| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B1840乳房高级别血管肉瘤(cqz-22)
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
About 70 y/f with breast lesion.
Noticed that 197 used the words "传说".I paste here another case for your guys. Do not say 传说 in future.
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-07-23 05:24:00 编辑
相关帖子
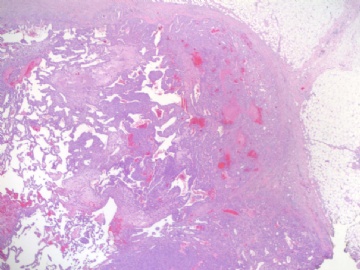
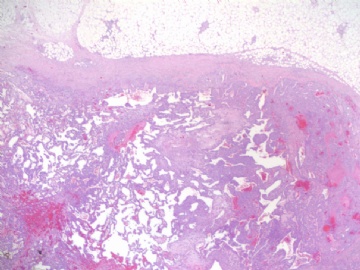
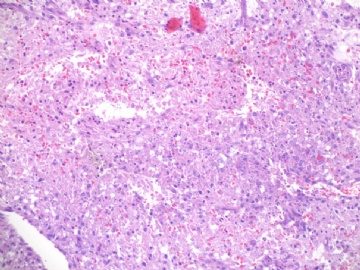
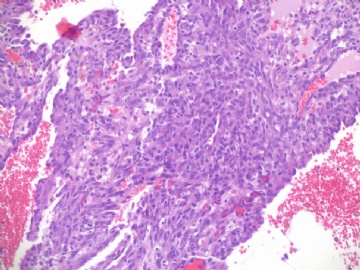
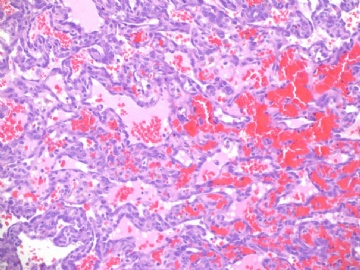
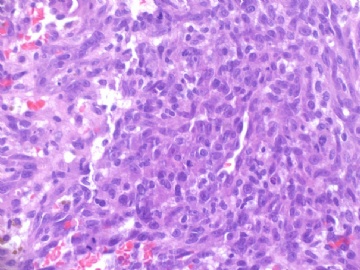
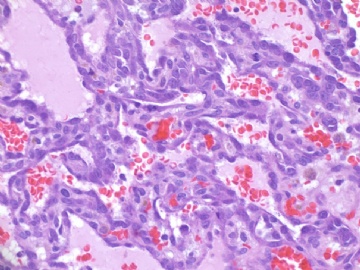
angiosarcoma罕见,却是乳腺最常见的纯间质恶性肿瘤。通常表现为无痛性肿块。某些病人可以为弥漫性乳腺肿大而无肿块。常累及双侧乳腺。总的预后不良。组织学分级是预后的重要指标。常发生广泛转移,最常见肝、肺、皮肤及对侧乳腺。
大体:大小不等,从2cm到11cm以上。恶性小于2cm者少见,大多在2-5cm。根据其分级不同而切面呈均质、血管瘤样到实性、伴出血坏死不等。
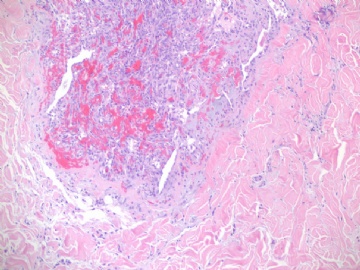
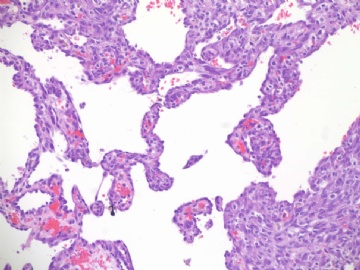
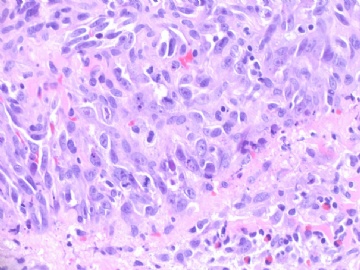
镜下:注意取材,尤其在肿瘤周边部、中心区。组织学一级者由相互吻合和沟通的血管腔构成,被覆1-2层内皮细胞,很少或无分裂像,可有内皮细胞核和血栓形成,无乳头实性间变细胞、梭形细胞区和坏死,难以与良性血管瘤鉴别(abin老师提到文献有讲可以用Ki-67)。有助于鉴别的指征为:1)肿瘤大小,良性者一般小于2cm,也可为镜下病变;血管肉瘤者一般大于2cm;2)良性病变血管腔不相互交织呈网,通常被覆扁平的内皮细胞,无增生现象;3)大约5%的良性血管瘤附近可有非肿瘤性肌性血管;4)良性血管周围可有一层平滑肌。罕见的微型(小于2mm)小叶周围血管瘤已有报道,它可有内皮细胞轻度异型性增生,有血管网形成,也有体积较大(3-25mm)的病变,有内皮细胞核异型,但无相互吻合的血管网。二级血管肉瘤为混合性结构,部分区域有上皮出芽和乳头形成,部分区域为实性梭形细胞成分,在乳头状结构病例常有明显的核分裂像。然而肿瘤的主要成分可能仅为一级,尤其在边缘区。因此更要注意强调充分取材的重要性。三级者主要由实性细胞团构成,无明显血管腔。出血、坏死、细胞多形性和分裂像显著,本型的主要问题是和其他梭形细胞肿瘤的鉴别诊断。
再次指出,同一肿瘤的形态在不同区域可以表现不同,从部分呈高度不分化的实性区域到细胞学表现及其温和区,因此多取材,很重要。

- 赚点散碎银子养家,乐呵呵的穿衣吃饭
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-21 21:41:00 编辑
血管源性肿瘤
良性
血管瘤(毛细、海绵状、动静脉性、静脉性、肌内、皮下/深部软组织、滑膜)
上皮样血管瘤
血管瘤病
中间型
Kaposi型血管内皮细胞瘤(局部侵袭性)
中间型(偶见转移型)
网状血管内皮细胞瘤
乳头状淋巴管内血管内皮细胞瘤
混合性血管内皮细胞瘤
Kaposi肉瘤
恶性
上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤
软组织血管肉瘤
