| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- NP (7) - PML
-
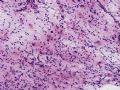
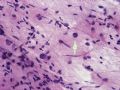
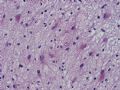
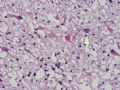
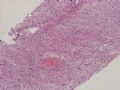
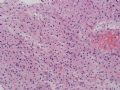
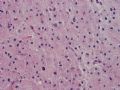
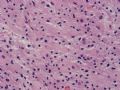
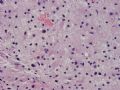
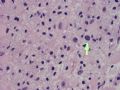
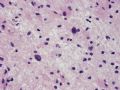
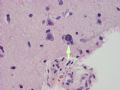
The following photos are taken from a stereotactic brain biopsy from the right frontal lobe of a 22-year-old man with AIDS. He complained of progressive headaches, and brain MRI found many non-enhancing lesions in the subcortical and deep white matter. Figures 1-2 are smear cytology, figures 3-4 are frozen section, and figure 5-12 are from paraffin sections at various magnifications. What are your differential diagnoses?
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-05-01 10:39:00 编辑

聞道有先後,術業有專攻
The smear, frozen section and paraffin sections show reactive astrocytosis, abundant foamy macrophages, and isolated atypical cells with enlarged, hyperchromatic and oval nuclei with abnormal chromatin pattern. These changes are diagnostic of progressive multifocal leokoencephalopathy (PML) caused by reactivated JC virus infection of brain parenchyma, a disease seen predominantly in immunosuppressed hosts (HIV infection, cancer patients with or without chemotherapy, immunosuppressive therapy after organ transplantation).
JC virus is a type of human polyomavirus (used to be papovavirus) related to BK virus and SV40 (simian vacuolating virus 40 or simian virus 40). JC viral infection is very prevalent - an estimated 70~90% of adults have serologic evidence of past JC virus infection, usually in childhood. In immunocompetent hosts, JC virus remain dormant in nuclei of rare scattered glial cells in brain and spinal cord parenchyma. With immunosuppression, the dormant JC virus in these cells may be reactivated and start active replication, causing cell death and tissue destruction. In the genitourinary tract, BK virus acts in a similar way. The name JC is derived from the initials of the name of one of the first patients with PML from which the virus was isolated. It has nothing to do with the CJ in CJD, or Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
PML lesions are found in white matter and at the corticomedullary junction of cerebral and cerebellar cortex. They are variable in size. The typical white matter lesions show loss of myelin and oligodendrocytes, scattered reactive astrocytes, and varying numbers of foamy macrophages. Inflammatory infiltrates are scant is any. The pathognomonic finding is two types of virally infected glia - (1) infected oligodendrocytes or type 2 PML cells with oval enlarged showing replacement of granular chromatin by basophilic or amphophilic, homogenized, ground-glass like viral inclusion bodies (different from eosinophilic viral inclusion bodies of Cowdry type), and (2) infected astrocytes or transformed astroctytes or type 1 PML cells with markedly enlarged, oval and MIB-1-positive nuclei showing corsely granular chromatin pattern and no viral inclusion bodies.
PML is a disease with grave prognosis. Although anecdotal cases of spontaneous remission have been reported, most cases diagnosed of PML dies within one year regardless of the cause of immunosuppression. Antiviral therapy has little beneficial effects.
Important differential diagnoses of PML include (1) varicella-zoster encephalomyelitis (demyelinating, often hemorrhagic and necrotic lesions with glial cells showing eosinophilic intranuclear viral inclusions), (2) acute demyelination (multiple sclerosis), (3) white matter damage by chemotherapeutic agents (such as methotrexate and cyclophosphamide), (4) toxoplasmosis (often suppurative, necrotic and hemorrhagic), and (5) treated CNS lymphoma. Finding the pathognomonic type 1 and type 2 PML cells is the key.

