| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
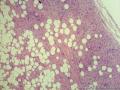
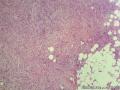
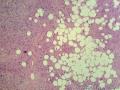
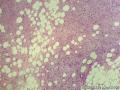
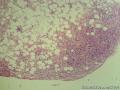
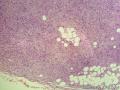
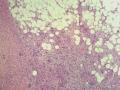
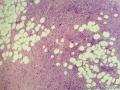
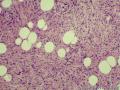
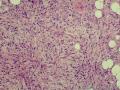
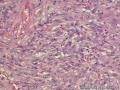
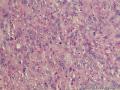
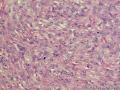
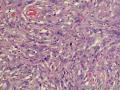
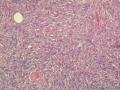
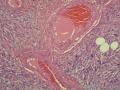
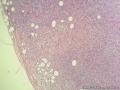
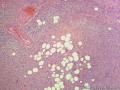
- 外阴软组织肿瘤,富于细胞血管纤维瘤?
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:857
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
| 性别 | 女 | 年龄 | 27 | 临床诊断 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般病史 | 外阴 | ||||
| 标本名称 | 外阴 | ||||
| 大体所见 | 27y,女性,外阴3.5*2.5*1.5cm扁圆形肿块,包膜完整,手术完整剥离。 | ||||
相关帖子
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:857
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 TK1905 于 2014-06-03 21:50:53 编辑
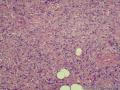
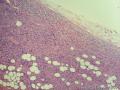
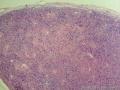
形态学上血管肌纤维母细胞瘤:上皮样、浆细胞样细胞或梭形细胞围绕血管生长,有一定的排列规律如索状等等,背景有疏密区,如水肿区域,可见脂肪组织、肥大细胞。血管很少玻璃样变
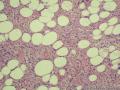
细胞性血管纤维瘤:小-中等大的血管遍布整个病变,管壁常增厚玻变;梭形细胞排列一般没有规律,多随意排列,或局部有束状等排列;背景可以含有脂肪细胞,边界清楚;
免疫组化:2者很难鉴别,但最近遗传学和免疫组化有很大进展。血管肌纤维母细胞瘤是不同于细胞性血管纤维瘤的,后者有13q14丢失,前者则无。后者表现为位于13q14上的rb1基因和FOXO1基因也丢失,理论上抑癌基因rb也丢失,表现在IHC就是rb标记缺失(即阴性),ajsp的研究证实rb能鉴别这些类似病变,结论是血管肌纤维母细胞瘤rb均(+),细胞性血管纤维瘤、梭形细胞/多形性脂肪瘤均(-),乳腺型肌纤维母细胞瘤89%(+)。因此从遗传学角度,现在的观点认为:细胞性血管纤维瘤、梭形细胞/多形性脂肪瘤、乳腺型肌纤维母细胞瘤是一种实体的不同形态;血管肌纤维母细胞瘤则是另外的实体。其它rb正常阳性的还有孤立性纤维瘤、各种脂肪肉瘤。值得注意的是有9%的普通脂肪瘤rb也(-)
本例图26更像细胞性血管纤维瘤,核分裂不少这点女性多见。也有非典型性和肉瘤转化的细胞性血管纤维瘤的报道
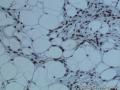
有条件做rb染色,定位于核。有更好的条件做FISH看有无13q14丢失
Hum Pathol. 2014 Apr 18.
Vulvovaginal angiomyofibroblastomas: morphologic, immunohistochemical, and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis for deletion of 13q14 region.
