| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
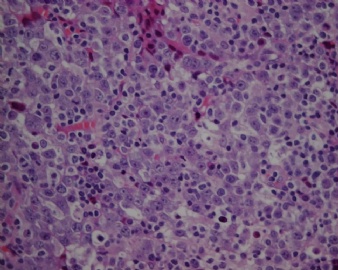
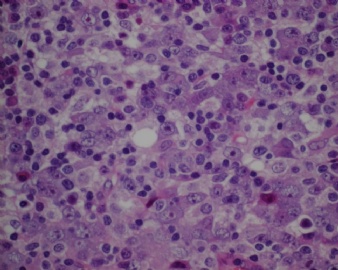
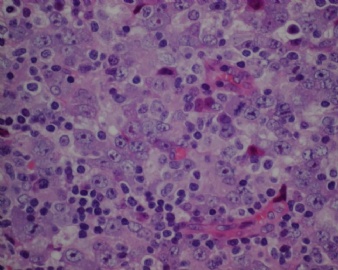
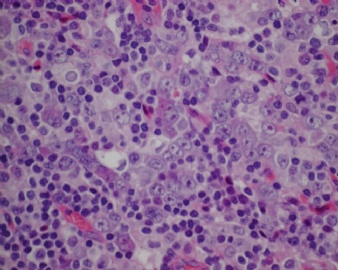
- CG256--ALK阳性大B
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-11-30 14:10:00 编辑
| 以下是引用指环王在2010-11-29 22:14:00的发言: ALK阳性大B的B细胞抗原表达特点如何? |
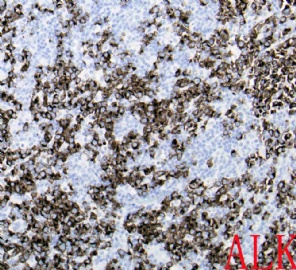
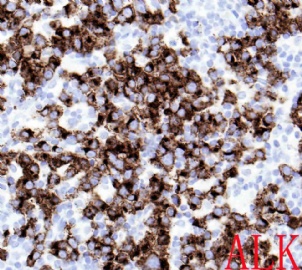
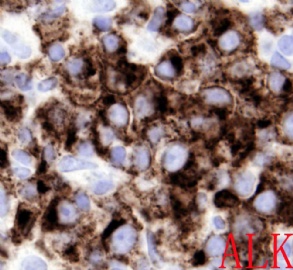
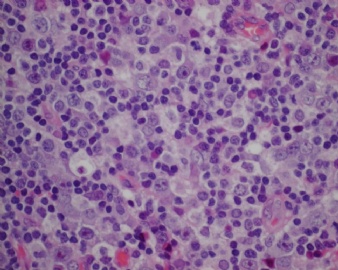
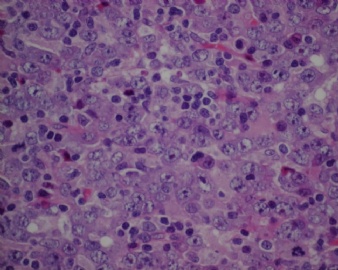
诊断线索为肿瘤细胞形态上表现为免疫母细胞样或浆母细胞样,免疫表型至少表达一种终末B细胞(浆细胞)分化标记,如CD138、VS38和Ig,而CD20、CD
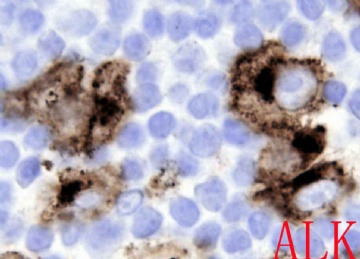
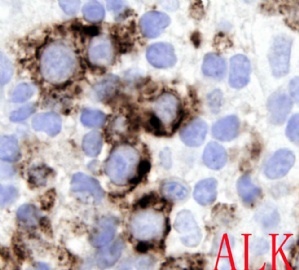
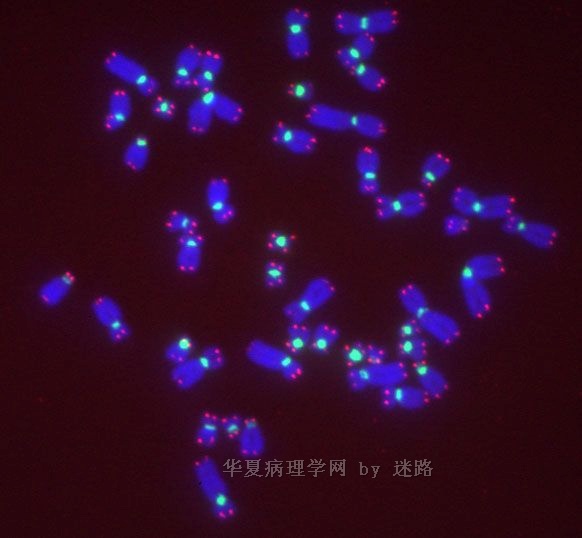
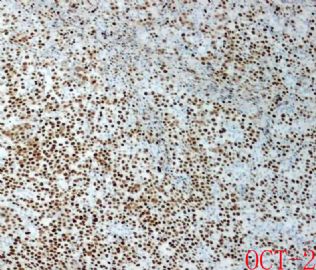
ALK阳性的大B细胞淋巴瘤的免疫表型特点为EMA和浆细胞分化抗原CD138、VS38强阳性,CD3、CD20、CD79a、PAX-5通常阴性。大部分肿瘤细胞表达伴轻链限制性胞质型Ig(通常为IgA)。CD30通常阴性,部分病例局灶弱阳性。CD4、CD43、CD57、MUM1和CD45不同程度阳性,其异常表达T细胞(CD4)和(或)NK细胞(CD57)标记原因尚不清楚。穿孔素可局灶或强阳性,而迄今尚未发现穿孔素在其他类型B细胞淋巴瘤中弥漫强阳性表达的报道。可表达B细胞转录因子BOB.1和Oct-2。多组研究还显示无论免疫组织化学检测LMP-1还是EBER原位杂交检测EBV编码的mRNA,ALK阳性的大B细胞淋巴瘤均未发现EB病毒感染的证据。此外,肿瘤细胞具有很高的增殖活性。
