| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
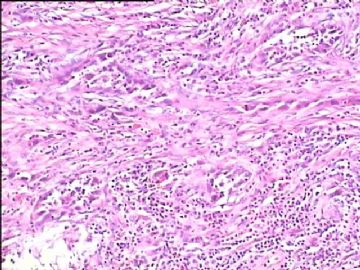
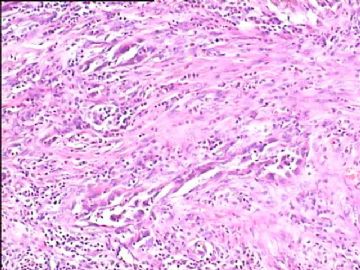
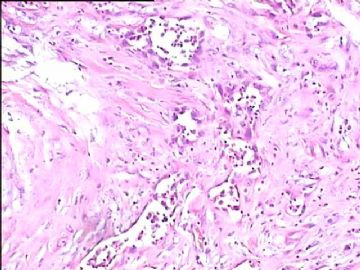
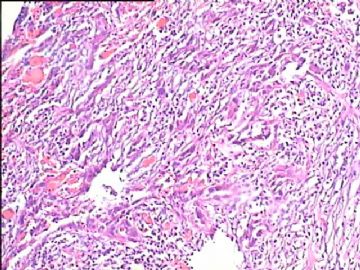
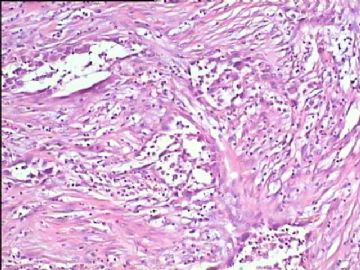
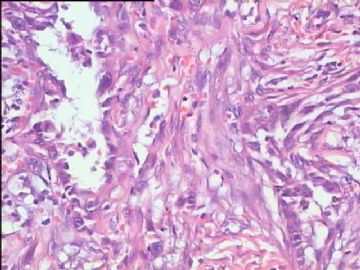
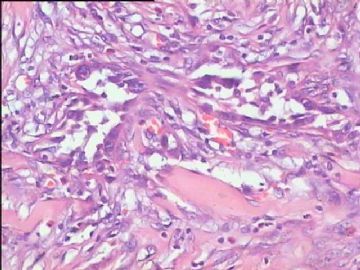
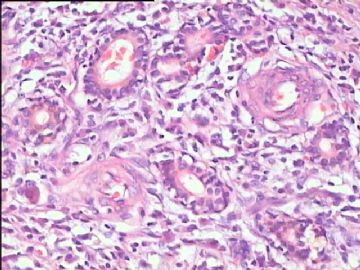
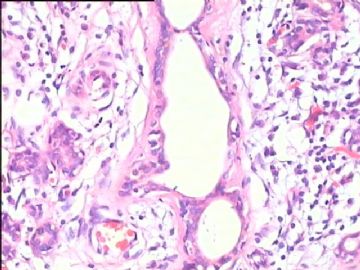
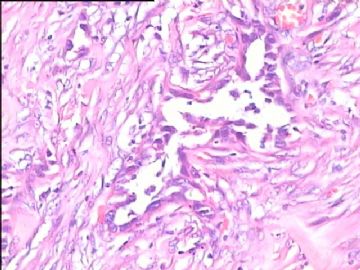
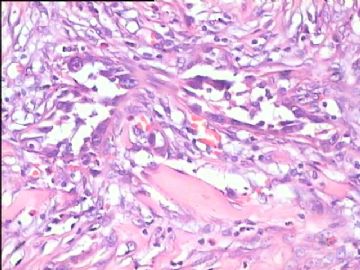
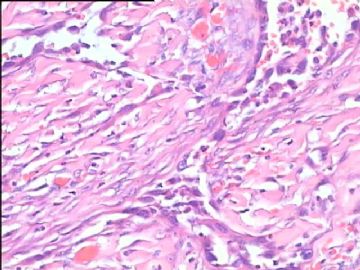
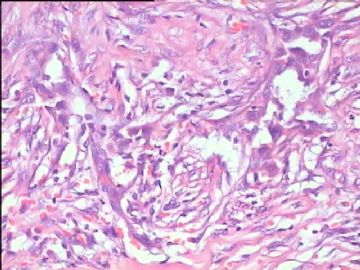
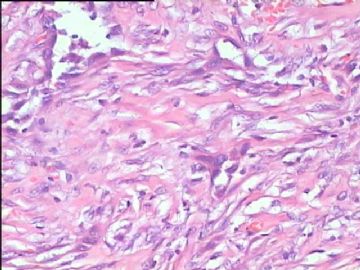
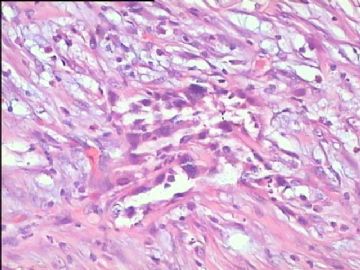
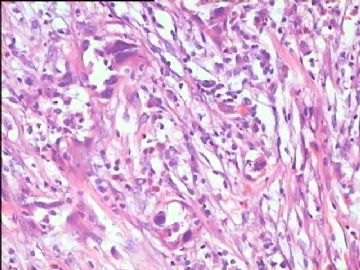
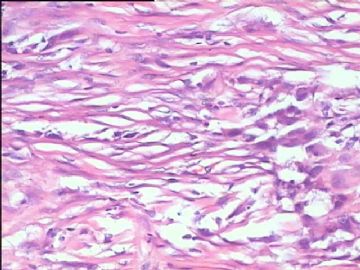
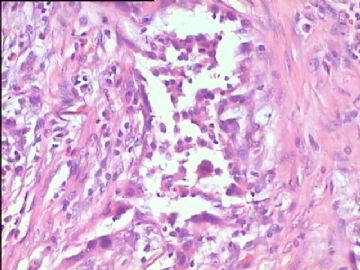
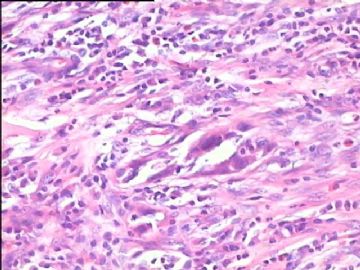
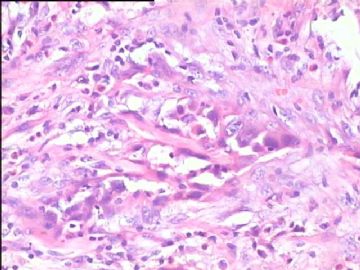
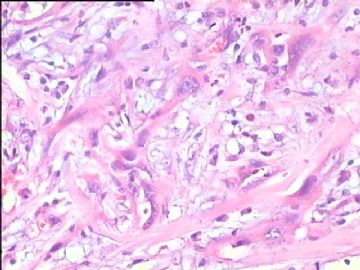
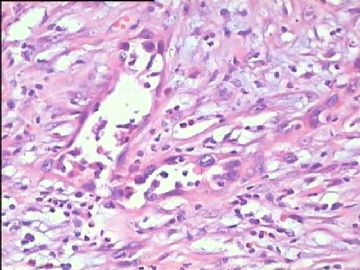
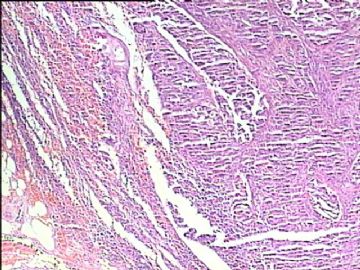
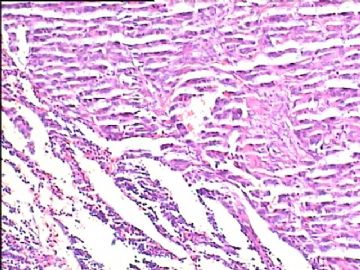
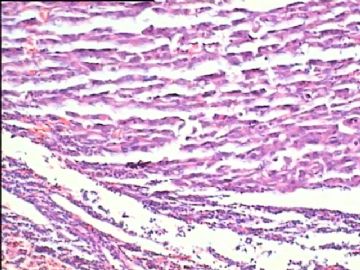
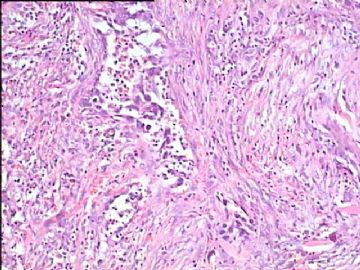
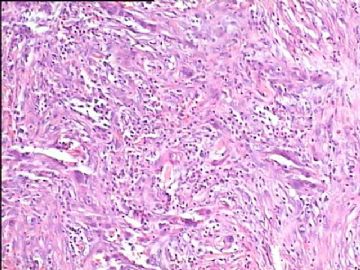
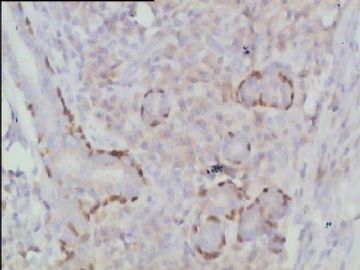
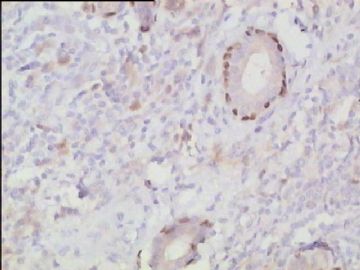
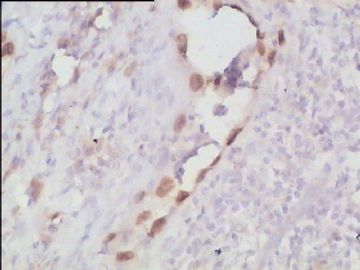
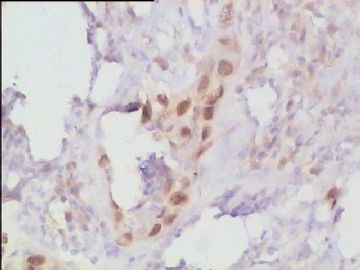
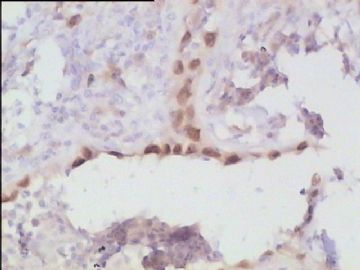
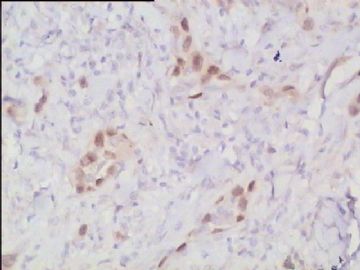
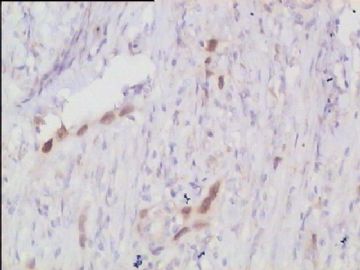
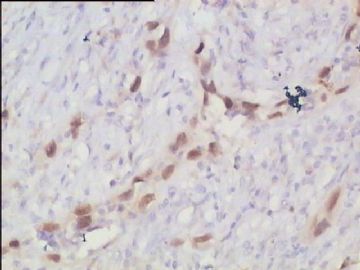
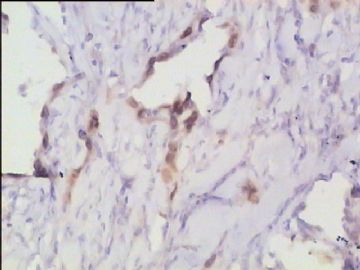
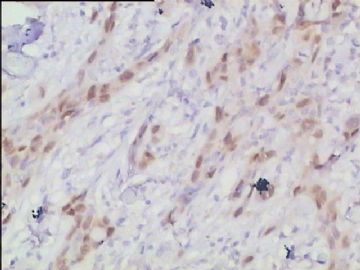
