| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
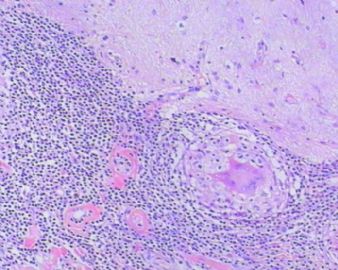
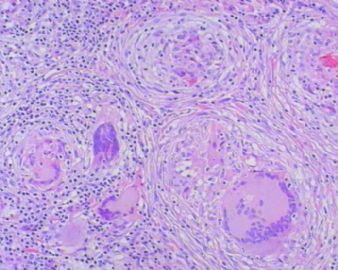
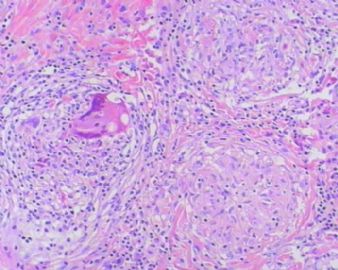
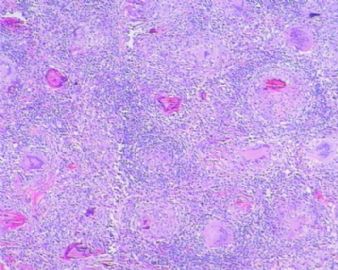
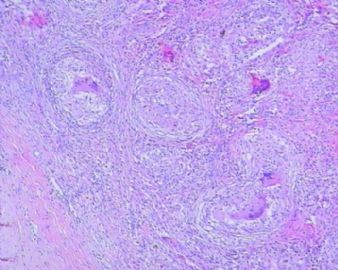
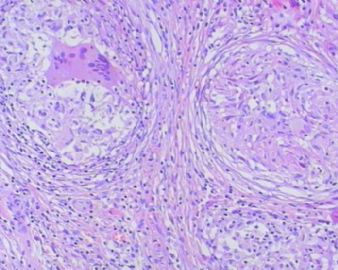
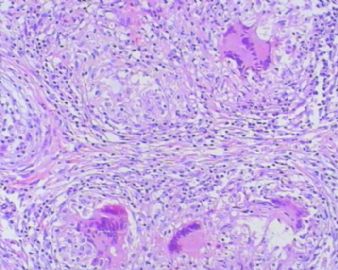
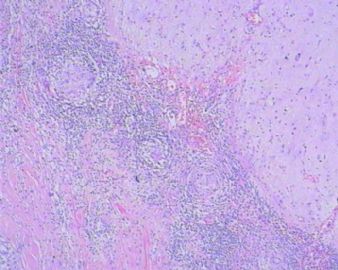
- 左额叶肿物
-
zhouyanping 离线
- 帖子:34
- 粉蓝豆:1550
- 经验:465
- 注册时间:2009-01-19
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
xiaoyan0290 离线
- 帖子:1179
- 粉蓝豆:512
- 经验:2063
- 注册时间:2008-07-15
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
liguoxia71 离线
- 帖子:4174
- 粉蓝豆:3122
- 经验:4677
- 注册时间:2007-04-01
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
The granulomas are accompanied by many mononuclear inflammatory cells with formation of multinucleated giant cells. No refractile foreign material, pigmented or calcified structures are included in these granulomas. No large or obvious areas of necrosis are seen, either. Judging from the sharp interface with cortical parenchyma, the lesion is mainly on the surface of cerebral hemisphere. In addition to tuberculosis (as many have suggested, and requires demonstration of acid-fast bacilli on stain or culture for a definitive diagnosis), what other differential diagnoses for granulomatous leptomeningitis should be considered?

聞道有先後,術業有專攻
-
liguoxia71 离线
- 帖子:4174
- 粉蓝豆:3122
- 经验:4677
- 注册时间:2007-04-01
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
lanyueliang 离线
- 帖子:679
- 粉蓝豆:11
- 经验:1424
- 注册时间:2008-11-12
- 加关注 | 发消息