| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
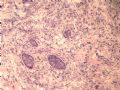
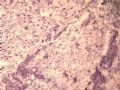
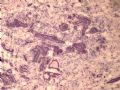
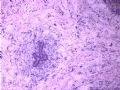
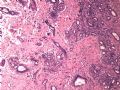
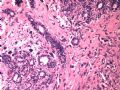
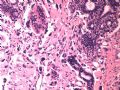
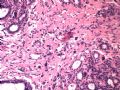
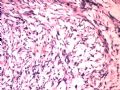
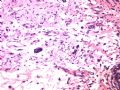
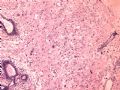
- B1614纤维腺瘤? 还是?
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
女 ,44岁,发现右乳房包块数日。大体:包块3.5×3.5×2.5cm,有完整被膜。
相关帖子
-
Diagn Pathol. 2008 Aug 1;3:33
A diagnostic dilemma in breast pathology - benign fibroadenoma with multinucleated stromal giant cells.
Dept, of Surgery, Mayo General Hospital, Ireland. helenheneghan@hotmail.com.
ABSTRACT: Fibroadenomas are common benign breast tumours that display a characteristic pathological morphology, although several epithelial and stromal variations exist. A very rare histological finding is the presence of multinucleated giant cells throughout the stroma of a benign fibroadenoma. Cells of this type, which are more commonly found incidentally within the interlobular stroma of breast tissue, are benign and should not be mistaken for malignant cells on microscopic examination. Unfortunately a lack of awareness of this pathological entity can lead to diagnostic confusion amongst pathologists resulting in the multinucleate giant cells being mistaken for highly mitotic cells and consequently the fibroadenoma being mistaken for a malignant lesion. This may have serious implications for the subsequent management of the patient. The presence of this unusual cell type in the stroma does not alter the prognosis of otherwise benign lesion. We encountered two such cases at our institution in a six month period recently. We present their histories along with relevant radiological, microscopic and immunohistochemical features, followed by a discussion of this unusual pathological entity
Virchows Arch. 2001 Dec;439(6):768-75
Benign tumors of the breast with multinucleated stromal giant cells. Immunohistochemical analysis of six cases and review of the literature.
Department of Pathology, Charles University Medical Faculty Hospital, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic. ryskaale@fnhk.cz
The authors present six cases of benign tumors of the breast with numerous multinucleated stromal giant cells (MSGC). All six patients were women aged 37-70 years (mean 48 years), presenting clinically with a breast mass 1.0-3.8 cm in size (mean 1.9 cm; median 1.5 cm). By standard H&E examination, all cases showed the presence of numerous MSGC haphazardly dispersed within the tumor stroma. Three cases revealed MSGC merging into the surrounding adipose tissue simulating infiltrative growth. The MSGC appeared to have multiple nuclei (5 to 25) with fine chromatin and sporadic small nucleoli. Their cytoplasm was inconspicuous. The MSGC expressed vimentin only and to lesser extent CD34. These cells were negative for muscle markers, keratins, S-100 protein, vascular markers, CD68 and hormone receptors. Interestingly, the majority of MSGC and mononuclear stromal cells showed reactivity for p53 protein and Ki-67 proliferation antigen. All patients were treated by simple excision and remain free of recurrence (mean 70 months, median 48 months.). The reactivity of p53 in MSGC and mononuclear stromal cells may play a key role in linking these two cell types. Nonetheless, the presence of MSGC does not alter prognosis of otherwise typical benign lesions.