| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- EB病毒淋巴增殖性疾病国际分类
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
EB病毒淋巴增殖性疾病(EBV LPD)国际分类会议于2008年9月8-9日在美国华盛顿Bethesda的美国国家卫生研究院(NIH)召开。会议由国家癌症研究所(NCI)、国家过敏和传染病研究(NIAID)和国家卫生研究院少见病办公室联合主办。Elaine S. Jaffe 和Jeffrey Cohen 教授是会议组织者,共有40人参加会议,其中美国学者28位、日本学者4位、中国香港学者1位(陈国章)、中国大陆学者1位(周小鸽)、韩国学者1位、德国学者1位、英国学者1位、西班牙学者1位、澳大利亚学者1位、秘鲁学者1位。40位与会者中包括14位病理学家和26位病毒学家和临床专家。这14位病理学家是:Elaine S. Jaffe,Nancy Harris, Lawrence Weiss, Steven Swerdlow, Stefania Pittaluga (以上5位来自美国), Leticia Quintanilla-Maritinez (德国), Miqueel Piris(西班牙), John Chan(中国香港), Xiaoge Zhou (中国大陆), Tadashi Yoshino, Koichi Oshima, Shigeo Nakamura(以上3位来自日本), Young Ko (韩国), Carlos Barrionevo (秘鲁)。会议的题目是“非免疫缺陷患者中的EB病毒淋巴增殖性疾病(EBV LPD),即Epstein-Barr Virus Lymphoproliferative Disease (EBV LPD) in Non-immunocompromised Hosts”。会议的总体目的是“更好认识和理解EB病毒淋巴增殖性疾病”,包括4个具体目标:1、从血液学、肿瘤学和传染病学的范畴更好的认识和理解EB病毒淋巴增殖性疾病;2、制定EBV+的B细胞和T细胞增殖性疾病的分类;3、提出研究这些疾病病因和治疗的构架;4、提出治疗这些疾病的临床新方案并考虑组织国际合作研究。为了达到以上目标,会议分成了4个部分:1、EBV+B细胞淋巴增殖性疾病的生物学;2、B细胞和T细胞性急性和慢性EBV综合症;3、EBV淋巴组织增生性疾病的并发症和治疗;4、病理读片。第1个部分由病毒学家介绍EBV的生物学特征和进展;第2部分由来自不同国家的病理和临床学者介绍;第3部分主要由临床血液专家介绍;第4部分病理读片,由各国学者提供EBV淋巴增殖性疾病病例进行读片讨论。具体时间安排如下:
|
|
|
|
| Day / Time | Speaker or Chair | Topic |
| Day 1 |
|
|
| 8:30 – 9:00 | J Cohen & ES Jaffe | Introduction: Charge to the Participants & Dedication |
| Session I | Chrs: Alan Rickinson & J Sixbey | Biology of EBV B cell lymphoproliferative disease |
| 9:00-9:30 | E. Kieff | Perspective of the Virus |
| 9:30-10:00 | G Tosato | The Host Cytokine Response |
| 10:00-10:30 | R Khanna | The Host Cellular Immune Response |
| 10:30-10:45 | K Bhatia | Variations of the virus in EBV + LPDs – significance and implications |
| 10:45-11:00 | Break |
|
| Session II | Chrs: NL Harris & YH Ko | Acute and Chronic EBV syndromes of B cells |
| 11:00-11:30 | J. Cohen | Chronic active/ persistent EBV infection of B-cells |
| 11:30-12:00
| S. Nakamura | Age-associated EBV-associated B-cell lymphomas |
| 12:00-12:15 | ES Jaffe | Non-neoplastic EBV-reactivation syndromes in adults – Pathological & biological features |
| 12:15-1:15 | Lunch |
|
| 1:15-1:30 | K. Dunleavy | Lymphomatoid granulomatosis |
| 1:30-2:00 | SH Swerdlow | PTLD – differences and similarities |
| 2:00-2:30 | Chrs. S Pittaluga & L Weiss | Panel Discussion: Classification and Spectrum of EBV + B-cell proliferations |
| 2:30-2:45 | Break |
|
| Session III | Chrs: M Piris & T Yoshino | Acute and Chronic EBV syndromes of T cells |
| 2:45-3:15 | H Kimura | Chronic Active EBV syndromes in Asia – Clinical features |
| 3:15-3:30 | K Oshima | Chronic Active EBV syndromes in Asia – Pathological features |
| 3:30-3:45 | Quintanilla-Martinez | Systemic EBV-associated T-LPD of childhood- comparisons with CAEBV |
| 3:45-4:00 | C. Barrionuevo | Hydroa vaccineforme –like lymphoma |
| 4:00-4:15 | Young-Hyeh Ko | EBV+ T-cell proliferations in children and adults |
| 4:15-4:30 | Zhou Xiaoge | EBV+ T-cell proliferations in China |
| 4:30-5:15 | Chrs: JKC Chan & J Jones | Panel Discussion: Classification of EBV+ T-cell proliferations |
|
|
|
|
| Day 2 | Speaker or Chair | Topic |
|
| Chrs: JKC Chan & J Jones | Conclusions and summary from Day 1 |
| 8:30-9:00 | ES Jaffe | Proposals for classification & discussion |
| Session IV | S. Kenney & R Little | Therapy & Complications of EBV related lymphoproliferative diseases |
| 9:00 - 9:30 | J Sullivan | EBV-related hemophagocytic syndromes |
| 9:30 - 9:45 | WH Wilson | Non-neoplastic EBV-reactivation syndromes in adults – Clinical Features and Management |
| 9:45 - 10:00 | Break |
|
| 10:00-10:30 | C Rooney | EBV-specific T cell infusions |
| 10:30-11:00 | H Heslop | Bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| 11:00-11:30 | WH Wilson | Novel therapies |
| 11:30-12:00 | Chrs. R Yarchoan & K Rao | Panel Discussion: Future approaches to novel therapies |
| 12:00-12:15 | A. Rickinson | Summing Up: What have we learned about EBV biology and pathogenesis of EBV lymphoproliferative disorders? |
| 12:15-12:30 PM | Conclusion J Cohen & ES Jaffe | Discussion: Action Items for Group |
| 12:30 - 2:00 | Lunch Break |
|
| 2:00-4:00 | ES Jaffe | Informal pathology review for pathologists and clinicians to be held in the Laboratory of Pathology, Clinical Center. Multi-headed scope and video projection available for all participants Participants are invited to bring representative cases for review and discussion |
| 4:15 | Adjournment |
|
经过2天紧张而充实的会议,大家一致认为达到了更好理解EBV淋巴增值性疾病的目的,同时提出了这些疾病分类草案(proposal),并进行热烈的讨论。下面的草案是我记录和理解的内容,仅供大家参考,解解馋,而正式草案要等Jaffe整理完大家的讨论意见以后通过杂志正式发表。会议还讨论了组成国际协作研究EBV+淋巴增殖性疾病。
EBV+淋巴增殖性疾病包括:
EBV+B细胞淋巴增殖性疾病
EBV+T/NK细胞淋巴增殖性疾病
EBV+B细胞淋巴增殖性疾病包括:
1、EBV associated reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (all in node).
