| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
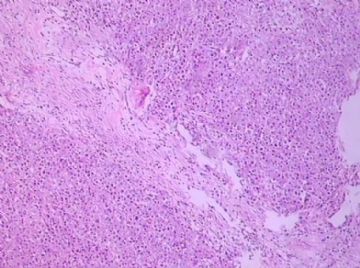
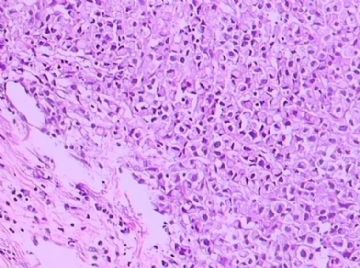
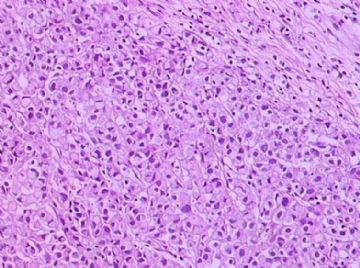
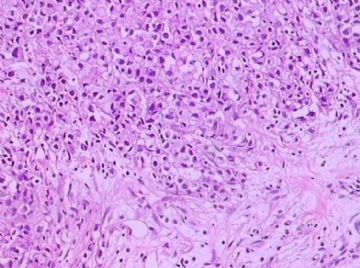
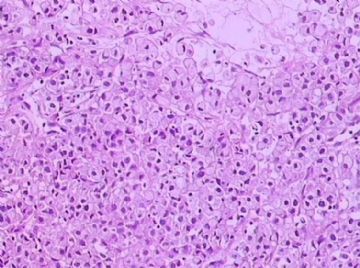
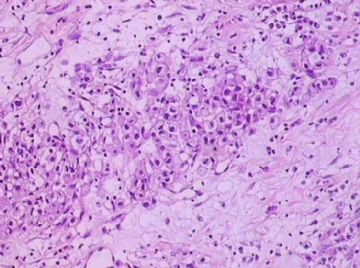
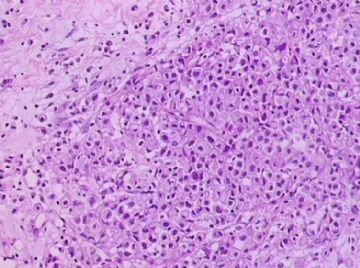
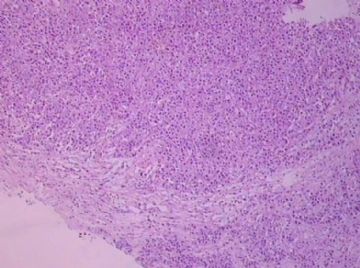
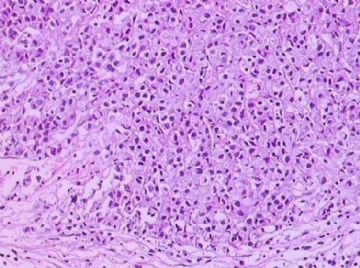
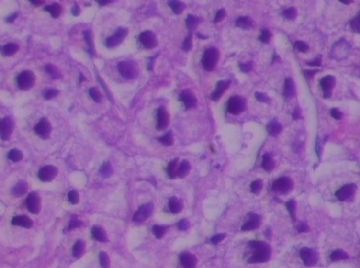
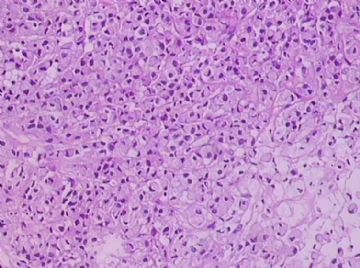
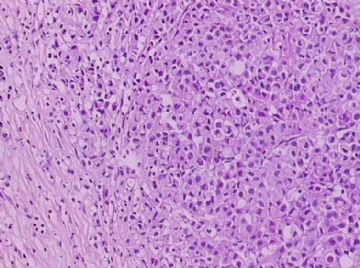
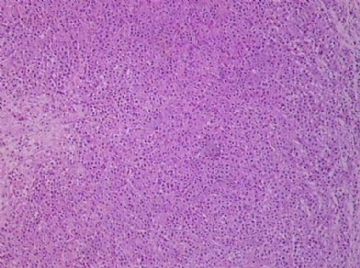
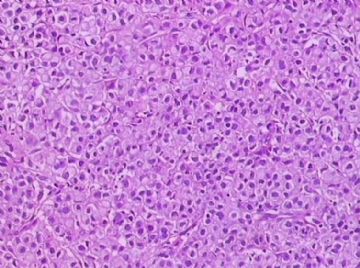
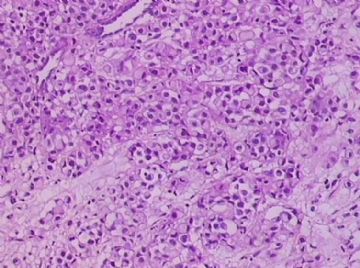
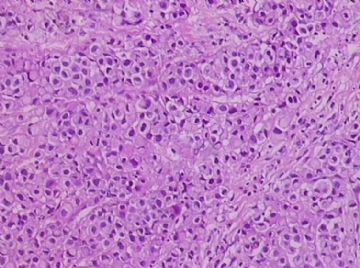
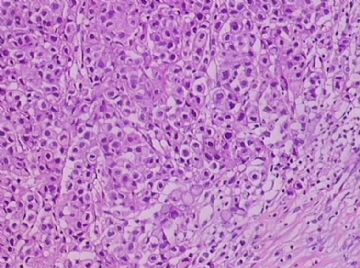
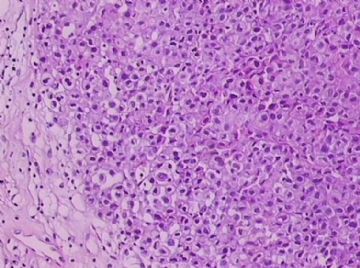
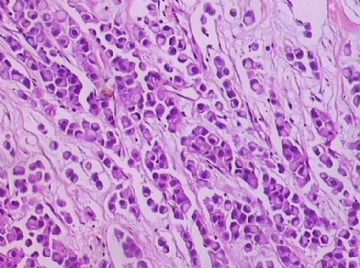
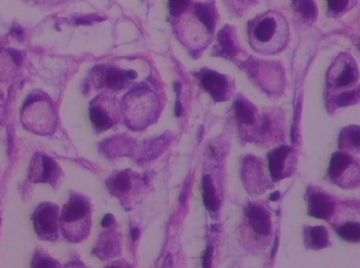
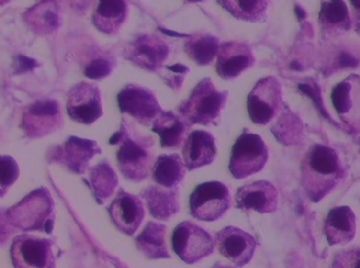
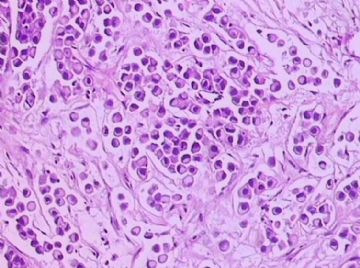
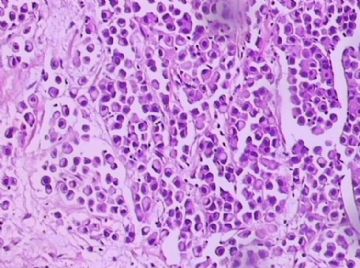
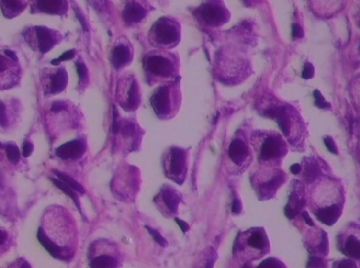
- B1762乳腺印戒细胞癌?
关于印戒细胞癌,WHO2003只有一段。最后一句还是翻译错的。
Signet ring cell carcinoma (8490/3)
Signet ring cell carcinomas are of two types. One type is related to lobular carcinoma and is characterized by large intracytoplasmic lumina which compress the nuclei towards one pole of the cell. Their invasive component has the targtoid pattern of classical lobular carcinoma. The other type is similar to diffuse gastric carcinoma, and is characterized by acidic mucosubstances that fill the cytoplasm and dislodge the nucleus to one pole of the cell. This type of signet ring cell carcinoma can be seen in association with the signet ring cell variant of DCIS.
印戒细胞癌有2型。其一与小叶癌有关,特征为瘤细胞浆内含大空腔并将核挤到边缘。浸润成分具有经典小叶癌的靶环状结构。另一型与弥漫性胃癌相似,特征是胞浆内含嗜酸性黏液物质并将核挤到边缘。后者可能与DCIS的印戒细胞亚型相伴随。

