| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- (已有最后诊断)乳腺肿瘤
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 女 | 年龄: | 45 |
| 标本名称: | 乳腺肿瘤 | ||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
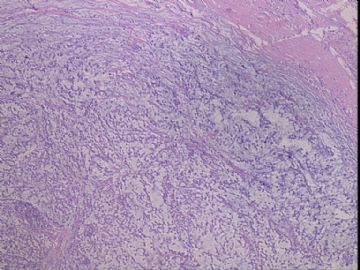
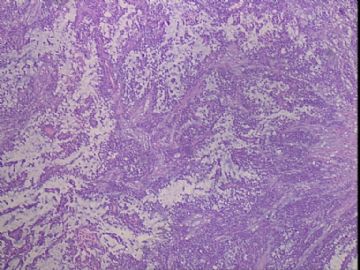
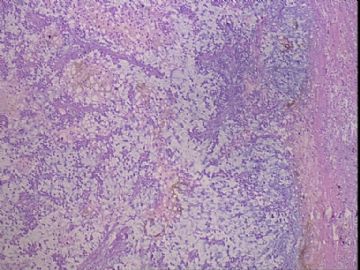
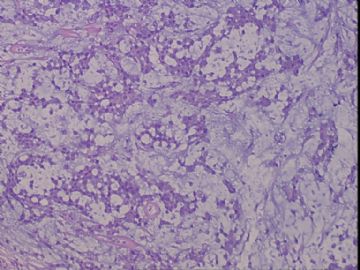
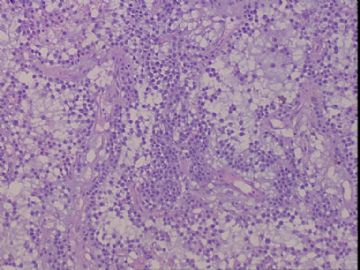
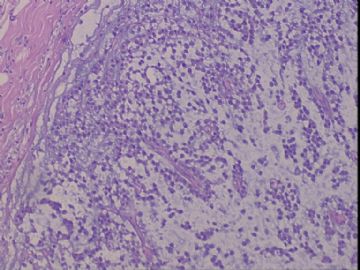
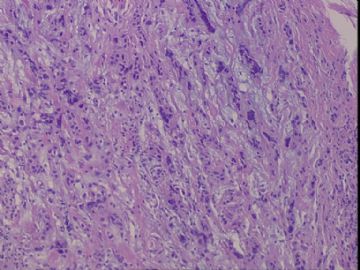
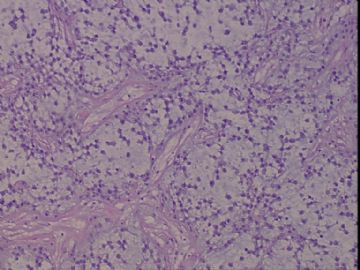
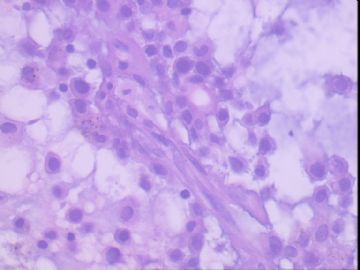
| 肉眼检查: | 右乳腺肿物,2*2cm,切面灰白质硬 | ||||
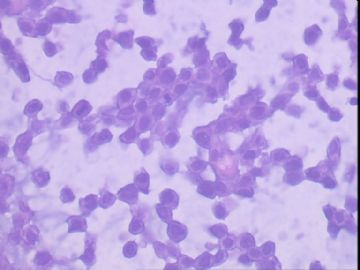
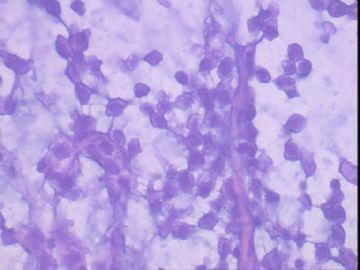
患者,女,45岁,右乳肿瘤,2*2cm,切面灰白质硬。镜下肿物呈分叶状,肿瘤细胞小,界清,排列方式多样,核偏位或居中,可见核分裂,粘液样背景显著,部分区域小血管丰富。肿瘤周边似有癌的区域。免疫组化:S100强阳性,CK、vimentin少部分细胞阳性,Ki67阳性指数大于90%,其余抗体ER,PR,cerbB2,E-cadherin,syn,HCK,EMA,P120,P53,SMA,CEA,CgA,P63均阴性。
本例肿瘤背景粘液非常丰富,血管较多,周边有类似癌的区域,但很少。免疫组化也不好解释,请各位发表意见。
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-04-13 05:02:00 编辑
Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2009 Mar;17(2):131-8.