聞道有先後,術業有專攻
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-05-19 15:37:00 编辑
谢谢马老师给我们又提供一例进行性多发性白质脑病(PML) 。
涂片、冰冻切片和常规切片都出现了反应性的星形细胞、 许多泡沫状的巨噬细胞和单个散在的非典型性细胞,这些细胞核大、染色深、核卵圆,并且伴有异常的染色质。
进行性多发性白质脑病(PML) 是由脑实质JC病毒感染所引起的反应所致。主要见于免疫抑制的人,如艾滋病人、癌症患者(有或无化疗)和用免疫抑制治疗的器官移植患者。
JC病毒(多瘤病毒)属于人多瘤病毒属(以前称为乳头状瘤多型空泡形病毒),与BK病毒和SV40(猿猴空泡病毒40或猿猴病毒40)有关。JC病毒感染很流行--估计70~90%成人的血清学检查发现曾经感染JC病毒的证据,通常在儿童期被感染。在免疫功能正常的宿主,JC病毒主要存在于脑、脊髓的少数神经胶质细胞的核内。在免疫抑制时,这些细胞中的大部分病毒可能重新活化,开始活跃复制,导致细胞死亡和组织破坏。在泌尿生殖道,BK病毒的作用方式相似。
JC病毒的命名,来自第一个分离出此病毒的PML患者的名字的首字母。对CJD(Creutzfeldt-Jakob病)患者,无法针对体内的CJ病毒进行治疗。
PML病变见于脑和小脑的白质和皮质-白质交界处。病灶大小不一。典型的白质病变显示脱髓鞘、少突胶质细胞、散在的反应性星形细胞,和不同数量的泡沫状巨噬细胞。即使有炎症浸润也很少。特征性表现是两种病毒感染的神经胶质:(1)感染的少突胶质细胞,或2型PML细胞,伴卵圆形拉长的核,显示颗粒状染色质变成嗜碱性或双嗜性、均质、毛玻璃样病毒包涵体(与Cowdry型的嗜酸性病毒包涵体不同)。(2)感染的星形细胞或转化的星形细胞或1型PML细胞,伴显著拉长的、卵圆形、MIB-1阳性的核,呈粗颗粒状染色质结构,且无病毒包涵体。
PML是一种预后差的疾病。尽管报道过一些无对照的自发性缓解病例,不论引起免疫抑制的原因如何,绝大多数病例死于1年以内。抗病毒治疗几乎无效。
PML的重要鉴别诊断包括:(1)水痘带状疱疹脑脊髓炎(脱髓鞘、常有出血坏死病变,胶质细胞显示嗜酸性核内病毒包涵体);(2)急性脱髓鞘(多发性硬化);(3)化疗所致的白质损害(如氨甲喋呤和环磷酰胺);(4)弓浆虫病(常化脓、坏死和出血);(5)治疗后CNS淋巴瘤。发现特征性的1型和2型PML细胞是鉴别诊断的关键。
为方便对照阅读,逐句对照翻译如下:
The smear, frozen section and paraffin sections show reactive astrocytosis, abundant foamy macrophages, and isolated atypical cells with enlarged, hyperchromatic and oval nuclei with abnormal chromatin pattern.
涂片、冰冻切片和常规切片都出现了反应性的星形细胞、 许多泡沫状的巨噬细胞和单个散在的非典型性细胞,这些细胞核大、染色深、核卵圆,并且伴有异常的染色质。
These changes are diagnostic of progressive multifocal leokoencephalopathy (PML) caused by reactivated JC virus infection of brain parenchyma, a disease seen predominantly in immunosuppressed hosts (HIV infection, cancer patients with or without chemotherapy, immunosuppressive therapy after organ transplantation).
这是改变对于进行性多发性白质脑病(PML)具有诊断价值。PML是由脑实质JC病毒感染所引起的反应所致。主要见于免疫抑制的人,如艾滋病人、癌症患者(有或无化疗)和用免疫抑制治疗的器官移植患者。PML是由脑实质JC病毒感染所引起的反应所致。主要见于免疫抑制的人,如艾滋病人、癌症患者(有或无化疗)和用免疫抑制治疗的器官移植患者。
JC virus is a type of human polyomavirus (used to be papovavirus) related to BK virus and SV40 (simian vacuolating virus 40 or simian virus 40).
JC病毒(多瘤病毒)属于人多瘤病毒属(以前称为乳头状瘤多型空泡形病毒),与BK病毒和SV40(猿猴空泡病毒40或猿猴病毒40)有关。
JC viral infection is very prevalent - an estimated 70~90% of adults have serologic evidence of past JC virus infection, usually in childhood.
