| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 2014年第06期(总第85期)——右侧卵巢肿瘤(已点评)
| 性别 | 女 | 年龄 | 63岁 | 临床诊断 | 考虑卵巢性索-间质来源肿瘤 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
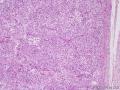
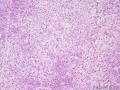
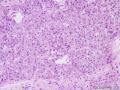
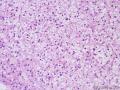
| 一般病史 | 因绝经10年后阴道出现半月,腹胀不适1周,加重2日来我院就诊。妇检子宫增大如孕2+月。盆腔MRI检查示盆块,腹水形成,倾向附件来源肿瘤。分段诊刮示子宫内膜增生期样改变。。予剖腹探查术。术中见腹腔暗红色积血2400ml,肝、胆、胰、脾、双肾未及异常,大网膜、小肠、结肠、肠系膜、阑尾等表面及双侧结肠旁沟均未见肿瘤结节。右侧卵巢增大呈12*13*8cm,实性,分叶哑铃状,包膜色灰白,局部破裂伴活动性出血,左卵巢及双输卵管未及异常。子宫大小正常,腹膜后淋巴结不大。行全子宫双附件大网膜阑尾切除术。 | ||||
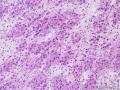
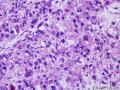
| 标本名称 | 右侧卵巢 | ||||
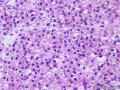
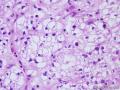
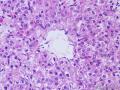
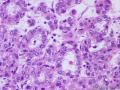
| 大体所见 | 右卵巢分叶状肿块16.5*12.5*6cm,切面淡黄灰红色,多结节状,部分区囊性变,内含粘液,质中;附输卵管及另送全子宫左附件标本,未及肿块。 | ||||
感谢 上海复旦大学肿瘤医院病理科徐晓丽老师为有奖读片专栏提供经典病例!
点评专家:徐晓丽(57楼 链接:>>点击查看<< )
获奖名单:youxueye(51楼 链接:>>点击查看<< )
-
本帖最后由 草原 于 2014-03-16 18:17:42 编辑

- Stop walking today and you'll have to run tomorrow.
-
本帖最后由 草原 于 2014-04-14 20:34:50 编辑
部分免疫组化图片已上传,徐老师发过来的读片讨论及结果:
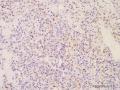
IHC results:
Positive:AE1/AE3、EMA、CK7、LeuM1、AFP、Hepar-1
Negative:Vim、α-inhibin、Calretinin、CD10、CD99、HMB45、S100、A103ER、AR、WT1、 PAX8、HNF1β、CgA、HCG、CEA
Discussion:(讨论)
1、Rare primary ovarian carcinoma. 2、Introduced by Ishikura and Scully in 1987 3、occurs almost exclusively in postmenopausal famales
4、Elevation of serum AFP and serum CA125 5、Most of the hepatoid carcinoma cases were clinically advanced tumors 6、large, polygonal, round or oval cells, abundant amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm, distinct cell borders resembling hepatocellular carcinoma 7、Arranged in sheets, trabecular pattern 8、May combine with other surface epithelial carcinomas, sex cord stromal tumor 9、Metastasis to lymph node, spleen, liver, lung, soft tissue, etc. 10、most likely a variant of common epithelial carcinoma by a process of neometaplasia or transdifferentiation
(• 罕见的原发性卵巢癌 •Ishikura 和 Scully 在 1987年首次介绍 • 几乎总是发生于绝经后妇女 • 血清AFP和血清 CA125都升高• 大多数肝样癌病例为临床晚期 • 细胞大、多角形、圆形或卵圆形,胞质丰富、嗜酸性,细胞边界清楚,类似肝细胞癌 • 排列成片状、小梁状结构 • 可合并其他表面上皮癌、性索-间质肿瘤 • 转移到淋巴结、脾、肝、肺、软组织等 • 很可能是普通上皮癌的一种亚型,发生了肿瘤性化生或转分化)
(1、average age 43 (2-80) years 2、average size 8.4cm, well circulmscribed, lobulated or multinodular, solid, yellow to brown 3、diffuse or cords pattern, >90% unilateral 4、medium to large cells with distinct cell membranes 5、granular eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm 6、round and centrally placed nucleus with single nucleolus 7、frequently no cytologic atypia and <2 mictoses/10HPF 8、a delicate fibrovascluar stroma 9、malignant: 43%, >2 mitoses/10HPF, 10、necrosis, >7cm, hemorrahage, high-grade nuclear atypia )(平均 年龄 43 (2-80) 岁;平均 大小 8.4cm,边界清楚,分叶状或多结节状,实性,黄色到褐色;弥漫或条索状结构,>90%为单侧性;中-大细胞,细胞膜清楚;颗粒性嗜酸性胞质或空泡状胞质;核圆形,中位,有单个核仁;通常没有细胞学异型性,核分裂<2/10HPF;纤细的纤维间质;恶性: 43%, 核分裂>2/10HPF, 坏死, >7cm,出血, 高度核异型性)
1、Inhibin and calretinin + 2、A103, CD10, CD56 and vimentin frequently + 3、S100 and HMB45 + in some cases
4、Some tumors may stain for CK or CD99
(Inhibin+,calretinin +、 A103, CD10, CD56 和 vimentin 通常 +、部分病例S100 +和 HMB45 +、部分肿瘤表达CK 或 CD99)
HCC metastasis
1、high risk of HCC: chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection, liver cirrhosis 2、in china, young patients with HBV+
3、Liver lesions 4、Bilateral ovary 5、bile ductal differentiation 6、IHC: CK7-, EMA-,Hepar-1+, Arg+, AFP+
(HCC 转移:HCC高危因素:慢性乙肝或丙肝,肝硬化;中国,年轻患者伴HBV+;肝脏发现疾病;累及双侧卵巢;肝细胞分化;免疫组化: CK7-, EMA-,Hepar-1+, Arg+, AFP+)
1、Solid pattern, always show other architectural patterns, tubulocystic, glandular and papillary, hobnail cells are common 2、Clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm 3、Adenofibromatous background and/or endometriosis 4、IHC: PAX8+, HNF1β+, AFP-, Hepar-1-
1、Mostly young (<20 yrs) 2、The most common is reticular and microcystic pattern 3、Pseudopapillary, hepatoid, glandular patterns 4、Solid pattern, may predominate in recurrences 5、Primitive cells display nuclei with prominent nucleoli and brisk mitotic activity
-
www810910: 学习了,谢谢老师精彩点评!2014-04-16 07:51

- Stop walking today and you'll have to run tomorrow.