| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
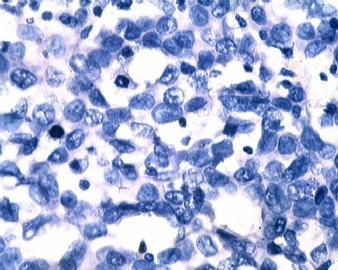
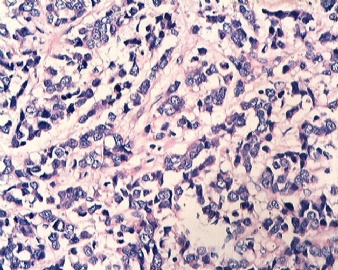
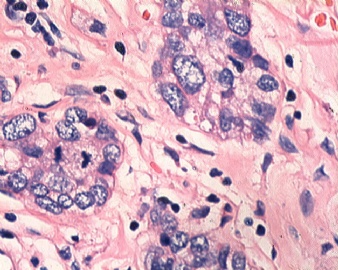
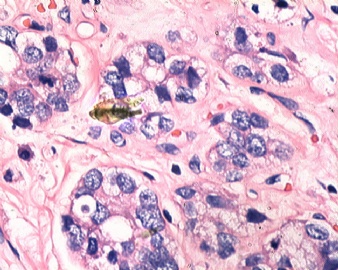
- B1833乳腺肿瘤,请教什么类型
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 女 | 年龄: | 46 |
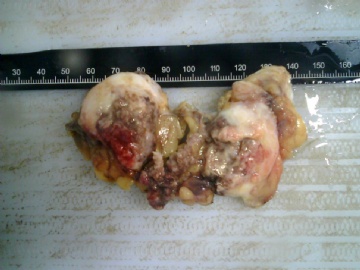
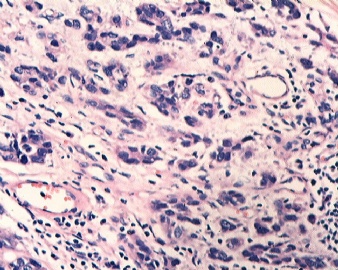
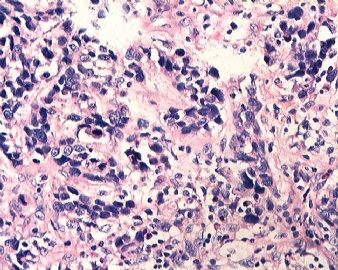
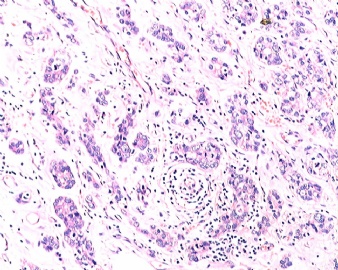
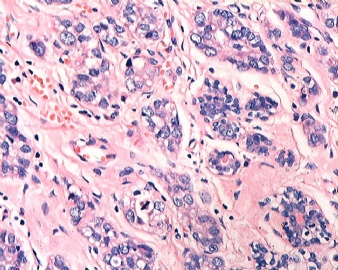
| 标本名称: | 乳腺肿块 | ||||
| 简要病史: | 发现肿物3天 | ||||
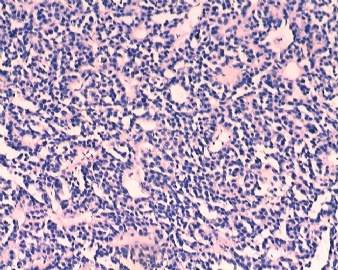
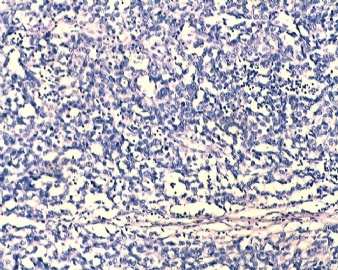
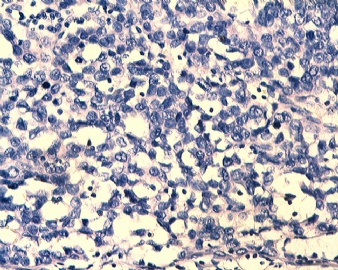
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-13 13:40:00 编辑
相关帖子
| 以下是引用cqzhao在2009-6-25 9:50:00的发言:
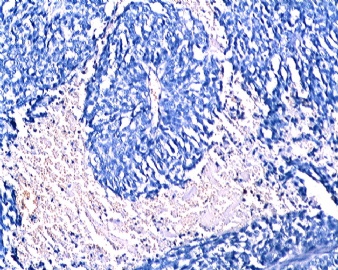
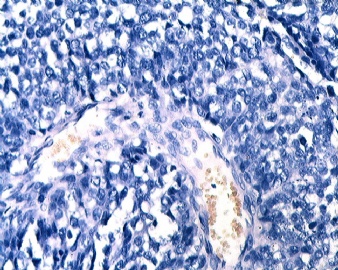
Think over the IHC for this case. If it was my case I would just call invasive ductal ca. In the comment: I will mention focally positive CD56 , not sue the meaning. It may be suggestive of the carcinoma with focal neuroendocrine differentiation. As I mention before chromo is most specific and synapt is more sensitive for neoroendocrine tumors. However this tumor is deadly neg for both. So I am not sure the neuroendocrine differentiation part. |

- 博学之,审问之,慎思之,明辨之,笃行之。
-
xianyuanqq82 离线
- 帖子:455
- 粉蓝豆:55
- 经验:456
- 注册时间:2009-02-04
- 加关注 | 发消息
Think over the IHC for this case.
