| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B1803少见乳腺肿物,鉴别诊断? (cqz-18, 5-7-2009)
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
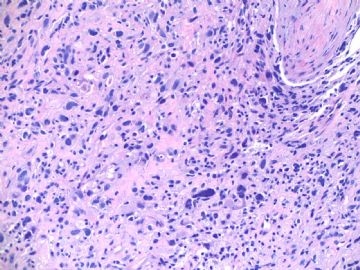
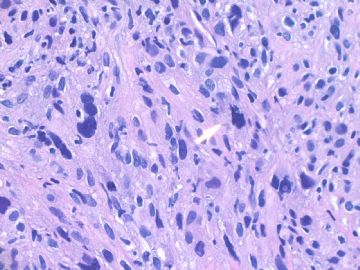
about 60 y/f, right breast mass 2 cm by imaging, breast core biopsy.
1. Your differential diagnosis?
2. What will you do next?
Please do not just give a diagnosis. Your dx is a guess dx even though your diagnosis may be right.
As pathologists we should learn how to analyse our cases with logic thought.We should have differential dx for all cases in our mind even for the easy cases. We can use available sources (such as IHC, molecular methods, history, consultation) to rule in or rule out the differential dx, then make the final dx.
Learning the priniciple for diagnosis is much more important than learning a few cases.
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-05-07 18:28:00 编辑
相关帖子
| 以下是引用在路上在2009-6-3 23:35:00的发言: 如果我遇到这样的病例,我的第一印象是:梭形细胞化生性癌---可以用CK7、CK8/18等确定其上皮性质;周围可能有原位癌成分;另外,梭形细胞癌也常标记肌上皮标记物(如P63、S-100、calponin等故需注意与肌上皮癌鉴别)。 当然一定要有其他鉴别诊断:1、恶性叶状肿瘤---寻找良性上皮成分;梭形细胞CK阴性而Vimentin阳性;或可有异源性分化(如骨、肌源性分化等)。2、乳腺间质肉瘤。3、乳腺非特异性软组织肉瘤。…… 期待Dr.zhao的结果与分 第一考虑梭形细胞化生性癌 |
Doctor,
Your analysis is very good. I will be more happy if you could spend a little time to read people's discussion and IHC photos.
-
zezexiaozi 离线
- 帖子:16
- 粉蓝豆:60
- 经验:313
- 注册时间:2009-06-02
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-05-30 19:28:00 编辑
Primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone is very rare also. The above paper may be the largest study.
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York is the largest cancer center in the USA.
Pathology dx is not difficult with IHC, but you need to think about this lesion.
Thank 笃 (du)行者 to share the bone tumor here.
-
Am J Surg Pathol. 1997 Nov;21(11):1281-94.
-
Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of 33 patients and a literature review.
Department of Pathology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York 10021, USA.
Leiomyosarcoma of bone is a rare tumor in an unusual location. Previous analysis of this entity mostly involved small numbers of cases with limited follow-up. Thirty-three patients with leiomyosarcoma of bone between 1977 and 1996 were studied, and the histologic appearance and grade were correlated with subsequent treatment and clinical behavior. To be included in this study the tumor had to be intraosseous, with other primary sites of origin clinically excluded. Also, most of the sarcomatous tissue (> or =70%) had to be of intramedullary location with only limited extraosseous extension. The patient's age at diagnosis ranged from 13 to 77 years (average 44.4). The gender distribution was equal. The long bones were preferentially affected (64%), with the lower extremity, around the knee joint, predominantly involved. Five patients (15%) developed postradiation leiomyosarcomas. The histologic analysis showed that the osseous leiomyosarcomas are most commonly of the classic type, followed by the epithelioid, myxoid, and pleomorphic variants. Immunoreactivity for smooth muscle markers (smooth muscle actin, common muscle actin, desmin) was positive in all tumors, and ultrastructural confirmation was obtained in 21% of cases. All sarcomas were histologically graded, which accurately reflected the subsequent prognosis. Seventy-five percent of the lesions were high-grade and the rest low-grade. The histologic grade of the tumors correlated with both the recurrence as well as the metastatic rates and together with the clinicopathologic stage of disease represented the cornerstone on which prudent therapy should be based.
-
Ann Surg Oncol. 1998 Oct-Nov;5(7):635-41.
