| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B2173比较特殊的病理,大家讨论下。
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 女 | 年龄: | 54 |
| 标本名称: | 左乳肿物 | ||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
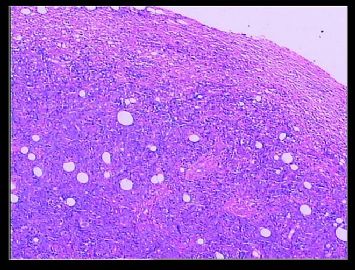
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
相关帖子
Breast Cancer. 2009 Aug 6. [Epub ahead of print]
Clinicopathological characteristics of triple-negative breast cancers.
Pathology Section, Clinical Laboratory Division,
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is defined as a group of breast carcinomas that are negative for expression of hormone receptors and HER2. Although patients with TNBC tend to have a poor prognosis, only chemotherapy is expected to be effective because no therapeutic targets have yet been established. DNA microarray analyses have proved that TNBCs are composed of the basal-like subtype and normal breast (or unclassified) subtype, the former being correlated with an aggressive clinical course. Histological types of TNBCs are reported to be common with those of basal-like subtype, comprising high-grade invasive ductal carcinoma, no special type [solid-tubular carcinoma (or atypical medullary carcinoma), invasive ductal carcinoma with a large central acellular zone], typical medullary carcinoma, and metaplastic carcinomas. The basal-like subtype is characterized by the expression of myoepithelial/basal markers and molecular changes including TP53 gene mutations, BRCA1 inactivation, and many chromosomal alterations. New target molecules for the treatment of TNBCs are under extensive investigation, and their clinical application is awaited.
Med Mol Morphol. 2009 Jun;42(2):128-31. Epub 2009 Jun 18.
The majority of triple-negative breast cancer may correspond to basal-like carcinoma, but triple-negative breast cancer is not identical to basal-like carcinoma.
Kuroda N, Ohara M, Inoue K, Mizuno K, Fujishima N, Hamaguchi N, Lee GH.
Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kochi Red Cross Hospital, 2-13-51 Shin-honmachi,
Recently, the concept of basal-like carcinoma has been proposed. However, there are only a few reports about the relationship between triple-negative cancer and basal-like carcinoma. In this article, we report the study of the expression of basal cell markers in 11 triple-negative cancers. Eight tumors (4 metaplastic carcinomas, 2 invasive ductal carcinomas, 1 invasive papillary carcinoma, and 1 medullary carcinoma) were positive for more than three markers among cytokeratins 5, 14, and 17, and p63. Three tumors (2 invasive ductal carcinomas and 1 apocrine carcinoma) were completely negative for all markers. Among 8 tumors positive for basal markers, cytokeratins 5 and 17 were expressed in all 8 tumors, cytokeratin 14 in 6 tumors, and p63 in 7 tumors. Finally, we conclude that the majority of triple-negative cancer may correspond to basal-like carcinoma, but the two entities are not identical. The use of combination immunohistochemistry including cytokeratins 5, 14, and 17 and p63 may contribute to the detection of basal-like carcinoma
Metaplastic breast carcinomas are basal-like tumours.
Original article
Histopathology. 49(1):10-21, July 2006.
Reis-Filho, J S 1,2; Milanezi, F 2,3; Steele, D 1; Savage, K 1; Simpson, P T 4; Nesland, J M 5; Pereira, E M 6; Lakhani, S R 4; Schmitt, F C 3,7
Abstract:
Aims: Recently, an immunohistochemical panel comprising antibodies against HER2, oestrogen receptor (ER), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cytokeratin (CK) 5/6 was reported to identify basal-like breast carcinomas, as defined by cDNA microarrays. Our aim was to analyse a series of metaplastic breast carcinomas (MBCs) using this panel plus two other basal markers (CK14 and p63) and progesterone receptor (PR), to define how frequently MBCs show a basal-like immunophenotype.
Methods and results: Sixty-five cases were retrieved from the pathology archives of the authors' institutions and reviewed by three of the authors. Immunohistochemistry with antibodies for HER2, ER, EGFR, CK5/6, CK14 and p63 was performed according to standard methods. All but six cases (91%) showed the typical immunoprofile of basal-like tumours (ER- and HER2-, EGFR+ and/or CK5/6+). When CK14 and p63 were added to the panel, two additional cases could be classified as basal-like. The majority of MBCs lacked PR, except 4/19 (21%) carcinomas with squamous metaplasia.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that MBCs show a basal-like phenotype, regardless of the type of metaplastic elements. Moreover, as these neoplasms frequently overexpress EGFR (57%), patients with MBC may benefit from treatment with anti-EGFR drugs.