Abstract
Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is a benign tumor that belongs to the category of the "stromal tumors of the lower female genital tract," together with cellular angiofibroma and myofibroblastoma. Previous studies have shown overlapping morphologic and immunohistochemical features between these tumors and spindle cell lipoma, mammary-type myofibroblastoma, and vulvovaginal cellular angiofibroma and myofibroblastoma. In addition, typical loss of genetic material from the 13q14 region has been documented in all the above-mentioned tumors, suggesting that they are histogenetically related. We report the clinicopathologic features of 11 new cases of vulvovaginal AMFBs. Histologically, the basic common theme was a proliferation of bland-looking spindle to round-to-epithelioid cells set in an edematous to fibrous stroma, frequently arranged around thin-walled blood vessels. Two cases were composed of a prominent mature fatty component closely admixed with typical areas of AMFB, and thus, they were designated as "lipomatous AMFBs." Notably, 1 case was closely reminiscent of Sertoli cell tumor, sclerosing type, because of its predominant cord-like arrangement. Immunohistochemically, all tumors were diffusely positive for vimentin, whereas desmin and α-smooth muscle actin were expressed in a minority of cases, suggesting a fibroblastic rather than myofibroblastic differentiation. Most cases of AMFBs coexpressed Bcl-2 protein and CD99. Interestingly, all 5 cases of AMFB with evaluable signals failed to show monoallelic loss of FOXO1 loci (13q14) by fluorescence in situ hybridization. These cytogenetic findings suggest that vulvovaginal AMFB is not genetically related to cellular angiofibroma and myofibroblastoma of the lower female genital tract.
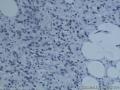
为什么前面13张图的细胞核形态与后面不同?
图14及后图示,空泡状核,有明显核仁,核分裂易见,估计已经超过1/10HPF,Ki指数也不低。这些特征不符合富细胞性血管纤维瘤的通常表现。免疫组化也不支持:Cellular angiofibromas are notable for strong and diffuse expression for CD34 (60%) with relatively less expression of smooth muscle actin (21%) and desmin (8%). Both estrogen and progesterone receptor proteins can be seen in a subset of cases but more often in tumors removed from women than men. (ENZINGER AND WEISS'S SOFT TISSUE TUMORS, 6ed)
我的处理方法:在明确诊断某个具体疾病之前,称为梭形细胞软组织肿瘤,核分裂易见,考虑低度恶性潜能,建议密切随访。

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:857
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
为什么前面13张图的细胞核形态与后面不同?
图14及后图示,空泡状核,有明显核仁,核分裂易见,估计已经超过1/10HPF,Ki指数也不低。这些特征不符合富细胞性血管纤维瘤的通常表现。免疫组化也不支持:Cellular angiofibromas are notable for strong and diffuse expression for CD34 (60%) with relatively less expression of smooth muscle actin (21%) and desmin (8%). Both estrogen and progesterone receptor proteins can be seen in a subset of cases but more often in tumors removed from women than men. (ENZINGER AND WEISS'S SOFT TISSUE TUMORS, 6ed)
我的处理方法:在明确诊断某个具体疾病之前,称为梭形细胞软组织肿瘤,核分裂易见,考虑低度恶性潜能,建议密切随访。
前面为冰冻切片,后面为石蜡切片图,此病例正在上级医院会诊。
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:857
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息
整张切片阳性比例超过10%了吗?另外还要区分是否是内对照的血管内皮和炎症细胞rb+,以及一些反应性的间质细胞rb+,如果能区分出来,那么不应计入阳性,只能视为内对照,血管和炎症细胞可能很好区分,但反应性的梭形细胞成分要单独识别出来可能很困难或是不可能的。最令人信服的答案可能需要FISH才能明确。
In some cases of cellular angiofibroma, interpretation of Rb staining required careful differentiation between loss of expression in lesional cells and intact nuclear staining in the frequent blood vessels and reactive stromal cells often found in these tumors. This was facilitated by comparing the Rb-stained slides with the corresponding hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections.
In all cases, nuclear staining of endothelial cells and inflammatory cells represented a consistent internal control for intact Rb expression. Because of the prominent vascular proliferation in cellular angiofibroma and the presence of reactive stromal changes, distinguishing tumor cells from vascular and reactive stromal cells was sometimes difficult.Careful morphologic assessment of highly vascularized lesions is therefore needed to determine Rb expression status.In some cases of non–13q-deleted tumors, nuclear Rb expression within tumor cells was somewhat heterogenous.The significance of this latter finding is unknown.
Cellular angiofibroma: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 51 cases.
