| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 舌缘肿块,上皮内瘤变分级?
-
zhoubingjuan 离线
- 帖子:261
- 粉蓝豆:366
- 经验:590
- 注册时间:2007-05-30
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-06-22 13:37:00 编辑
| 以下是引用xljin8在2010-6-22 6:30:00的发言: Normal/hyperplastic epithelia was defined by K19+ cells only in the first basal
2.Angiero F, Berenzi A, Benetti A, et al. Expression of p16, p53 and Ki-67 proteins in the progression of epithelial MATERIALS AND METHODS: The nuclear expression of p53 and Ki-67 and nuclear and/or RESULTS: p16 was negative in all the group 1 specimens, while both p53 and Ki-67, In the group 2 specimens, the number of p16-, p53-, and Ki-67-positive cells increased as the grade of dysplasia progressed. In group 3 (invasive carcinomas), p53 and p16 expression occurred respectively in 81.8% and 54.5% of cases, while Ki-67 was elevated in all the cases. CONCLUSION: The expression of the cell-cycle proteins p16 and p53 in the dysplastic epithelium, in association with Ki-67, may represent significant markers to recognize evolution of precancerous disease in the oral cavity and to improve identification of the degree of dysplasia. |

- xljin8
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-06-21 10:32:00 编辑
非常好的病例。
口腔、舌、口咽部的鳞状上皮癌前(非浸润性)病变的分类和诊断标准与宫颈鳞状上皮病变基本相似。WHO2005年分类:1)鳞状上皮增生、2)轻度异型增生-SIN1、3)中度异型增生SIN2、4)高度异型增生-SIN3、5)原位癌-SIN3;也有将其命名为鳞状上皮内瘤变(SIN)。当然, 还有其他分类(参考WHO2005头颈部诊断肿瘤分类)。
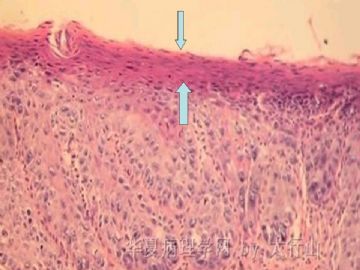
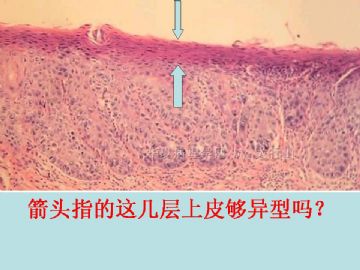
临床上口腔鳞状上皮病变表现为白斑(单纯增生)、红斑(异型增生/原位癌)、白-红斑(异型增生)。本病例比较特殊,既有鳞状上皮增厚和角化过度的病灶、又有鳞状上皮钉脚增生、细胞异型、表面上皮不全角化的鳞状上皮较薄的病灶(箭头指示), 二者相互交错。异型增生明显区域的固有层有较多慢性炎症细胞浸润,存在损伤后修复伴不典型性的可能。倾向诊断为SIN2/中度异型增生。此病例关键在于病灶是否已完整切除, 切缘有无病变残留。SIN演变为浸润性癌需要一定的时间,如病变无残留,可建议临床随访。
仅供参考。谢谢!

- xljin8