JC病毒感染很流行--估计70~90%成人的血清学检查发现曾经感染JC病毒的证据,通常在儿童期被感染。
In immunocompetent hosts, JC virus remain dormant in nuclei of rare scattered glial cells in brain and spinal cord parenchyma.
在免疫功能正常的宿主,JC病毒主要存在于脑、脊髓的少数神经胶质细胞的核内。
With immunosuppression, the dormant JC virus in these cells may be reactivated and start active replication, causing cell death and tissue destruction.
在免疫抑制时,这些细胞中的大部分病毒可能重新活化,开始活跃复制,导致细胞死亡和组织破坏。
In the genitourinary tract, BK virus acts in a similar way.
在泌尿生殖道,BK病毒的作用方式相似。
The name JC is derived from the initials of the name of one of the first patients with PML from which the virus was isolated.
JC病毒的命名,来自第一个分离出此病毒的PML患者的名字的首字母。
It has nothing to do with the CJ in CJD, or Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
对于CJD(Creutzfeldt-Jakob病)患者,无法针对体内的CJ病毒进行治疗。
PML lesions are found in white matter and at the corticomedullary junction of cerebral and cerebellar cortex.
PML病变见于脑和小脑的白质和皮质-白质交界处。
They are variable in size.
病灶大小不一。
The typical white matter lesions show loss of myelin and oligodendrocytes, scattered reactive astrocytes, and varying numbers of foamy macrophages.
典型的白质病变显示脱髓鞘、少突胶质细胞、散在的反应性星形细胞,和不同数量的泡沫状巨噬细胞。
Inflammatory infiltrates are scant if any.
即使有炎症浸润也很少。
The pathognomonic finding is two types of virally infected glia -
特征性表现是两种病毒感染的神经胶质:
(1) infected oligodendrocytes or type 2 PML cells with oval enlarged showing replacement of granular chromatin by basophilic or amphophilic, homogenized, ground-glass like viral inclusion bodies (different from eosinophilic viral inclusion bodies of Cowdry type),
(1)感染的少突胶质细胞,或2型PML细胞,伴卵圆形拉长的核,显示颗粒状染色质变成嗜碱性或双嗜性、均质、毛玻璃样病毒包涵体(与Cowdry型的嗜酸性病毒包涵体不同)。
and (2) infected astrocytes or transformed astroctytes or type 1 PML cells with markedly enlarged, oval and MIB-1-positive nuclei showing corsely granular chromatin pattern and no viral inclusion bodies.
(2)感染的星形细胞或转化的星形细胞或1型PML细胞,伴显著拉长的、卵圆形、MIB-1阳性的核,呈粗颗粒状染色质结构,且无病毒包涵体。
PML is a disease with grave prognosis.
PML是一种预后差的疾病。
Although anecdotal cases of spontaneous remission have been reported, most cases diagnosed of PML dies within one year regardless of the cause of immunosuppression.
虽然报道过一些无对照的自发性缓解病例,但是不论引起免疫抑制的原因如何,绝大多数病例死于1年以内。
Antiviral therapy has little beneficial effects.
抗病毒治疗几乎无效。
Important differential diagnoses of PML include
PML的重要鉴别诊断包括:
(1) varicella-zoster encephalomyelitis (demyelinating, often hemorrhagic and necrotic lesions with glial cells showing eosinophilic intranuclear viral inclusions),
(1)水痘带状疱疹脑脊髓炎(脱髓鞘、常有出血坏死病变,胶质细胞显示嗜酸性核内病毒包涵体);
(2) acute demyelination (multiple sclerosis),
(2)急性脱髓鞘(多发性硬化);
(3) white matter damage by chemotherapeutic agents (such as methotrexate and cyclophosphamide),
(3)化疗所致的白质损害(如氨甲喋呤和环磷酰胺);
(4) toxoplasmosis (often suppurative, necrotic and hemorrhagic),
(4)弓浆虫病(常化脓、坏死和出血);
and (5) treated CNS lymphoma. Finding the pathognomonic type 1 and type 2 PML cells is the key.
(5)治疗后CNS淋巴瘤。发现特征性的1型和2型PML细胞是鉴别诊断的关键。