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-08-11 23:15:00 编辑
To 路在何方,
Thank you for sharing this case and your discussion about basal-like ca. Happy to know that you are a very considerable pathologist and have a lot of knowdge on basal-like ca.
I totally agree with your dx of basal-like ca based on the definition.
Basal-like carcinoma is a relative new term based on gene expression profiling studies. It can be identified using an IHC panal, triple negative (ER/PR/Her2) and positive for one or several basal-like markers (ck5/6, CK14, ck17, 34b-E12, EGFR).
In fact most cases of metaplastic carnoma belong to the spectrum of basal-like carcinomas based on the definition, such as spindle cell ca, squamous cell ca, adenosqumous.
Basal-like carcinomas include several different subtypes. Currently we call metaplastic ca if the cases have classic of metaplasic components, such as spindle cells, squamous cells, chondro-osseous. To typical basal-like ca we call invasive ductal carcinoma with basal-like phenotypes.
Fibromatosis-like spindle cell carcinoma also belongs to the spectrum of basal-like ca. However, unlike most basal-like tumors, FLSpCC is not associated with an unfavorable clinical prognosis.
Another concept is that triple negative ca is not identical to basal-like ca even though most triple negative carcinomas are basal-like ca.
The importance is that the clinicians or surgens know the meaning of the terms of pathologic diagnosis. Pathologists have the duty to educate the clinicians.
感谢你分享这个病例和关于基底细胞样乳腺癌的讨论。很高兴了解到你是个非常善于思考的病理医生,并且对基底细胞样乳腺癌非常熟悉。
我完全同意你的诊断------基底细胞样乳腺癌。基底细胞样癌是个相对较新的基于基因表达分析的诊断术语。它可以通过免疫组织化学方法来识别,ER PR Her2三阴性和一种或几种基底细胞样指标阳性(ck5/6, CK14, ck17, 34b-E12, EGFR)。实际上,按照定义大多数化生性癌属于基底细胞样癌的范围,如:梭性细胞癌、鳞状细胞癌和腺鳞癌。基底细胞样癌包括几个亚型。一般,如果病例中有典型的化生成分,如:梭形细胞,鳞状细胞、软骨,我们则称之为化生性癌。对典型的基底细胞样癌我们称之为具有基底细胞样表现的浸润性导管癌。纤维瘤病样梭形细胞癌也属于基底细胞样癌的范围。然而,与大部分基底细胞样肿瘤不一样,fibromatosis-like spindle cell carcinoma 临床预后not bad。另外一种观念是三阴性的癌不等同于基底细胞样癌,虽然大部分三阴性癌是基底细胞样乳腺癌。