Abstract
Cellular angiofibroma is a recently described histologically distinctive benign mesenchymal neoplasm composed of 2 principal components, the cellular spindle cell component and prominent stromal blood vessels. Cases in males have sometimes been called "angiomyofibroblastoma-like tumor." We describe a series of 51 cases of cellular angiofibroma to further characterize its clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical features. There were 26 women and 25 men, ranging in age from 22 to 78 years (mean 53.5, median 52 years). Men tended to be older than women. Tumor size ranged from 0.6 to 25.0 cm (overall median size 3.9 cm, median in women 2.7 cm, median in men 6.7 cm). Most common sites were the vulvovaginal region (22 cases) and the inguinoscrotal region (19 cases). Preoperative duration (known for 25 patients) ranged from 1 week to 5 years, with presentation as a painless mass, except for 1 case each with intermittent genital bleeding and a painful mass. Most lesions were located primarily in subcutaneous tissue. Most cases were grossly well marginated. Two cases showed foci of hemorrhage and 1 case showed foci of necrosis. Microscopically, 41 tumors were well circumscribed, and 2 tumors infiltrated into the surrounding tissue. All tumors consisted of bland, spindle-shaped cells, short bundles of wispy collagen and numerous small- to medium-sized thick-walled vessels. Intralesional fat(病变内脂肪) was present in 12 cases (6 female and 6 male cases). Mild cytologic atypia (5 cases/5例微小的非典型性) and frequent mitoses (3 cases/3例可见较高的核分裂) were infrequent; significant nuclear atypia and abnormal mitoses were absent. By immunohistochemistry, 29 of 48 tumors (60%) expressed CD34, 10 of 48 (21%) SMA, 4 of 48 (8%) desmin, but none expressed S-100 protein. Follow-up information was available for 40 patients (range 4-168 months; mean 31.2 months) and no patient has developed recurrence or metastasis to date.
Cellular angiofibroma with atypia or sarcomatous transformation: clinicopathologic analysis of 13 cases.(细胞性血管纤维瘤伴有非典型性或肉瘤转化:13例的临床病理分析)
Abstract
Cellular angiofibroma is a mesenchymal neoplasm that is characterized by a bland spindle cell component, morphologically reminiscent of spindle cell lipoma, and thick-walled vessels. The tumor occurs equally in men and women and usually arises in the inguino-scrotal or vulvovaginal regions. An earlier study of 51 cases from our group showed that the tumor follows a benign course without any tendency for recurrence. In 1 case, an intralesional microscopic nodule of pleomorphic liposarcoma was observed. The biologic significance of atypia or sarcomatous transformation in cellular angiofibroma remains uncertain. In this study, we characterized clinicopathologic features in 13 cases of cellular angiofibroma with morphologic atypia or sarcomatous transformation. Thirteen cases with atypia or sarcomatous transformation among 154 usual cellular angiofibromas identified between 1993 and 2009 were retrieved from consultation files. There were 12 females and 1 male ranging in age from 39 to 71 years (median age, 46 y). Tumor size ranged from 1.2 to 7.5 cm. In 11 cases, the tumors occurred in the vulva. One case each occurred in the paratesticular and hip regions. Most tumors were located in subcutaneous tissue. There were 4 cases of cellular angiofibroma with atypia. Three showed severely atypical cells as scattered foci within the cellular angiofibroma. One case showed a discrete nodule of atypical cells. There were 9 cases of cellular angiofibroma with morphologic features of sarcomatous transformation. In each case, abrupt transition to a discrete sarcomatous component was seen. Of these 9 cases, the sarcomatous component in 2 cases showed features of pleomorphic liposarcoma with multivacuolated lipoblasts readily identified. Three of these 9 cases showed discrete nodule(s) closely resembling atypical lipomatous tumor within usual cellular angiofibroma. In the remaining 4 cases, the sarcomatous component was composed of pleomorphic spindle cells arranged in various patterns. By immunohistochemistry, atypical cellsand sarcomatous areas showed either multifocal or more diffuse p16 expression compared with either scattered or negative expression in the conventional cellular angiofibroma. The 3 cases with atypical lipomatous tumor-like areas were negative for MDM-2 and CDK4. Follow-up information was available for 7 patients (range from 2 to 75 mo; median: 14 mo). Six patients did not develop recurrence or metastasis. One patient died of metastatic carcinoma of unknown primary site 27 months after the diagnosis of cellular angiofibroma with sarcomatous transformation. Cellular angiofibroma with atypia or morphologic sarcomatous transformation occurs predominantly in the subcutaneous tissue of the vulva and, as yet, shows no evident tendency to recur based on limited clinical follow-up available for 7 cases. The sarcomatous component can show variable features including atypical lipomatous tumor, pleomorphic liposarcoma, and pleomorphic sarcoma NOS. Overexpression of p16 in the atypical cells and sarcomatous component suggests a possible underlying molecular mechanism.
-
panyl10055 离线
- 帖子:258
- 粉蓝豆:857
- 经验:1331
- 注册时间:2008-08-12
- 加关注 | 发消息