血管肉瘤最重要的是细胞异型性,一般既有上皮样区又有梭形细胞区,以前者为主。本例没看到明显的细胞异型,也没看到上皮样细胞区,所以我有点怀疑。我看Breast lesion (cqz-21) 符合血管肉瘤。

- 有福不在忙
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-22 20:57:00 编辑
- Malignant neoplasm of the breast exhibiting blood vascular differentiation
- 表现为血管特征的乳腺恶性肿瘤。
- All grades are characterized by infiltration of breast parenchyma by cells exhibiting vascular differentiation 所有级别都可见到有血管特征的细胞浸润乳腺实质。
- Low grade tumors 低级别肿瘤
- Prominent freely anastomosing vascular channels 显著的大量相互交叉的血管窦
- Papillary growth and endothelial tufting minimal to absent 缺乏乳头状生长和鞋钉状内皮
- Cytologic atypia may be difficult to identify even after extensive sampling 细胞的非典型性很小
- Intermediate grade tumors 中级别肿瘤
- Freely anastomosing vascular channels 大量相互交叉的血管窦
- Papillary growth and endothelial tufting 乳头状生长和鞋钉样内皮
- May have focal solid areas with polygonal or spindle cells 局部可有多边形或梭性细胞构成的实性区
- High grade tumors 高级别肿瘤
- Prominent solid areas of clearly malignant cells 明显的恶性细胞构成的实性区
- Polygonal and spindled cells多边形和梭性细胞
- Blood lakes and necrosis are common 血液湖和坏死常见
- Vascular channels may be difficult to identify 血管窦可能不易见到
- May require extensive sampling, especially at edge of lesion 需要多取材,尤其在肿瘤的边缘部
- Demonstration of vascular nature may require immunohistology可能需要免疫组化来证实其血管源性。
- Prominent solid areas of clearly malignant cells 明显的恶性细胞构成的实性区
- Awareness of the varying patterns exhibited by the above grades is useful for diagnostic purposes but it is not clear that it has any predictive value。分级模式对诊断目的是有用的,但对预后的价值不清楚。
在 在斯坦福大学医学院网站上看到的关于乳腺血管肉瘤的诊断标准。
http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/angiosarcbreast/
本例血管特征明显,可见较多实性区,其内细胞非典型性明显,核分裂象多见,可见坏死,血液湖,据此诊断高级别血管肉瘤。免疫组化:表达CD31,CD34,部分表达血管因子Ⅷ相关抗原。以CD31最敏感和特异。本例似乎不需要。
Definition
Diagnostic Criteria诊断标准

- 我思故我在! know something about everything,know everything about something.
