| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
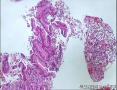
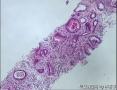
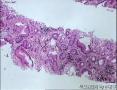
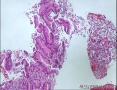
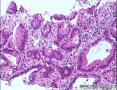
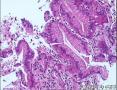
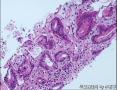
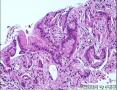
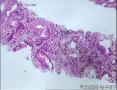
- 肺穿刺
请看文献:
1)Strickland-Marmol LB, Khoor A, Livingston SK, Rojiani A. Utility of tissue-specific transcription factors thyroid transcription factor 1 and Cdx2 in determining the primary site of metastatic adenocarcinomas to the brain.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007 Nov;131(11):1686-90.
结果提示,Cdx2 和 TTF-1分别对判读转移性胃肠道腺癌和肺腺癌的价值是相等的。其特异性及阳性预测价值分别均为100%
Source
Abstract
CONTEXT:
Brain metastases of adenocarcinoma of unknown primary pose a diagnostic dilemma to the surgical pathologist. Although the most common source in these cases is the lung, determining a primary source is difficult on routinely stained slides. Immunohistochemical stain panels including differential cytokeratins, hormone receptors, and breast-specific proteins are commonly used in these cases. Recently, attention has turned to tissue-specific transcription factors, such as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) and Cdx2, in the appraisal of metastatic adenocarcinomas.
OBJECTIVE:
To characterize the previously unpublished immunohistochemical expression of the relatively new tissue-specific transcription factor Cdx2 in metastatic adenocarcinomas to the brain.
DESIGN:
We reviewed the surgical pathology files of the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, Tampa, Fla, and retrieved 38 consecutive cases of metastatic adenocarcinoma (22 pulmonary, 10 breast, 6 gastrointestinal [2 esophagus/gastroesophageal junction, 4 colorectal]) to the brain with confirmation of the primary site by chart review and histologic evaluation. Sections were immunohistochemically stained with antibodies to TTF-1, Cdx2, and cytokeratins 7 and 20 by standard methods.
RESULTS:
Specificities and positive predictive values for Cdx2 and TTF-1 equaled 100% for metastatic gastrointestinal and pulmonary adenocarcinomas, respectively. The negative predictive value of Cdx2 was also very high at 97%.
CONCLUSIONS:
Cdx2 is a specific and valuable tool for the surgical pathologist when faced with the common problem of metastatic adenocarcinoma of unknown primary. In conjunction with TTF-1, cytokeratin 7, and cytokeratin 20, Cdx2 can accurately differentiate the most common sources of metastatic adenocarcinoma to the brain.
2)Saad RS, Essig DL, Silverman JF, Liu Y.Diagnostic utility of CDX-2 expression in separating metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma from other metastatic adenocarcinoma in fine-needle aspiration cytology using cell blocks. Cancer. 2004 Jun 25;102(3):168-73.
结果显示,CDX-2 阳性核染色在胃肠道腺癌表达率为86%,而在其他部位的腺癌则CDX-2表达为阴性。 TTF-1在转移性胃肠道腺癌为0表达 (0%),而肺腺癌阳性率为80%。
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
CDX-2 gene is a transcription factor that is involved in the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells. Recent studies have shown that CDX-2 could be used as an immunohistochemical marker to differentiate metastatic gastrointestinaladenocarcinoma from other metastatic adenocarcinomas in surgical pathology. The objective of the current study was to investigate the diagnostic value of CDX-2 to separate metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma from other metastatic adenocarcinomas in fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC).
METHODS:
Sixty-two FNAC specimens of metastatic adenocarcinomas with corresponding cell blocks were retrieved from the hospital computer system. There were 22 specimens of metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma, 20 specimens of metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinoma, and 20 specimens of metastatic adenocarcinomas from other sites, including 10 from the breast, 3 from the ovaries, 4 from the pancreas, and 3 from the prostate. Radiology and histologic evaluation confirmed all cases. Sections were immunostained for CDX-2 and thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) using a heat-induced epitope retrieval technique.
RESULTS:
In metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma, CDX-2 demonstrated positive nuclear staining in 19 of 22 specimens (86%). Other specimens of metastatic adenocarcinoma were negative for CDX-2. TTF-1 expression was detected in 0%, 80%, and 0% of metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma, pulmonary adenocarcinoma, and other adenocarcinoma specimens, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of the current study demonstrated that CDX-2 is a sensitive and a specific marker to separate metastaticgastrointestinal adenocarcinoma from other metastatic adenocarcinomas in FNAC specimens.

- 王军臣