| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 讨论:乳腺小叶癌与导管癌
-
在这个帖子里我们将讨论乳腺小叶原位癌、导管原位癌、浸润性小叶癌、浸润性导管癌。希望大家积极参与、共同提高。
乳腺小叶原位癌(lobular carcinoma in situ,LCIS)
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-09-18 07:18:00 编辑
谢谢yueban老师提出这个很有意义的讨论主题。最近学习了陈国璋教授的讲课,分享如下:
PROBLEMS IN DIAGNOSIS OF LOBULAR NEOPLASMS
*Is the invasive carcinoma of lobular or ductal type?
*Is the in-situ carcinoma lobular or ductal type?
*Recognition of the pleomorphic variants of lobular neoplasms
*Does the cellular proliferation in the lobules represent LCIS/ALH or nonspecific lobular hyperplasia?
Lobular or ductal carcinoma?
*Invasive lobular carcinoma has certain distinctive clinical characteristics versus invasive ductal carcinoma:
–More frequently bilateral
–Tumor borders often much more difficult to define
–Greater frequency of metastasis to peritoneum, retroperitoneum, leptomeninges, GI tract, gynecologic organs; lower frequency of pulmonary/pleural involvement
Lobular or ductal carcinoma?
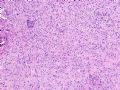
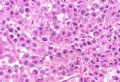
*Lobular carcinoma is characterized by noncohesive cellular growth, but distinction from some ductal carcinomas (especially when cells appear deceptively noncohesive due to poor fixation) can be difficult
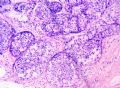
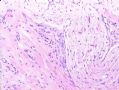
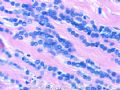
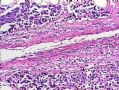
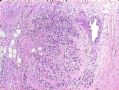
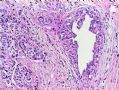
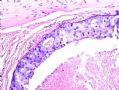
*Immunohistochemical aid for distinction: Ecadherin is consistently lost in lobular carcinoma, while it is expressed in ductal carcinoma (albeit sometimes weak) 图248-251
E-cadherin
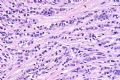
*Cadherin is a cell adhesion molecule mediating cell to cell adhesion via calcium-dependent homophilic binding
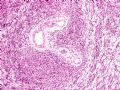
*Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) is a specific subtype of cadherin expressed in practically all epithelial cells (including myoepithelial cells)
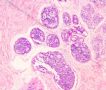
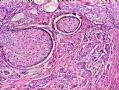
*E-cadherin plays a major role in organization and integrity of epithelial tissues 图253
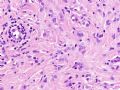
Lobular carcinoma of breast
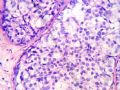
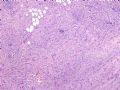
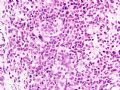
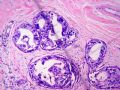
*Loss of E-cadherin (due to mutation in the gene) is a characteristic and defining feature of lobular carcinoma of breast – 图254
E-cadherin in lobular carcinoma
*The loss of cell adhesion (lack of E-cadherin) provides a neat explanation for the observed non-cohesive growth
*Families showing germline mutations in Ecadherin gene often have increased risk for lobular carcinoma of breast and diffuse-type gastric cancer
The reverse!
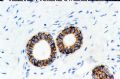
Loss of E-cadherin expression:
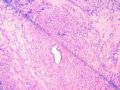
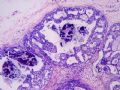
Now utilized to define the pleomorphic variant of lobular carcinoma 图257-259
BEWARE
*Entities that can potentially be mistaken for invasive lobular carcinoma
-Lymphoma
-Leukemia
-Extramedullary hematopoiesis

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-09-18 01:01:00 编辑
小叶肿瘤的诊断问题
*浸润性小叶癌OR浸润性导管癌?
*小叶原位癌OR导管原位癌?
*小叶肿瘤的多形性亚型的识别?
*小叶内的细胞增生:LCIS/ALH或非特异性小叶增生?
小叶癌OR导管癌?
*与导管癌相比,小叶癌有独特的临床特征:
–双侧性更常见
–肿瘤边界更难界定
–更常见转移到腹膜、后腹膜、软脑膜、消化道、女性生殖器官;少见累犯肺/胸膜
小叶癌OR导管癌?
*小叶癌特征:细胞非粘附性生长,但与某些导管癌难以区分(特别是固定不佳产生的非粘附性假象)
*IHC有助于区分:Ecadherin小叶癌阴性,导管癌阳性(尽管有时呈弱表达)
图248-251
E-cadherin
*Cadherin为钙依赖性粘附蛋白,介导细胞间粘附
*E-cadherin为上皮细胞钙粘附蛋白,表达于所有止皮细胞(包括肌上皮)
*E-cadherin对上皮组织的器官整合起重要作用
图253
乳腺小叶癌
*基因突变引起E-cadherin丢失,对乳腺小叶癌的具有特征性决定性意义
图254
E-cadherin与小叶癌
*失去细胞粘附性(缺乏E-cadherin)恰好解释其非粘附性生长
*E-cadherin基因突变:小叶癌和消化道癌的风险增大
失败!
E-cadherin不表达:现用作界定小叶癌的多形性亚型
图257-259
注意!
*可能误诊为浸润性小叶癌:
-淋巴瘤
-白血病
-髓外造血
(未完待续)

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-09-22 09:50:00 编辑
随着乳腺X线照相技术的进步和乳癌普查的广泛开展,乳腺导管原位癌的发生率显著增加。根据其结构可分为以下四型:乳头型、筛状型、实体型、粉刺型。
多中心乳腺导管原位癌虽然少见,但可呈多灶性分布。低分化病变约90%呈连续性;而高分化病变约70%呈非连续性。故后者病变范围的评估较前者困难。
乳腺导管原位癌微浸润:癌细胞浸出乳腺导管或小叶的肌上皮细胞层不超过
乳腺导管原位癌腋窝淋巴结转移率低于2%;乳腺导管原位癌伴微浸润的腋窝淋巴结转移率低于5%。
这个题目贴出后讨论一直较冷淡,也可能大家对乳腺小叶癌及导管癌的诊断都掌握了。在这里我向大家谈几个我在工作中遇到的问题。
1、乳腺癌为什么多见于外上象限?
2、为什么在WHO的新分类中将小叶原位癌与导管原位癌不视为真正意义上的乳腺癌?
3、导管原位癌累及小叶时怎样与小叶癌鉴别?
4、乳腺小叶癌原位癌后期可发生浸润性导管癌而不是浸润性小叶癌吗?
5、乳腺癌常发生于那种类型的乳腺中?
6、为什么充分的哺乳对预防乳癌的发生有积极的意义?
7、乳癌转移部位与预后有关吗?
8、小叶癌与导管癌的转移部位有什么不同?
9、当乳癌发生血行转移时,为什么有相当多的患者已发生骨转移,而没有肺转移?
10、贵院外科对腋窝淋巴结进行分组吗?这样做有什么意义?
11、什么是前哨淋巴结?对临床治疗有什么意义?
12、 byq老师提的问题“浸润性导管癌和浸润性小叶癌合并的临床意义?即预后与单纯的浸导癌和单纯的浸润性小叶癌有何不同?”我认为此问题提的非常好,谢谢!