-
Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular biologic aspects.
Department of Trauma, Hand and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Saarland, Homburg, Germany.
BACKGROUND: Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone is a very rare malignant tumor with uncertain pathogenicity. METHODS: The authors studied five cases of surgically treated primary leiomyosarcoma of bone. Clinical histories and radiographic findings were recorded. Regular clinical and radiographic controls were obtained postoperatively. In all cases, immunohistochemical studies were used to confirm the diagnosis. Molecular biologic examinations, using the polymerase chain reaction technique with microsatellite DNA markers from regions of tumor-relevant genes, were performed to determine the stability of the genome or to detect some typical genomic changes. RESULTS: The study included three women and two men, with an average age of 42 years. The tumor was located in the pelvis in two patients, in the femur in two patients, and in the proximal tibia in one patient. All tumors were classified as high-grade tumors (four stage IIB, one stage IIA). Radiographically, all tumors appear as purely osteolytic lesions, with a geographic or moth-eaten appearance and without any sclerotic margin. Three patients underwent limb salvage surgery followed by endoprosthetic replacement. The other two patients required amputation. The mean follow-up was 19 months (range, 8-29 months). Three patients died of disease, with a mean postoperative survival period of 18 months (range, 6-27 months). Four patients developed diffuse pulmonary metastases after an average of 10.5 months. One of those patients responded well to chemotherapy. In all cases, immunohistochemistry showed strong reactivity of the tumor cells for (alpha-SMA and vimentin. Molecular biologic investigations revealed a high rate of genomic instabilities in all of the stage IIB tumors. CONCLUSION: Clinical follow-up suggests that primary osseous leiomyosarcoma has an aggressive biologic behavior. The immunohistochemical studies are useful tools and suggest that osseous leiomyosarcoma arise from the vascular smooth muscle cells within the bone. The molecular biologic findings of a high rate of genomic instability confirm the hypothesis that this rare entity is of an aggressive nature.
-
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999 Mar;172(3):771-6.
-
Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone.
Department of Radiology, St. Louis University Health Sciences Center, MO 63110-0250, USA.
OBJECTIVE: This study describes radiographic and MR imaging features of primary leiomyosarcoma of bone. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: Twelve patients (five men and seven women, 39-79 years old) who were treated at two oncology centers for primary leiomyosarcoma of bone involving the femurs, tibia, ilium, and inferior pubic ramus were studied. None of the patients had preexisting disease or disease elsewhere at the time of diagnosis. Pathologic diagnosis was obtained in all patients. RESULTS: Radiographs of all patients showed a matrix that was exclusively osteolytic. In long bones (seven patients), the tumor had an average length of 11 cm (range, 7-17 cm) and revealed an elongated configuration. In the pelvis (five patients), the average length of the tumor was 10 cm (range, 4-15 cm). MR imaging confirmed an intramedullary lesion in all patients, with extension into the soft tissues in eight patients and no identifiable soft-tissue mass in the remaining four patients. Four of the five pelvic tumors had a prominent soft-tissue mass, whereas only four of the seven long bone lesions revealed a soft-tissue mass that was, in all instances, small. The tumor was hypointense on T1-weighted images and showed heterogeneous signal intensity on T2-weighted conventional and fast spin-echo sequences. We saw low signal intensity (short T2) in eight patients and homogeneous hyperintense signal intensity in one patient. In the remaining three patients, T2-weighted spin-echo sequences obtained with fat saturation showed high signal intensity (long T2) in the tumors. CONCLUSION: Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone is a rare tumor that on radiography reveals no matrix and on MR imaging reveals areas of T2 shortening in relation to fat on conventional and fast spin-echo sequences.
-
Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2000 Feb;86(1):63-73.
-
[Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone. Report of 5 anatomo-clinical cases and review of the literature]
[Article in French]Service de chirurgie orthopédique et traumatologique B, Hôpital Cochin, 27 rue du faubourg Saint Jacques, 75014 Paris, France.