- 腮腺肿瘤(附免疫组化)
Salivary duct carcinoma cytologically diagnosed distinctly from salivary gland carcinomas with squamous differentiation.
Kawahara A, Harada H, Akiba J, Kage M.
Department of Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Japan. akihiko4@med.kurume-u.ac.jp
Abstract
It has been difficult cytologically to distinguish salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) from high-grade carcinoma. We investigated the microscopic cytological findings, morphometric image analyses, and immunohistochemical features of SDC, focusing on how we achieved an accurate differential diagnosis distinguishing SDC from salivary gland carcinomas with squamous differentiation. Immunohistochemical staining was performed for androgen receptor (AR), gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 (GCDFP15), mammaglobin, human gastric mucin, MUC1, MUC2, p63, and cytokeratin high molecular weight. Of the 13 cases of SDC, 9 cases showed typical cytological findings of sheet clusters with polygonal granular cytoplasm with fine chromatin. The other 4 cases showed unusual cytological findings of a pseudo-papillary cluster or scattered cells only, and the tumor cells showed coarse chromatin. Morphometric image analysis showed that the nucleus area was statistically different between SDC and salivary gland carcinomas with squamous differentiation. AR-positive expression (P = 0.008), GCDFP15-positive expression (P = 0.005) and p63-negative expression (P = 0.001) were effective as SDC-specific markers in immunohistochemistry. An accurate cytological diagnosis of SDC can be determined by immunostaining with AR, GCDFP15, and p63, based on the nuclear findings.

