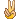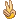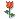| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
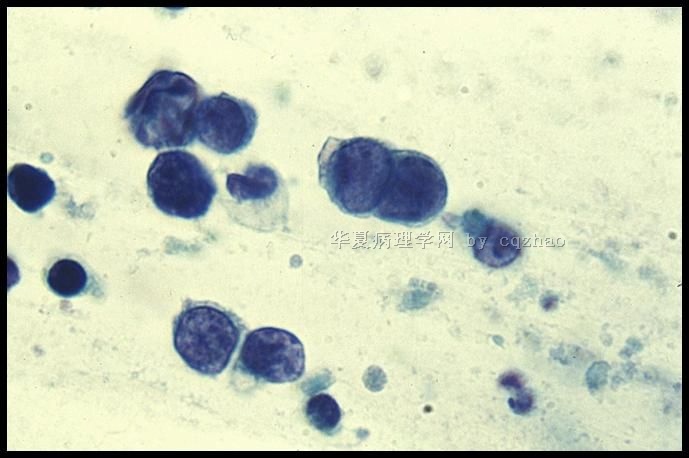
- case1 宫颈小细胞癌; case2宫颈ADC; case 3 50 y/f月经增多
I showed a case here a few days ago. It was a very complicated law-suit case and I cannot find more photos now. So I deleted it because it is not good for education.Sorry for that.(几天前我贴了一个病例在这里。那是一个非常复杂的法律诉讼病例,由于我没有更多的图片,对于教学不是很好所以我删除了它。为此我深感抱歉。)
Our fellow showed an interesting case. I put here for your review.(我们的住院医有一个很有趣的病案,我贴在这里一起分享)
42 y women with LMP 5 days ago and no previous Pap history (女性,42岁,末次月经5天前,既往无巴氏检查)
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-05-07 07:28:00 编辑
谢谢赵老师的一步步提示;其实在前面就回青青姐姐的回复就提示了;其实证明我们学习不仔细。
到现在我再来试着解释解释。
1、最后一副图,下图如果说是正常的内膜细胞脱落;上面那团细胞应该是非典型内膜细胞,核明显的增大,核的颗粒感更明显;但是不足以诊断腺癌。再回头看前几副图的时候,大多比较大的核浆比的细胞都是跟上面那副图相似的异常细胞。
2、月经周期和出血性背景的关系不得不考虑的问题。
3、没有临床病史,临床随机的筛查的时候,我们在看片子也要三思,注意片子中的内对照;那些是正常的成份,那些是异常的成份。(深感自己的基本功没有过关)
4、当然想到子宫内膜腺异常的时候也要同时想到上面我已经回复过的鉴别诊断:小圆细胞的肿瘤和淋巴细胞的异常和正常等等,但是没有100%肯定是恶性的时候还是要慎重直接叫一个恶性诊断,即使组织出来是恶性的。
最后,这个病例现在要我再诊断的话,就诊断;AEM,建议阴道镜下子宫颈管、内膜和宫颈活检。最后等赵老师来解密。谢谢!

- 掌心0164
|
谢谢赵老师非常精彩的点评!得到赵老师的支持与肯定,非常非常高兴! 赵老师说得非常好!一下就点中要害了。 异型性即差异性。差异越大,问题越大。观察、并认识正常形态与非正常形态之间的差异,这是形态学实践过程中最简单,最实用,最常用,也是最经典的观察方法。 |




-
本帖最后由 于 2010-03-13 16:07:00 编辑
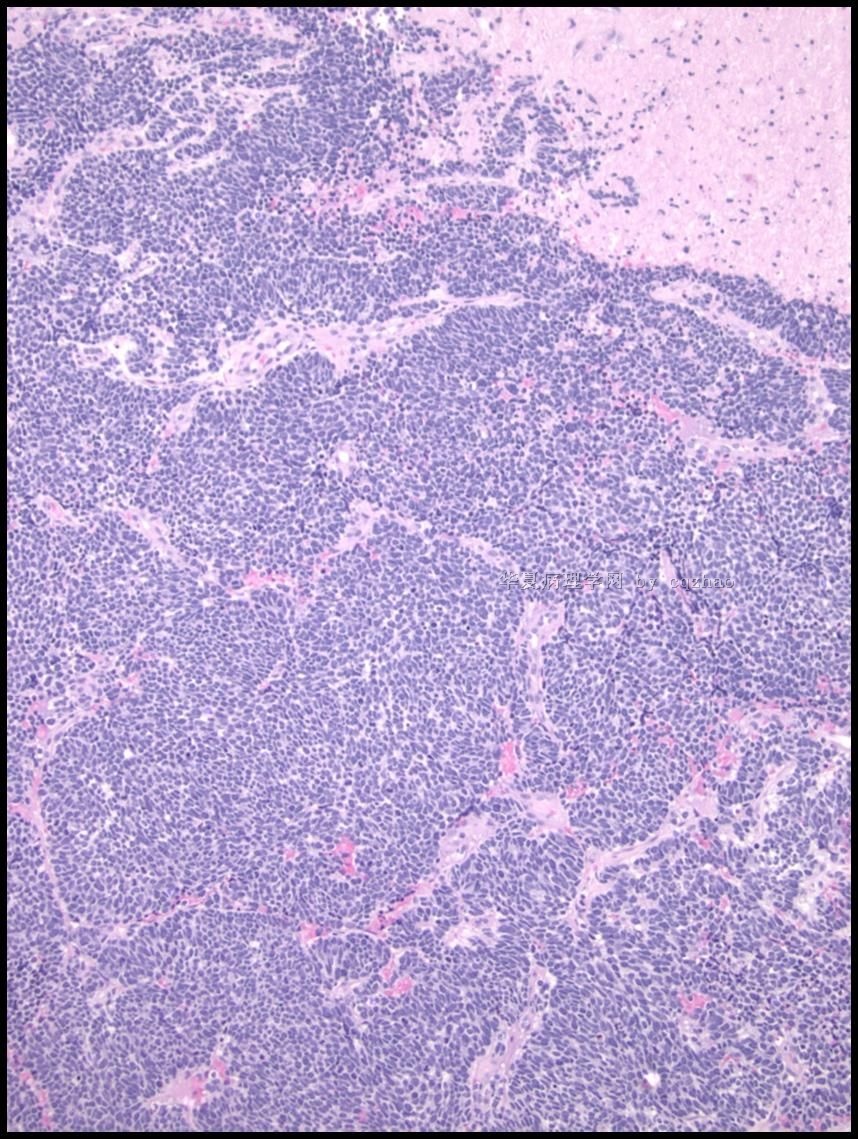
Some features of cervical small cell carcinoma
-Rare (2-5% of invasive cervical carcinomas)
-Clinically aggressive with rapid metastases; frequently presents with parametrial invasion and pelvic lymph node metastases