INTRODUCTION: Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant smooth muscle tumor occurring most frequently in uterus or soft tissues and more rarely in bone. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We report the clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural findings of five cases of primary leiomyosarcoma of bone treated in our Department between 1991 and 1994. The pertinent medical literature is discussed. RESULTS: The tumors were located respectively in the distal tibia (n=2), the distal femur, the sternum and the ilium (n=1). Four lesions were high-grade and one low-grade. All patients (3 women and 2 men) underwent wide surgical resection associated with polychemotherapy in four cases. Two patients died of metastatic disease, two had local recurrence and one is alive with no evidence of disease at the last follow-up. DISCUSSION: Excluding cases which involve the facial skeleton, there are to our knowledge 95 cases of primary leiomyosarcoma of bone reported in the literature. This tumor arises more commonly in adults (mean age: 49 years) with an equal gender distribution and involves predominantly the long bones near the knee. In the majority of cases, plain X-rays exhibit an osteolytic lesion with cortical penetration and indistinct margins. The diagnosis is based on microscopic features demonstrating fusiform tumor cells arranged in interwoven bundles, and the immunohistochemical results of widespread cytoplasmic positivity for smooth muscle actin. The best pronostic parameter is the histologic grade correlated with both the recurrence and metastatic rates as well as the survival rate. Surgery constitutes the main treatment since chemotherapy or radiotherapy did not provide an improved prognosis over a wide resection.
-
J Orthop Sci. 2002;7(2):267-73.
-
Primary leiomyosarcoma of the femur.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8655, Japan.
Leiomyosarcoma usually arises in the uterus, gastrointestinal tract, retroperitoneum, or soft tissue. Primary leiomyosarcoma of bone is rare. We encountered two patients with primary leiomyosarcoma of the femur; one was a 24-year-old woman and the other, a 41-year-old woman. Bone destruction observed on plain radiographs was minimal in both patients. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images, with these areas being much larger than the findings to be expected from the plain radiographs. Histological examination revealed spindle-cell sarcoma, with an interlacing pattern, acidophilic cytoplasm and blunt-ended or "cigar-shaped" nuclei, in both patients. In both patients, immunohistochemical examination showed positive staining for vimentin, desmin, and alpha-smooth muscle actin. Extensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract and uterus revealed no primary lesion. Therefore, the leiomyosarcoma in the femur was considered to be primary rather than metastatic. Histological examination, including immunohistochemistry, and the exclusion of an extraskeletal primary lesion, is necessary in diagnosing primary leiomyosarcoma of bone
-
Cancer. 2007 Dec 25;111(6):491-8.
-
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of high-grade sarcoma: a report of 107 cases.
Department of Pathology, The Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus, Ohio 4320, USA.
BACKGROUND: To the authors' knowledge, few studies exist demonstrating the reliability of fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy for high-grade sarcoma (HGS). METHODS: In the current study, the authors reviewed their cytopathology database (March 2001 through January 2007) and identified all FNA cases diagnosed as HGS. They also searched their tissue database for all HGS cases that had prior FNA biopsy findings. RESULTS: A total of 107 FNA samples from 98 patients (age range, 13-90 years, with a male:female ratio of 1:1) had an FNA diagnosis of HGS, or had HGS and a prior FNA diagnosis of another entity. Ten cases were nondiagnostic. Of the 97 remaining samples, 6 were diagnosed as something other than HGS (sensitivity of 94%). The positive predictive value of an FNA diagnosis of HGS was 97% (88 of 91 cases). Fifty-four cases were diagnosed as HGS, not otherwise specified, 8 as myxofibrosarcoma, 8 as osteosarcoma, 5 as malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, 5 as leiomyosarcoma, 4 as Ewing sarcoma, 4 as liposarcoma, 2 as epithelioid sarcoma, and 1 as angiosarcoma. Approximately 71% of patients presented with a primary tumor, 23% with disease recurrence, and 7% with metastasis. Sites of disease included the lower extremity (59%), upper extremity (19%), trunk (15%), groin (4%), and head and neck (4%). FNA diagnosis was confirmed histologically in 88% of cases, clinically in 7% of cases, and cytogenetically in 1% of cases; 3% of cases had false-positive results and 1 patient was lost to follow-up. Sixteen of 19 patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on the FNA diagnosis alone. CONCLUSIONS: A cytopathologic diagnosis of HGS was found to be accurate in 88 of 97 cases (91%) with follow-up. A FNA biopsy diagnosis of HGS appears to be clinically reliable in a high percentage of cases when used in close conjunction with the orthopedic team.