Immunohistochemical comparison of chordoma with chondrosarcoma, myxopapillary ependymoma, and chordoid meningioma.
Cho HY, Lee M, Takei H, Dancer J, Ro JY, Zhai QJ.
Department of Pathology, The Methodist Hospital, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
Chordoma originates from embryonic notochordal remnants in the midline along the spinal axis and is characterized by cords and lobules of neoplastic cells arranged within myxoid matrix. Because of histologic similarities with myxoid matrix and overlapping immunohistochemical profile, chondrosarcoma, myxopapillary ependymoma, and chordoid meningioma enter in the histologic differential diagnosis at this site. Therefore, the judicious use of a panel of selected immunostains is unquestionably helpful in diagnostically challenging cases. To find useful immunohistochemical markers for assisting in differential diagnosis between chordoma and other tumors with chordoid morphology, an immunohistochemical study using D2-40, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), pan-cytokeratin (panCK), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), S-100 protein, galectin-3, neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), beta-catenin, E-cadherin, and carcinoembryonic antigen was performed on 14 chordomas, 7 chondrosarcomas, 9 myxopapillary ependymomas, and 4 chordoid meningiomas. Chordoma typically showed positive for EMA and panCK and negative for D2-40 and GFAP; whereas chondrosarcoma revealed positive for D2-40, and negative for EMA, panCK, and GFAP; myxopapillary ependymoma positive for GFAP and negative for EMA; and chordoid meningioma positive for EMA, and negative for panCK and GFAP. On the basis of our immunohistochemical study, a panel of D2-40, EMA, panCK, and GFAP allowed the correct recognition of all tumors examined. Other immunohistochemical markers including S-100 protein, galectin-3, NCAM, beta-catenin, E-cadherin, and carcinoembryonic antigen were of little value in differential diagnosis. In summary, the best immunohistochemical markers useful for the evaluation of tumors with chordoid morphology were D2-40, EMA, cytokeratin, and GFAP. D2-40 was a true chondroid marker to be useful for the differential diagnosis with chordoma.
肌上皮分化的富含基质(或曰产基质,Matrix-producing carcinoma)癌是非常罕见的,形态上有两大特征:基质很丰富和肿瘤细胞呈肌上皮表型。将两个不同分类的融入一体。但它绝不同于传统的肌上皮癌,也不同于异源性化生性癌,有可能源自未分化肉瘤那样的组织起源。上皮样成分看似低级别软骨样,并浸没在软骨样基质中。然而,标记却显示高增殖活性,提示为高级别肿瘤,但在形态上没有像梭形细胞肉瘤那样的形态表型所见。目前由于病例稀少,还不明确它的确切起源。
该肿瘤易发生腋窝淋巴结转移,提示是极具侵袭性的肿瘤
本例如果角蛋白标志物不阳或灶阳,而Vim与S-100阳性,按照文献需要再追加标记,至少两个肌上皮标志物阳性 (从actin S, calponin, GFAP, CK14, CD10, p63 and P-cadherin中选4-5个做IHC) 。由于以前认识的限制,很可能将这样的肿瘤诊断为良性(酷似软骨细胞,看似良性,实际上接近未分化)。需要与 良性混合瘤、分叶状肿瘤、 乳腺原发性肉瘤、黏液癌相鉴别。

- 王军臣
请看这篇文献,具有软骨样分化的乳腺癌。像吗?基底类的角蛋白需要重新标记。
Int J Surg Pathol. 2010 Feb;18(1):27-35. Epub 2009 Mar 11.
Breast carcinoma with chondroid differentiation: a clinicopathologic study of 21 triple negative (ER-, PR-, Her2/neu-) cases.
Gwin K, Wheeler DT, Bossuyt V, Tavassoli FA.