-Similar age as squamous cell carcinoma (mean 43 years, range 23 to 63 years)
-Associated with HPV, usually HPV-18
-Occasionally presents with paraneoplastic syndromes (Cushing etc)
-Coexisting SIL is rare; endocrine cell hyperplasia may be a precursor lesion
-Can be a part of squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma
Immuno:
-Chromo+, Synapto+, CD56 (most senstitive) at least one neuroendocrine marker should be positive.
-p16+ almost all cases positive
CK (AE1/3)+, few case TTF-1 +,
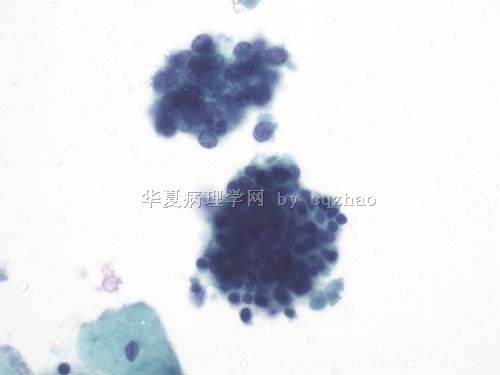
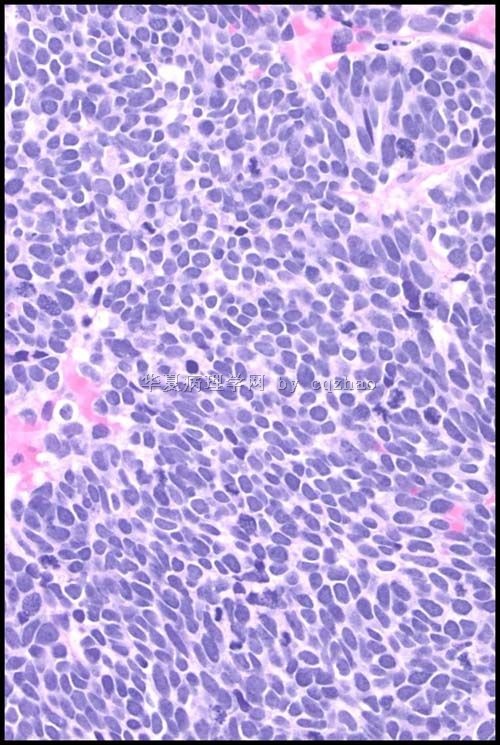
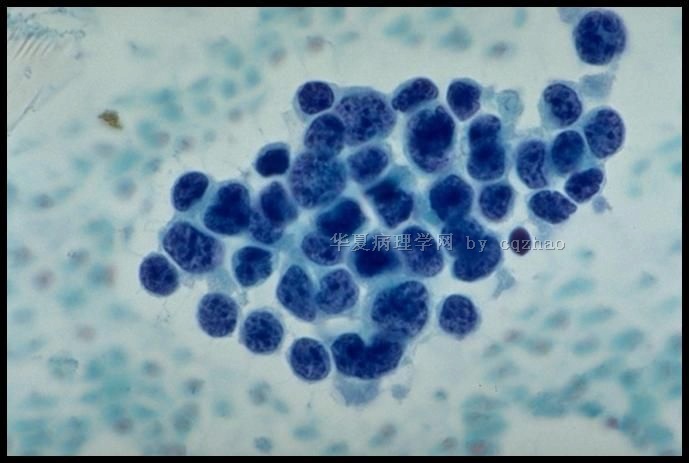
Typical cytology of small cell ca
– Small cells (2xlymphs)
– Carrot-shaped nuclei
– Even powdery chromatin
– Nuclear molding
– Indistinct nucleoli
– Paranuclear blue bodies
– Mitoses
– Scant cytoplasm
– Background of nuclear debris and crush artifact (chromatin streaks)
How do we tell difference of the small cell ca from different location? Some IHC stains may be helpful.
Histopathology. 2007 Sep;51(3):305-12.
Biomarker-assisted diagnosis of ovarian, cervical and pulmonary small cell carcinomas: the role of TTF-1, WT-1 and HPV analysis.
Carlson JW, Nucci MR, Brodsky J, Crum CP, Hirsch MS.
Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Comment in:
AIMS: Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcaemic-type (SCCOH) is morphologically similar to small cell carcinomas from other sites. The aims of this study were to (i) determine if a biomarker panel would distinguish small cell carcinomas of the ovary, cervix (SCCCx) and lung (SCCLu) and (ii) potentially determine the histogenesis of SCCOH. METHODS AND RESULTS: Nine