2、Chronic active EBV infection (CAEBV-B), (chronic/persistent IM)
-Polymorphic B cell lymphoproliferative disease (nodal)
-Polymorphic B cell lymphoproliferative disease (extranodal)
-Monomorphic B cell lymphoproliferative disease (EBV+ large B-cell lymphoma-plasmablastic lymphoma type)
3、EBV+ large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly
EBV+T/NK细胞淋巴增殖性疾病:
EBV+ T-cell/NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases of childhood (CAEBV-T/NK)
(1)、Systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoproliferative diseases (mono-, oligo-, polyclonal)
(2)、Cutaneous T-cell and NK-cell variants
-hydro vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative diseases (hyperplasia to lymphoma)
-Mosquito bite allergy (hyperplasia to lymphoma)
Criteria for CAEBV-B is:
1. severe illness (fever) over than 6 months.
2. serum abnormal EBV antibody titer elevated, and/or high viral loads.
3. histological evidence of major organ involvement such as lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and so on.
4. increased quantities of EBV B-cells in affected tissues (EBER/LMP1+B-cells)
Criteria for CAEBV-T/NK
1、severe illness (fever) over than 3 (or 6) months.
2、serum abnormal EBV antibody titer elevated, and/or high viral loads.
3、histological evidence of major organ involvement such as lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and so on.
4、increased quantities of EBV T/NK-cells in affected tissues (EBER/LMP1+T/NK-cells)
Grades of Systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoproliferative diseases
A1: polymorphic histology and polyclonal of TCell.
A2: polymorphic histology and monoclonal of T-cell.
A3: monomorphic histology and monoclonal of T-cell.
B: infantile fulminant LPD/hemophagocytic syndrome
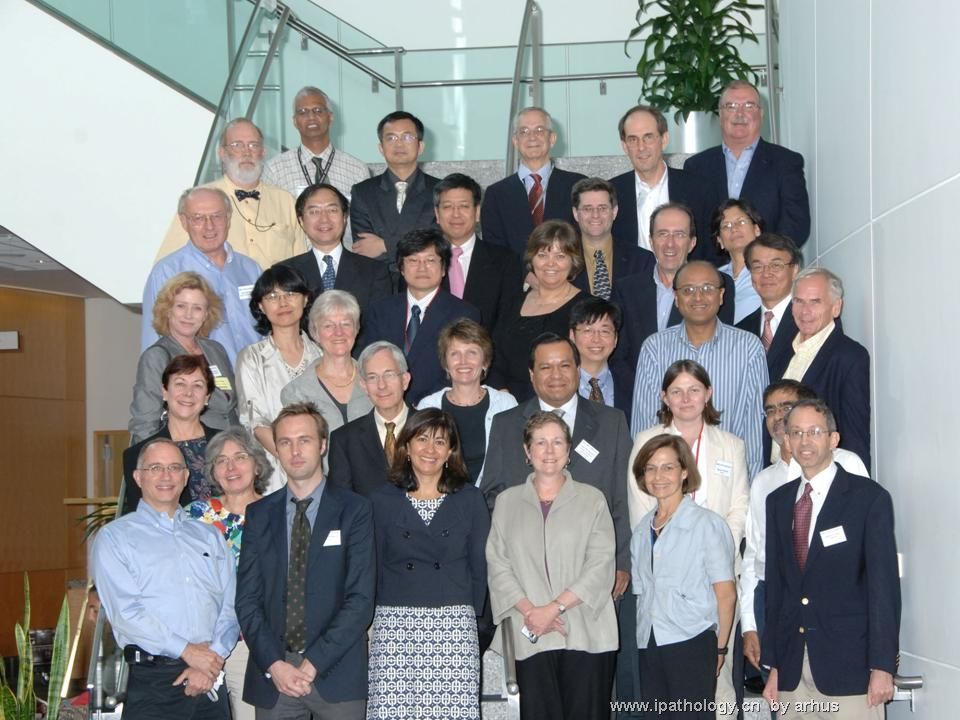

名称:图1
描述:图1
-
本帖最后由 于 2008-09-16 21:21:00 编辑
-
zhanghuadong 离线
- 帖子:172
- 粉蓝豆:1
- 经验:172
- 注册时间:2010-05-05
- 加关注 | 发消息