The frequency of expression of the various immunophenotypic markers is as follows: CD45,71%; CD20,3%(weak and focal); CD79a,16%; EMA,100%; CD30,6%(weak and focal); kappa or lambda light chain, 90%(most often IgA); CD138, 100%;CD4, 64%; and CD57, 40%. By definition, this lymphoma expresses ALK, with staining frequently confined to the cytoplasm, usually in a granular pattern. Cytokeratin exression has rarely been described, adding to the possible confusion with metastatic carcinoma, especially in combination with EMA positivity.(《Hematopathology》)
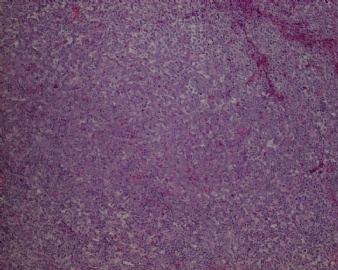
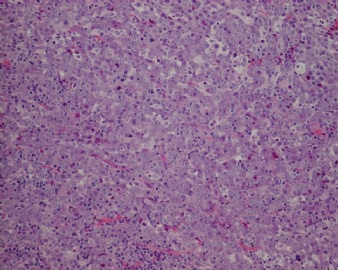
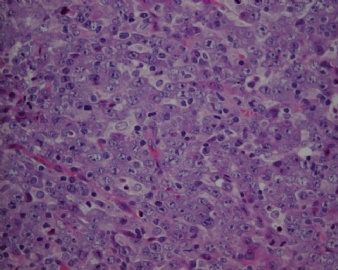
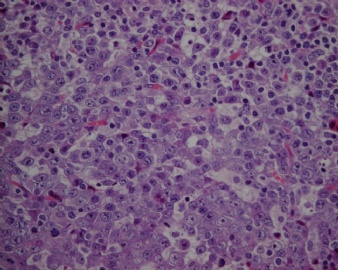




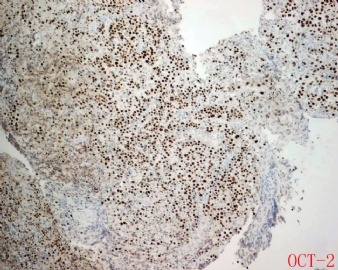
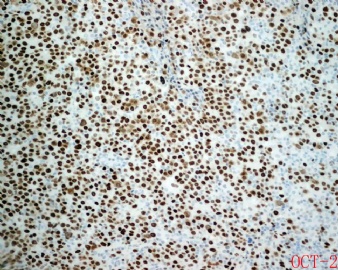
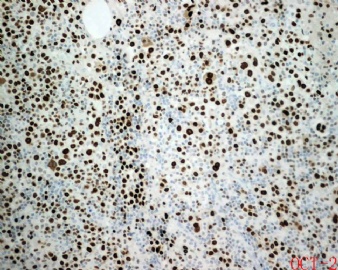
 大B淋巴瘤?!
大B淋巴瘤?!