- 嫁人就嫁灰太狼,学习要上华夏网。
Salivary duct carcinoma in the sinonasal tract.
Higo R, Takahashi T, Nakata H, Harada H, Sugasawa M.
Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Saitama medical university, Morohongo 38, Moroyama-cho, Iruma-gun, Saitama, Japan. rhigo-tky@umin.ac.jp
Abstract
Salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) is an uncommon malignant tumor, characterized by aggressive behavior and poor prognosis. SDC usually arises from ductal epithelium of the major salivary glands, and it is quite infrequent elsewhere. We present a rare case of a 73-year-old man with SDC, which is possibly originated from the paranasal sinuses or the lacrimal system. Microscopic evaluation revealed that the tumor cells, with pleomorphic nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, formed cell nests and duct-like structure. A cribriform growth pattern was also seen. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for cytokeratins (CAM 5.2 and 34betaE12), gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15), and androgen receptor protein, while p63 and involucrin were negative. The patient already had multiple metastasis of the tumor in the lung at diagnosis, and he could not undergo definitive surgical procedures, because of severe restrictive lung disease. Although SDC in the sinonasal tract is quite rare, SDC should be in the differential diagnosis in these regions, due to its aggressive behavior and poor prognosis.

- 嫁人就嫁灰太狼,学习要上华夏网。