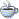| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B1776Rosai-Dorfman Disease present in breast (cqz 16)
| 以下是引用笃行者在2009-4-9 20:34:00的发言: 这种图像在乳腺还真没见过,如果在软组织我倒想到Rosai-dorfman病 |
You are great.
RD is rare in breast. I saw three breast cases for one year when I was at AFIP. In fact i work in Magee women's hospital (about 30,000 surgical cases with half for breast and half for gyn) for three years and we do not have any breast RD case. AFIP is a consulting institute and this is why there are many rare and difficult cases.
Dr. 笃行者 can tell us why you think it is RD in your first impression?
Also please have a brrief summary about RD, clinical, morphologic, IHC, treatment, prognosis et al.
Thank,
cz
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-04-19 18:45:00 编辑
Differential Diagnosis of all lymphoid lesions in breast (from Rosen's Breast Pathology)
infiltrating lobular carcinoma浸润性小叶癌
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma非Hodgkin淋巴瘤
Atypical Lymphoid Infiltrates with Uncertain Clinical Course (Pseudolymphoma)临床行为不确定的不典型淋巴样浸润(假淋巴瘤)
Extranodal Sinus Histocytosis with Massive Lymphadenopathy(Rosai-Dorfman's disease)见下
Hodgkin's Disease
Plasmacytic Tumors浆细胞肿瘤
Leukemic Infiltration (Granulocytic Sarcoma, Lymphocytic Leukemia)白血病浸润(粒细胞肉瘤,淋巴细胞性白血病)
Myeloid Metaplasia (extramedullary hematopoiesis) 髓样化生(髓外造血)
other inflammatory lesions in breast其它乳腺典型的炎症性病变

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-04-16 21:12:00 编辑
Extranodal Sinus Histocytosis with Massive Lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman's disease)
结外的窦组织细胞增生症伴巨淋巴结病(Rosai-Dorfman病)
The differential diagnosis of lymphohistiocytic infiltrative disease in the breast also includes extranodal sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman's disease). Involvement of virtually every organ including the breast has been described (72) (Fig. 40.20). Mammography reveals a dense mass that may be nodular or ill-defined (73,74). Axillary adenopathy is present in some but not all patients. Lymph node infiltration is characterized histologically by diffuse expansion of sinuses due to a histiocytic infiltrate. Subcutaneous lesions have been described in the breast, and there are rare examples of nodular unilateral or bilateral mammary parenchymal involvement (73,75). The lesion may have plasma cells, germinal centers, and appear to be a reactive process when spindled histiocytic cells are associated with collagen deposition in a storiform pattern (Fig. 40.20). The infiltrating histiocytic cells have single or multiple nuclei that contain one or more nucleoli, and there may be occasional mitotic figures. The histiocytes exhibit lymphophagocytosis or erythrophagocytosis. Aspiration cytology of the breast lesion is likely to suggest an inflammatory process or lymphoma (75). The infiltrating histiocytic cells are reactive for S-100 and histiocytic markers such as CD68 in almost all cases, but there is usually an inverse relationship in the intensity of staining for these markers. The immunohistochemical phenotype will rule out most metastatic tumors, but lesions with strong S-100 staining and weak or absent histiocytic markers (CD68) may require more extensive study for HMB45, lysozyme, and other markers.
要点:
RD累犯乳腺皮下,罕见累及乳腺实质。病变可以有浆细胞、生发中心,当梭形组织细胞伴随胶原沉积于编织结构时,可呈反应性病变。浸润的组织细胞可为单核或多核,含一或多个核仁,偶有核分裂。组织细胞的胞浆内吞噬淋巴细胞或红细胞。浸润的组织细胞表达S-100和CD68等组织细胞标记物。当S-100强阳性而CD68弱阳性或阴性时,要增加HMB45和lysozyme等其它标记物。
以上是从Rosen's Breast Pathology中学习到的,谢谢Dr.Zhao赠书!不当之处请指正。

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
The differential dx of RDD also includes Langerhans' cell histoiocytosis which is positive for S-100.
Which mark can distingush these two?
Are the lymphocytes T or B or mixed?
Are the plasma cells polyclonal or monoclonal?
The etiology of RDD remains unknown.
What are the most two likely possibilities?
Is there effective treatment?
What is the prognosis?
What age and what race are more common for RDD?
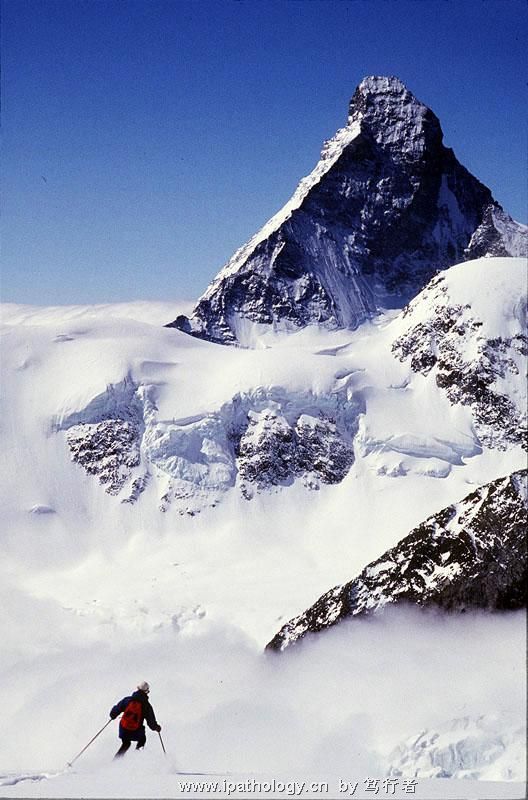
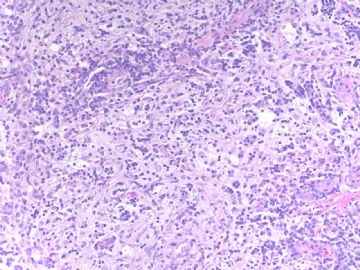
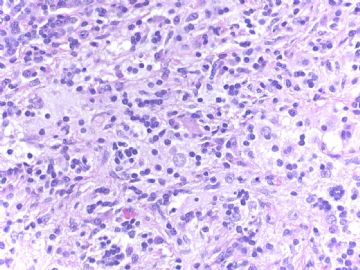
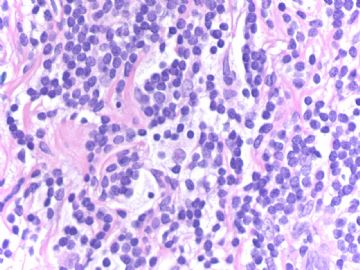




 从图片上看很难断定是否为肿瘤,但总体上看细胞小,需免疫组化除外癌还是淋巴瘤。
从图片上看很难断定是否为肿瘤,但总体上看细胞小,需免疫组化除外癌还是淋巴瘤。