Department of Pathology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, USA. katja.gwin@uchospitals.edu
A total of 21 metaplastic breast carcinomas (MCs) with chondroid differentiation were evaluated to better establish the clinicopathological features of this variant. The tumors exhibited mainly invasive carcinoma admixed with areas of cartilaginous matrix production. An associated ductal intraepithelial neoplasia component grade 2 or 3 was observed in 43% of cases. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed a triple negative (ER-, PR-, and Her2/neu-) immunoprofile and no expression of the androgen receptor. EGFR-positivity was found in 88% of evaluated cases, consistent with the proposed basaloid phenotype for all MC. Compared with previous studies that reviewed MC with osseus and cartilaginous elements, the incidence of axillary lymph node metastasis was significantly higher in our study and 60% of positive nodes exhibited chondroid differentiation. Available follow-up data (n = 10) revealed aggressive behavior of this MC variant with frequent metastasis, including visceral involvement and local chest wall recurrence despite chemotherapy and radiation. Three patients subsequently died of metastatic disease.

- 王军臣
按照下列文献至少要2个肌上皮标记(actin S, calponin, GFAP, CK14, CD10, p63 and P-cadherin) ,仅一个标记阳性难以特指。请在其中再选择2-3个肌上皮标记。如果再有一个标志阳性,就支持伴有肌上皮分化的富含基质的乳腺癌。我比较倾向这个诊断。已有标记显示增殖活性高,应该是恶性的。
Ceska Gynekol. 2004 May;69(3):229-36.
[Matrix-producing breast carcinoma with myoepithelial differentiation--description of 11 cases and review of literature aimed at histogenesis and differential diagnosis]
[Article in Czech]
Kinkor Z, Boudová L, Ryska A, Kajo K, Svec A.
Bioptická laborator, s.r.o., Plzen.
OBJECTIVE: Presentation of variable morphology of the so-called matrix-producing carcinoma, the rare variant of metaplastic breast carcinoma. Establish the extent of myoepithelial phenotype by immunohistochemistry and assess behaviour of the lesion. DESIGN: Review of clinicopathologic data of 11 cases. SETTING: Private Biopsy Lab s.r.o., Pilsen and Sikl's Department of Pathology, Charles University and Faculty Hospital, Pilsen. METHODS: Included are eleven cases from Breast Registry, Biopsy Lab s.r.o., Pilsen and Pathology Department, Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové and Martin and from Biopsy Lab in Horovice. Analyzed were morphology, stage, grade and follow up. Myoepithelial phenotype was demonstrated immunohistochemically by LSAB+ system (DAKO) and seven conventional myoepithelial markers (GFAP, aktin S, calponin, cytokeratin 14, p63, CD10 and P-cadherin) were used. Oncogene p53 and Her2/neu were also detected. RESULTS: Matrix-producing carcinoma is an extremely rare type of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast, where high-grade epithelial component continually merges with heterologous mesenchymal chondroid component without overt spindle cell sarcomatoid pattern in between. There were all women at the age of 32 to 86-years (average 54 years, median 52 years) and the maximum tumor diameter ranged from 18 to 60 mm (average 32 mm). The axillary LN was positive in six cases in the time of diagnosis. The follow up available in 9 women ranged from three months to ten years (average 24 months); dissemination of the disease was observed in three cases; 2 of these patients died of disease after three and ten years, respectively. The heterologous mesenchymal chondroid component was produced in two different ways; one displayed typical structure of low-grade hyaline cartilage, in the second one the epithelial tumorous cells were embedded in the homogenous eosinophilic extracellular matrix giving appearance of chondroid aura. Metaplastic component constituted 5-75% of the tumor volume. Immunohistochemical evidence of myoepithelial differentiation in all neoplasms was demonstrated, with at least two conventional myoepithelial markers (actin S, calponin, GFAP, CK14, CD10, p63 and P-cadherin) being positive in every case. Expression of p53 was identified in six cases, all tumors were Her2/neu negative. Histologically the metastases were formed either by carcinoma cells only, or more frequently, they replicated the structure of primary lesion. CONCLUSION: As a rare entity, matrix-producing carcinoma of breast displaying myoepithelial phenotype, deserves separate position in tumor classification. It differs from conventional myoepithelial carcinoma and from heterologous metaplastic carcinoma, where the matrix emanate from undifferentiated sarcomatous tissue, but precise histogenesis in not clear yet. This is a very aggressive lesion and our findings show that previous reports of indolent behaviour were preliminary. Spectrum of differential diagnosis, namely benign mixed tumor, phylloid tumor, primary breast sarcoma and colloid carcinoma warrant clear knowledge about this unique entity.

- 王军臣