重要的是临床医生或外科医生要知道病理诊断名称的含义,病理医生有义务让临床医生了解它。
Thank above translation, cz
-
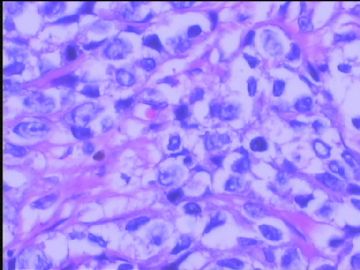
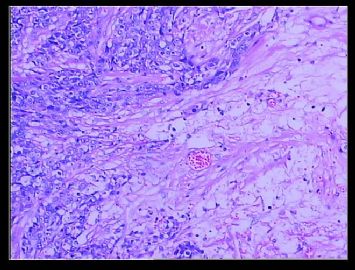
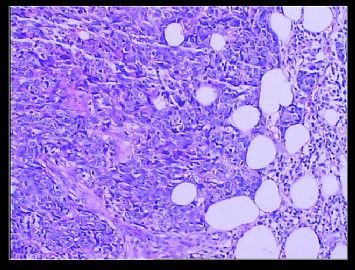
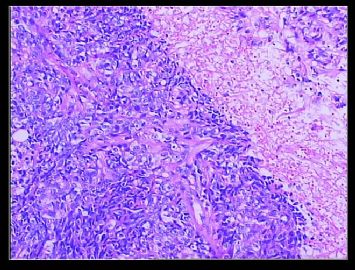
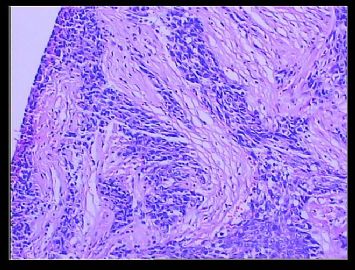
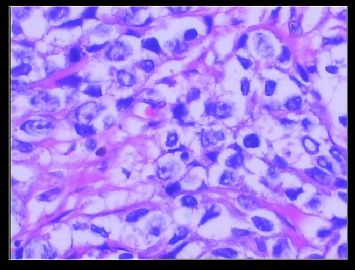
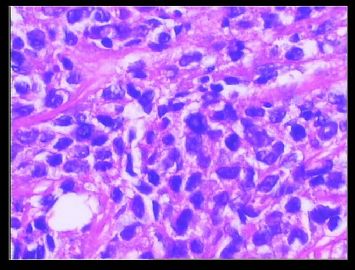
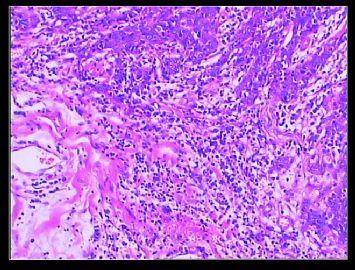
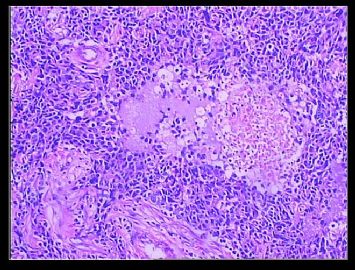
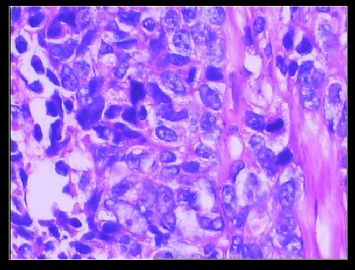
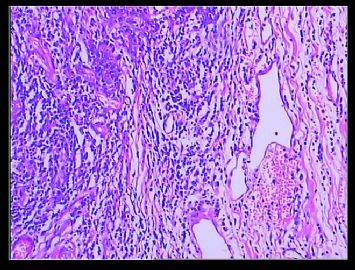
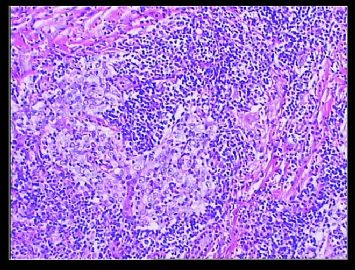
赵老师的意思是化生性癌和基底细胞样乳腺癌有重叠的地方,并且化生性癌让临床医生比较好理解、接受,是这个意思吧?这个病例我们已经发了基底细胞样乳腺癌,不知您觉得可否。基底细胞样乳腺癌可能还有部分病理医生不甚理解,经过我们查阅文献我觉得这个病例比较吻合,首先从低倍镜下看,肿瘤无侵润性生长,对周围有推挤性生长,中央有小片状坏死和纤维间隔分隔、包绕,细胞合胞体状,圆形、椭圆形,核分裂像多见>50个/HPF。基底细胞样乳腺癌主要是根据免疫表型来分类的,ER、PR、HER2三联阴性,CK5/6+,这基本符合文献报道,文献认为以上三联阴性加上CK5/6,或CK14、CK17,或EGFR阳性即可诊断,在基底细胞样乳腺癌中EGFR60%阳性。亦有认为基底细胞样乳腺癌可能就是侵润星导管癌III级或化生性癌,总之此类型癌以其独特的免疫表型以及临床预后较差而引起人们的关注,其基因通路还有待于进一步研究,如有不完善之处还请各位前辈指正。总之希望此类病例能引起广大病理工作者的重视与关注,欢迎继续讨论。
-
cnlzh20060 离线
- 帖子:224
- 粉蓝豆:58
- 经验:378
- 注册时间:2009-02-27
- 加关注 | 发消息
If you can confirm the positivity of epithelail markers and some spindle cells present, this case can be called metaplastic ca. Basal-like ca is a different method of calssification. I think metaplastic ca and basal-like ca have some overlapped. I never understand the relation of these two in some cases. Metaplastic ca is more easy to be understood by clinicians.
Just for your reference, cz
Intersting case. Thank 路在何方for sharing.
Before we can call carcinoma, we should see some positivity for epithelial markers.
1. Suggest to stain for AE1/AE3, cam5.2, CK7. If at least one of the above epithelial markers, we know it is a carcinoma.
2. Because this case is triple negative (ER/PR/Her2-), please add CK14, Ck17 stains to confirm if it is a basal-like carcinoma. Notice other markers for basal-like ca are negative already (CK5/6-,P63-,EGFR-).
3. If no any epithelial marker is negative, it may be a sarcoma case.