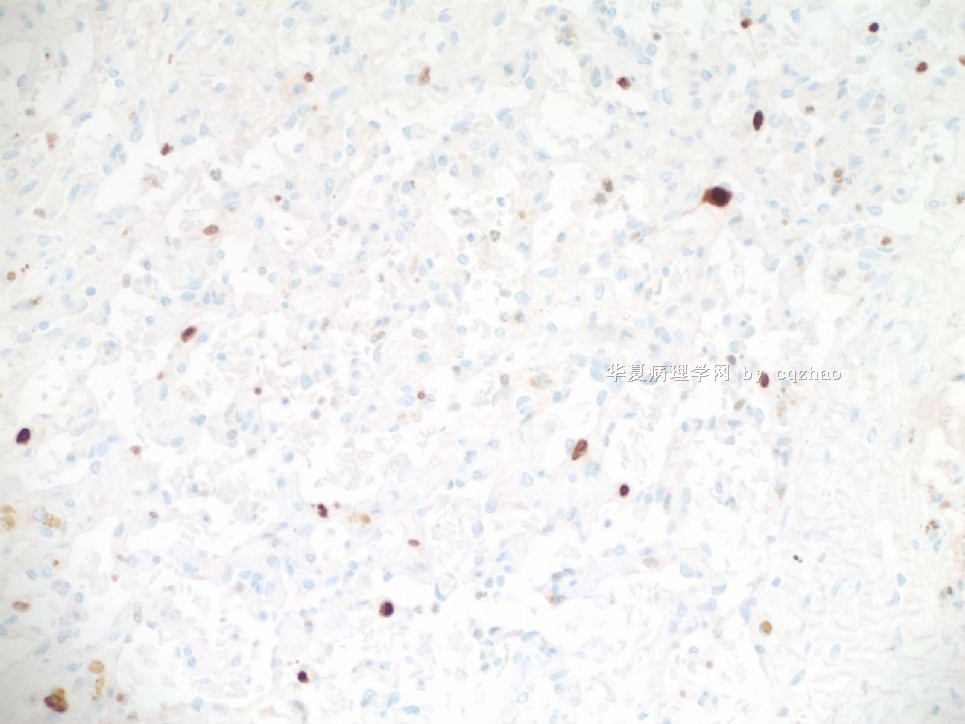
F6 CD31stain
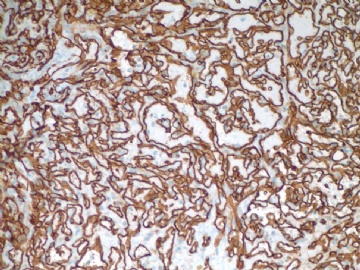
F7 CD34 stain
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-18 09:31:00 编辑
相关帖子
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-08 23:02:00 编辑
Above paper about 207 autopsy cases is a very good one.
Please remember the number: 11.2% of these women have perilobular haemaniomas.
Just hope all of you know that breast vascular lesions includes many different types, benign, atypial, malignant. It is totally wong that all breast vascular lesions are malignant. Also as a pathologist we cannot make our dx based on the incidence of lesions. We cannot have this concept for our dx and differential dx. If you think in this way others will think you still are a 门外汉。If you are my residents or fellows, you will get very low evaluation scores for your rotations.
I will be happy for my time in this subject if you can change your wrong concept about the breast vascular lesions
Wish some one can translate the autopsy abstract above. Thanks, cz
njwbhuang译:
上面的关于207例尸检病理的文章是非常好的文章。请记住这个数字:11.2%女性有小叶周围血管瘤。
只是希望你们所有人都知道乳腺血管性病变包括许多不同类型:良性、不典型和恶性。所有乳腺血管性病变是恶性的观点是完全错误的。而且作为一个病理医生,我们不能根据疾病的发生率做出诊断,我们不能有这个概念而做出诊断和鉴别诊断。如果你是这样想的,那么你仍然是个门外汉。如果你是我的住院医生或fellows,你轮转时得到的将是很低的评价分。
如果你能改变有关乳腺血管性病变中的错误观点,我将很高兴在这个主题花费的时间。
希望有人将上面的尸检摘译翻译过来,谢谢。
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-28 20:25:00 编辑
Am J Surg Pathol. 2008 Dec;32(12):1896-904.![]()
Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: clinicopathologic analysis of 49 cases, suggesting that grade is not prognostic.
49例乳腺原发性血管肉瘤临床病理分析表明肿瘤分级和预后无关联Nascimento AF, Raut CP, Fletcher CD.
Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women's Hospital,
Mammary angiosarcoma is a rare neoplasm, accounting for about 0.05% of all primary malignancies of the breast. It is currently believed that histologic grading of mammary angiosarcomas plays an important role in prognostication. Forty-nine cases of primary angiosarcoma of the breast were retrieved from our files. Clinical details and follow-up information were obtained from referring pathologists and clinicians, and by chart review. All statistics were performed using Fisher exact test and only P<0.05 was considered significant. Recurrence-free survival and overall survival curves were established using Statistica software version 5.5 (StatSoft Inc). All patients were female with ages ranging from 15 to 74 years (mean 41.5, median 40). Peak incidence was between the ages of 30 and 50 years. All tumors examined were located within breast parenchyma with or without minor cutaneous involvement. The right side was more commonly affected than the left side (66% vs. 29.5%). Tumor was bilateral at presentation in 2 cases (4.5%). Tumor size varied from 0.7 to 25 cm (mean 6.7, median 5). Most patients presented with a palpable, painless mass. Two patients had a history of prior radiation treatment for breast carcinoma. Histologically, primary tumors were graded using Rosen's 3-tier system: 17 tumors (35.4%) as low grade, 17 (35.4%) as intermediate grade, and 14 (29.2%) as high grade. Forty-six patients were treated surgically, 11 underwent chemotherapy, and 12 patients received radiotherapy. Follow-up was available in 41 patients (83.7%, median duration 29 mo). Ten patients (24.4%) showed evidence of local recurrence within 11 to 60 months (median 36) after diagnosis. Twenty-four patients (58.5%) thus far have developed metastases, which were most commonly to lung, liver, skin, and bone. Time interval between diagnosis and metastasis ranged from 2 to 144 months (median 34). Eighteen patients (44%) so far have died of disease and 1 died of presumably disseminated breast carcinoma. Five patients (12.2%) are alive with disease and 15 patients (36.6%) are alive with no evidence of disease. Statistical analysis evaluating correlation between tumor grade and size, and rate of local recurrence, metastasis, and death owing to disease showed no significant difference among tumors of different grades. The median recurrence-free and overall survival rates for the entire cohort were 2.8 and 5.7 years, respectively. In conclusion, mammary angiosarcoma is a rare disease that affects relatively younger patients. This tumor seems to have an overall similar clinical course as other types of angiosarcoma arising in skin or soft tissue; it carries a moderate risk of local recurrence, and a high risk of metastasis and death. In this large series, there is no correlation between histologic grade and patient outcome, more in line with angiosarcomas at other sites.
乳腺血管肉瘤是罕见肿瘤,约占乳腺原发恶性肿瘤的0.05%。目前认为乳腺血管肉瘤的组织学分级有重要的预后意义。我们回顾分析了49例乳腺原发血管肉瘤。临床详细资料和随访信息来自相关病理学医生和临床医生,通过图表分析。所有统计数据都进行Fisher确切检验并且仅当P<0.05时才认为是有意义的。无复发生存曲线和总体生存曲线用统计软件版本5.5(statsoft公司)建立。所有病人均为女性,年龄范围从15到74岁(平均41.5岁,中位数40岁)。高发期在30岁至50岁之间。所有肿瘤都位于乳腺实质伴或不伴有微小皮肤浸润。右侧通常较左侧易累及(66%vs.29.5%)。肿瘤累及双侧者2例(4.5%)。肿瘤大小范围0.7cm到25cm(平均6.7,中位数5)。大多数病人表现为可触及的、无痛性的肿块。2例病人有先期乳腺癌放射治疗病史。组织学上,原发肿瘤用Rosen3等级系统进行分级:低级别17例(35.4%),中级别17例(35.4%),高级别14例(29.2%)。46例病人手术治疗,11例化疗,12例进行了放射治疗。有效随访病例41例(83.7%,中位持续时间29个月)。10例(24.4%)病人在11至60个月内(中位数36)局部复发。24例病人(58.5%)迄今为止出现远处转移,大部分转移至肺、肝、皮肤和骨。诊断和转移之间的时间间隔范围为2到144个月(中位数34)。迄今为止18例(44%)病人死于该病,1例推测死于乳腺癌播散。5例病人(12.2%)带瘤生存,15例(36.6%)无瘤生存,各组织学级别间的肿瘤致死性无明显差别。无瘤生存期和总体生存期的中位数分别是2.8年和5.7年。总之,乳腺血管肉瘤是相对多发生于年轻患者的罕见肿瘤。该肿瘤总体看来同发生于皮肤和软组织的血管肉瘤有类似的临床过程;它有中等风险的局部复发性,和高风险的远处转移及致死性。在该研究系列中,组织学分级与病人预后间无关联,与其他部位的血管肉瘤较符合。
quyibl译,不妥处请及时指正。
非常感谢所有参与者,收益匪浅,也谈一点自己的看法(绝不是事后诸葛亮),本网站另外两例乳腺“血管肉瘤”得到大家的认可,是因为大家都看到了(特别是双侧一例)是发生在乳腺实质内,而非乳腺区软组织或乳腺小叶周围,本例界限清楚,而又没有看到乳腺小叶结构,更何况病变内有明显的出血和“机化”现象,难怪有人提出Masson瘤的观点;
关于"乳腺没有良性的血管瘤"我也听过类似的专题讲座,但是我听到的这位专家讲这句话时是有一定条件的,是具有这些形态学特征的血管处于真正的乳腺内而非乳腺区皮下软组织和乳腺小叶周围!!!!