-
I copy the abstract and quyibl's excellent translation from my case cqz-20 and put here
|
Am J Surg Pathol. 2008 Dec;32(12):1896-904. Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: clinicopathologic analysis of 49 cases, suggesting that grade is not prognostic. Nascimento AF, Raut CP, Fletcher CD. Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Mammary angiosarcoma is a rare neoplasm, accounting for about 0.05% of all primary malignancies of the breast. It is currently believed that histologic grading of mammary angiosarcomas plays an important role in prognostication. Forty-nine cases of primary angiosarcoma of the breast were retrieved from our files. Clinical details and follow-up information were obtained from referring pathologists and clinicians, and by chart review. All statistics were performed using Fisher exact test and only P<0.05 was considered significant. Recurrence-free survival and overall survival curves were established using Statistica software version 5.5 (StatSoft Inc). All patients were female with ages ranging from 15 to 74 years (mean 41.5, median 40). Peak incidence was between the ages of 30 and 50 years. All tumors examined were located within breast parenchyma with or without minor cutaneous involvement. The right side was more commonly affected than the left side (66% vs. 29.5%). Tumor was bilateral at presentation in 2 cases (4.5%). Tumor size varied from 0.7 to 25 cm (mean 6.7, median 5). Most patients presented with a palpable, painless mass. Two patients had a history of prior radiation treatment for breast carcinoma. Histologically, primary tumors were graded using Rosen's 3-tier system: 17 tumors (35.4%) as low grade, 17 (35.4%) as intermediate grade, and 14 (29.2%) as high grade. Forty-six patients were treated surgically, 11 underwent chemotherapy, and 12 patients received radiotherapy. Follow-up was available in 41 patients (83.7%, median duration 29 mo). Ten patients (24.4%) showed evidence of local recurrence within 11 to 60 months (median 36) after diagnosis. Twenty-four patients (58.5%) thus far have developed metastases, which were most commonly to lung, liver, skin, and bone. Time interval between diagnosis and metastasis ranged from 2 to 144 months (median 34). Eighteen patients (44%) so far have died of disease and 1 died of presumably disseminated breast carcinoma. Five patients (12.2%) are alive with disease and 15 patients (36.6%) are alive with no evidence of disease. Statistical analysis evaluating correlation between tumor grade and size, and rate of local recurrence, metastasis, and death owing to disease showed no significant difference among tumors of different grades. The median recurrence-free and overall survival rates for the entire cohort were 2.8 and 5.7 years, respectively. In conclusion, mammary angiosarcoma is a rare disease that affects relatively younger patients. This tumor seems to have an overall similar clinical course as other types of angiosarcoma arising in skin or soft tissue; it carries a moderate risk of local recurrence, and a high risk of metastasis and death. In this large series, there is no correlation between histologic grade and patient outcome, more in line with angiosarcomas at other sites.
乳腺血管肉瘤是罕见肿瘤,约占乳腺原发恶性肿瘤的0.05%。目前认为乳腺血管肉瘤的组织学分级有重要的预后意义。我们回顾分析了49例乳腺原发血管肉瘤。临床详细资料和随访信息来自相关病理学医生和临床医生,通过图表分析。所有统计数据都进行Fisher确切检验并且仅当P<0.05时才认为是有意义的。无复发生存曲线和总体生存曲线用统计软件版本5.5(statsoft公司)建立。所有病人均为女性,年龄范围从15到74岁(平均41.5岁,中位数40岁)。高发期在30岁至50岁之间。所有肿瘤都位于乳腺实质伴或不伴有微小皮肤浸润。右侧通常较左侧易累及(66%vs.29.5%)。肿瘤累及双侧者2例(4.5%)。肿瘤大小范围0.7cm到25cm(平均6.7,中位数5)。大多数病人表现为可触及的、无痛性的肿块。2例病人有先期乳腺癌放射治疗病史。组织学上,原发肿瘤用Rosen3等级系统进行分级:低级别17例(35.4%),中级别17例(35.4%),高级别14例(29.2%)。46例病人手术治疗,11例化疗,12例进行了放射治疗。有效随访病例41例(83.7%,中位持续时间29个月)。10例(24.4%)病人在11至60个月内(中位数36)局部复发。24例病人(58.5%)迄今为止出现远处转移,大部分转移至肺、肝、皮肤和骨。诊断和转移之间的时间间隔范围为2到144个月(中位数34)。迄今为止18例(44%)病人死于该病,1例推测死于乳腺癌播散。5例病人(12.2%)带瘤生存,15例(36.6%)无瘤生存,各组织学级别间的肿瘤致死性无明显差别。无瘤生存期和总体生存期的中位数分别是2.8年和5.7年。总之,乳腺血管肉瘤是相对多发生于年轻患者的罕见肿瘤。该肿瘤总体看来同发生于皮肤和软组织的血管肉瘤有类似的临床过程;它有中等风险的局部复发性,和高风险的远处转移及致死性。在该研究系列中,组织学分级与病人预后间无关联,与其他部位的血管肉瘤较符合。 quyibl译,不妥处请及时指正。 |
cqzhao老师意见:
angiosarcoma罕见,却是乳腺最常见的纯间质恶性肿瘤。可以是自发性的,也可以继发于放射治疗或乳腺根治后的淋巴管水肿。乳腺血管肉瘤包括发生于乳腺皮肤和乳腺实质的,或二者兼有,其临床过程类似。一般说来,血管肉瘤边界不清,具有细胞的非典型性、核分裂活跃、坏死区等多个特征不同的区域。在不同病例可能某些特征更明显一些。高级别血管肉瘤可能含有低级别或交界性血管肉瘤成分。具体到该例:梭形细胞构成实性区域、显著的细胞非典型性、核分裂、坏死,是个典型的高级别血管肉瘤。

- 赚点散碎银子养家,乐呵呵的穿衣吃饭