If it was my case I would just call invasive ductal ca.
In the comment: I will mention focally positive CD56 , not sue the meaning. It may be suggestive of the carcinoma with focal neuroendocrine differentiation.
As I mention before chromo is most specific and synapt is more sensitive for neoroendocrine tumors. However this tumor is deadly neg for both. So I am not sure the neuroendocrine differentiation part.
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-24 19:55:00 编辑
Generally neuroendocine tumors may have better prognosis. Of cause small cell carcinoma is different.
It is ok to call invasive ductal carcinoma with focal neuroendocrine differentiation for this case. The treatment and prognosis should be no much difference between IDC with focal neuroendocrine differentiation and IDC.
一般来说,神经内分泌肿瘤预后较好,当然小细胞癌不同。
这例诊断为伴有灶性神经内分泌分化的浸润性导管癌就可以了。浸润性导管癌和伴有灶性神经内分泌分化的导管癌二者间的治疗和预后没有太大的差别。
-
Int J Surg. 2008;6 Suppl 1:S113-5. Epub 2008 Dec 13.
-
Neuroendocrine carcinomas of the breast.
Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy. francesca.rovera@uninsubria.it
INTRODUCTION: Neuroendocrine (NE) breast cancers encompass a heterogeneous group of tumours showing morphological features similar to those of NE neoplasms of the gut and lung and expressing one or more neuroendocrine markers (neuron specific enolase, chromogranins synaptophysin) in at least 50% of tumour cells. They are rare lesions representing about 2-3% of all breast cancers and affecting more frequently elderly patients. AIM: Prospective observational study is to analyse the clinico-pathological aspects of NE carcinomas of the breast undergone surgical resection compared to breast carcinomas with a minor neuroendocrine component and to conventional invasive ductal or lobular cancers. MATERIAL AND METHOD: Thirty-five consecutive breast carcinomas showing morphological features suggestive of an endocrine differentiation were selected among breast cancers undergone surgical treatment during the period of January 1979-December 2004. RESULTS: The 35 patients were divided into two categories: 13 neuroendocrine carcinomas (NECs) and 22 ductal carcinomas with a minor neuroendocrine component (DC-NE). The average follow-up was 60 months. The patients with CNE developed breast cancer in an advanced age compared to the patients with infiltrating ductal carcinoma NAS or infiltrating lobular carcinoma. We did not find recurrent disease in the NEC group, while it was observed in 2 patients (9%) with DC-NE, in 6 cases (17%) with infiltrating ductal carcinoma NAS and in 7 cases (20%) with infiltrating lobular carcinoma. DISCUSSION: The CNE compared with the infiltrating ductal and lobular carcinoma are statistically different in relation to the expression of the receptor of c-erb-B2, p53, progesterone, for the lymph node state at diagnosis and the risk of reappearance of breast tumour. Our study confirms the choice to consider the neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast as a separate histological group and seems to suggest a less aggressiveness of this type of tumour.
As I mentioned before chromgranin is more specific. CD56 can be positive in many cells or tumors. Copy from pathologyoutline.
Positive staining (normal): NK cells (80-90%), large granular lymphocytes, activated T cells, osteoblasts; cerebellum and cortex at neuromuscular junctions, neuroendocrine tissue and neurons (membranous pattern), glia; skeletal muscle
Positive staining (disease) - leukemia/lymphoma - acute myeloid leukemia (some), cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders, granulocytic sarcoma (variable), myeloma, NK/T cell lymphomas, T cell lymphomas (various)
Positive staining (disease): other - cardiac ischemic damage (Verh Dtsch Ges Path 2004;88:246), extrahepatic biliary atresia (AJSP 2003;27:1454), Merkel cell carcinoma (J Dermatol Sci 2003;31:219), mesotheliomas (some), neuroblastoma (adult), neuroendocrine carcinomas (AJSP 2006;30:684), pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma, pancreatic solid pseudopapillary tumor (Mod Path 2006;19:1409), pheochromocytoma, small cell carcinoma of cervix (Int J Gynecol Path 2005;24:113), small cell carcinoma of lung and prostate (AJSP 2006;30:705), sustentacular cell tumor (AJSP 2006;30:268), synovial sarcoma (usually, Mod Path 2006;19:659), thyroid carcinoma (AJCP 2003;120:64), Wilm’s tumor
Negative staining: granulocytes, monocytes, B cells; ALL, large granular NK cell lymphocytosis, (some cases, Am J Path 2004;165:1117), plasma cell leukemia, PNET/Ewing’s sarcoma
-
Syn is more senstive and chrom is more specific for neuroendocrine tumors. They are neg in this case. But CD56 is true positive. Rare cells seems pr positive. Until you know some history or clinical information for the sondary tumor. Otherwise it is invasive ductal ca. Do not know the meaning of CD56 positivity.