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-08 23:44:00 编辑
-
Atypical vascular lesions after surgery and radiation of the breast: a clinicopathologic study of 32 cases analyzing histologic heterogeneity and association with angiosarcoma.
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA.
We report the clinicopathologic study of 32 cases of atypical vascular lesions (AVLs) after surgery and radiation of the breast, which were referred to us in consultation over a 17-year period. The patients, all women, ranged in age from 41 to 95 years (mean 61 y). The lesions developed within the radiation field from 1 to 12 years (median 6.0 y) after therapy. They occurred as one (n=18) or more (n=10) flesh-colored papules or erythematous patches/plaques ranging in size from 1 to 60 mm (mean 8.0 mm, median 4.0 mm). Tumors could be divided into 2 histologic types: a lymphatic type (LT) (n=22) and a vascular type (VT) (n=10). LT AVLs consisted predominantly of thin-walled, variably anastomosing lymphatic vessels that were usually confined to the superficial dermis but occasionally extended into the deep dermis and even subcutis. The VT (n=10) typically consisted of small, irregularly dispersed, often blood-filled, pericyte-invested, capillary-sized vessels involving the superficial or deep dermis. VTs were often associated with extravasated erythrocytes, hemosiderin, and a surrounding minor LT component. In 4 cases, endothelial atypia, consisting of nuclear and nucleolar enlargement, was noted. Follow-up of 21 patients with LT AVLs (1 to 106 mo; mean 47 mo) disclosed recurrence/additional lesions in 6, all of whom had additional surgery. Of the 21 patients, 17 are alive without disease, 1 is alive with disease, 1 died of breast carcinoma, 1 died of unknown causes, and 1 showed progressive histologic changes in the AVLs over a period of 5 years resulting in a well-differentiated angiosarcoma. Follow-up in 8 patients with VT AVL (2 to 181 mo; mean 40 mo) disclosed that 6 were alive and well, but 2 of the 4 patients whose lesions displayed endothelial atypia had additional complications. One patient underwent a mastectomy that revealed extensive residual AVL and the second developed a high-grade angiosarcoma after 14 months. We conclude that AVLs encompass a wider spectrum of changes than previously appreciated, ranging from superficial lymphatic proliferations to more complex lymphatic and capillary vascular lesions. There seems to be an association of AVL with angiosarcoma that differs depending on the histologic features, with the VT AVLs having the higher risk. In the 2 patients who developed angiosarcoma, morphologic evidence suggested AVLs to be a precursor rather than simply a risk factor. Future outcome and management studies should take into account these differences.
-
abin译:这是Dr. Weiss(《软组织肿瘤》一书的作者)的另一篇好文章。我以前贴过一篇。
乳腺手术后和放射后在不典型血管病变:32例临床病理联系,分析组织学异质性及其与血管肉瘤的关系
我们报道32例乳腺手术后和放射后的不典型血管病变(AVLs)的临床病理研究,病例包括17年间我们接受的会诊病例。患者均为女性,年龄41-95岁(平均61岁)。在接收放射区域形成病变的时间为1-12年(平均6年)。它们表现为一个(n=18)或多个(n=10)肉色丘疹或红斑,大小1-60mm(平均8mm,中位4mm)。肿瘤分为两个组织学类型:淋巴管型(LT)(n=22)和血管型(VT)(n=10)。LT AVLs主要由薄壁的、不同程度想相互吻合的淋巴管组成,通常局限于真皮浅层,但偶尔扩展到真皮深层甚至皮下组织。典型的VT由小而不规则散在的、通常充满血液的、包围着血管周细胞的、毛细血管样大小的血管组成,累及真皮浅层或深层。VT通常伴随着红细胞外渗、含铁血黄素和周围小灶LT成分。4例出现内皮细胞不典型性,可以注意到核和核仁增大。对21例LT AVLs患者随访1-106月(平均47月),发现6例复发和新增病变,她们都再次手术。这21名患者中,17例无病生存,1例有病生存,1例死于乳腺癌,1例死于不明原因,1例显示AVLs内的进展性组织学改变,形成高分化血管肉瘤。8例VT AVLS患者的随访2-181月(平均40月),发现6例健在,但4名患者中的2人,病变显示内皮细胞不典型性,有新增的并发症。一名患者经乳房切除,发现广泛残留AVL,后者在14月后发展成高级别血管肉瘤。我们的结论:AVLs包含比以前的认识更为宽广的病变谱,范围从表浅的淋巴管增生到较复杂的淋巴管和毛细血管病变。似乎AVL与血管肉瘤的相关性有与组织学特征有关,VT AVLs的风险更高。发展成血管肉瘤的2名患者,形态学证据提示AVLs是前驱病变,而不仅仅是危险因素。后续的关于结局和管理的研究将会说明这些差异。
This is another good paper from Dr. Weiss (author of the Book- soft tissue tumors), I pasted in another topic already
Am J Surg Pathol. 2008 Jun;32(6):943-50.