ovarian small cell carcinomas (seven hypercalcaemic type; two pulmonary type), eight SCCCx and 22 SCCLu were immunostained for thyroid transcription factor (TTF)-1, WT-1, p16, cKIT and OCT3/4; a subset of cases were tested for human papillomavirus (HPV). WT-1 was diffusely positive in 6/7 SSCOH versus two of 33 other small cell carcinomas (P <or= 0.001). TTF-1 was diffusely positive in 20/22 SCCLu and 1/8 SCCCx, and negative in all SCCOH. p16 and cKIT demonstrated variable patterns of immunoreactivity in all cases. HPV was identified in 5/6 SCCCx; SCCOH and SCCLu were negative for HPV. CONCLUSIONS: Combined staining with WT-1 and TTF-1 will distinguish SCCOH from SCCLu and SCCCx with a sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 97%. HPV is specific for tumours of cervical origin, but p16 immunohistochemistry is not useful for this purpose. The presence of diffuse WT-1 supports a Müllerian origin for SCCOH, whereas the absence of cKIT and OCT3/4 argues against a germ cell origin.
When we read Pap, we should consider the patients, clinical situation, clinical managment, histology et al.
These also can make the Pap more interesting.
Some one can make a list for the differential diagnosis of small cell carcinoma in Pap test. Thanks, cz
应太阳要求,翻译了赵老师的总结部分,供参考
宫颈小细胞癌的部分特征:
——少见(约占宫颈浸润性癌的2-5%)
——临床侵袭性强,易快速转移,常浸润子宫旁组织及盆腔淋巴结转移
——发病年龄和鳞癌类似(23-63岁,平均43岁)
——和HPV感染相关,尤其是HPV-18
——有时出现类肿瘤综合征(如Cushing综合症等)
——很少合并SIL,内分泌细胞增生可能是其癌前病变之一
——可以是鳞癌或腺癌的一部分
免疫标记:
神经内分泌标记至少有一个阳性:CgA+, Syn+, CD56+ (最敏感)
几乎所有病例p16+
CK (AE1/3)+,少数病例TTF-1 +
宫颈小细胞癌的典型细胞学特征:
——小细胞
——胞核可出现胡萝卜样外形,并易见胞核扭曲
——染色质粉尘状,分布均匀
——核仁不清楚
——核旁蓝染小体
——可见核分裂相
——胞质稀少
——背景核碎片和人为挤压