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-12 22:58:00 编辑
This patient had excisional biopsy. My colleague has the case. He showed me the case today. I will let you know how we sign out the excisional biopsy specimen.
abin译:
患者做了切除活检。我的同事经手这个病例,他今天给我看了。我将让大家知道,我们是怎样签发切除活检标本的报告。
to Dr.zhao and Dr.Njwbhuang, 为了保持本贴的连贯完整,我整理了本贴的部分内容,主要是把翻译的中文内容直接粘贴到原贴后面了。事先未征求二位同意为歉!__abin
-
bzlixinjun 离线
- 帖子:63
- 粉蓝豆:23
- 经验:64
- 注册时间:2007-10-28
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-12 23:24:00 编辑
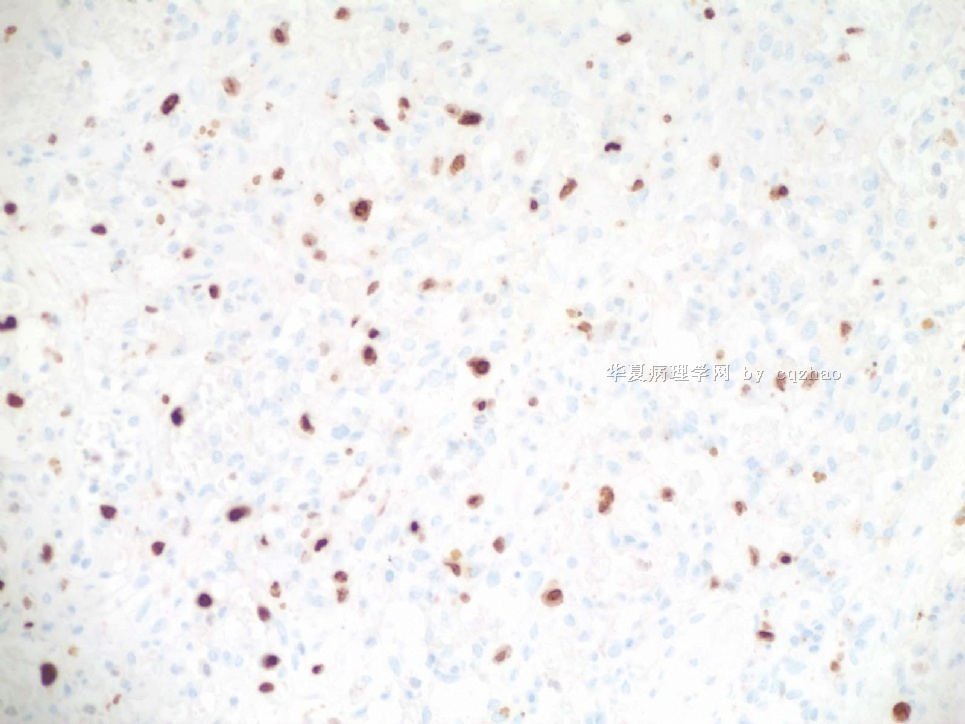
Focally higher rates of labeling may be found in a hemangioma at sites of organizing thrombi or where a biopsy was previously performed on the lesion.(Rosen's Breast Pathology ,3ed).This case had a breast core biopsy, so high area of Ki-67 index can be able to interpret. Moreover ,complete capsule and very small lesion all suggested benign outcome. We also see the complex structure and atypical nuclear after all. A diagnois of atypical vascular lesions may be appropriate to this case. And a follow-up is essential.
abin译:
Ki67标记表现为局灶较高的核增殖指数,可见于一些血管瘤的机化血栓局部,或者以前做过活检的部位(Rosen's Breast Pathology ,3ed)。本例做过粗针穿刺活检,因此存在Ki-67高指数区也就可以解释了。而且,病变有完整包膜,非常小,也提示为良性过程。然而我们也能看到复杂结构和不典型核。本例诊断为不典型血管病变也许比较合适,并且,随访也很重要。