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-03-08 21:07:00 编辑
Seem every one agree this is a signet ring cell ca, breast primary (one type of lobular ca) or metastatic ca. Generally it is a primary tumor. But we can do IHC, CK7, ck20, ER, CDX2 pr to rule out GI primary.
Often
Breast: ck7+/ck20-, ER+, CDx2-
GI: CK7-/ck20+, er-, CDx2+
In fact GI: gastric + colonic origin
E-cadherin seems not very useful (see below article). No lot study for p120.
abin译:似乎所有人都同意印戒细胞癌,乳腺原发(小叶癌的一个亚型)或转移癌。它一般是原发肿瘤。可以做CK7, ck20, ER, CDX2 pr 排除消化道转移(胃和结肠)。
乳腺:ck7+/ck20-, ER+, CDX2-
消化道:CK7-/ck20+, ER-, CDX2+
E-cadherin似乎没有太大帮助(见以下论文)。p120研究不多。
-
Am J Clin Pathol. 2004 Jun;121(6):884-92.
-
Immunohistochemical characterization of signet-ring cell carcinomas of the stomach, breast, and colon.
Division of Pathology, City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA 91010, USA.
We studied the immunophenotype of signet-ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) of the stomach (30 cases), breast (21 cases), and colon (9 cases) with the following expression patterns: (1) breast: consistent, MUC1 (21 [100%]), cytokeratin (CK) 7 (20 [95%]), estrogen receptor (ER; 17 [81%]); infrequent, E-cadherin (6 [29%]), MUC2, MUC5AC, CK20 (1 [5%] each); negative, CDX2 and hepatocyte paraffin 1 (Hep Par 1; 0 [0%] each); (2) gastric: frequent, CDX2 (27 [90%]) and Hep Par 1 (25 [83%]); variable, E-cadherin and CK20 (17 [57%] each), MUC2 and MUC5AC (15 [50%] each), MUC1 (5 [17%]); negative, ER (0 [0%]); and (3) colon: frequent, MUC2 (9 [100%]), CDX2 and MUC5AC (8 [89%] each); infrequent or negative, MUC1 (3 [33%]), Hep Par 1 (2 [22%]), ER (0 [0%]). Immunohistochemical staining distinguished breast from gastric SRCC (ER, MUC1, Hep Par 1, CDX2) and colon SRCC (ER, CDX2, MUC2, and MUC5AC). Gastric and colon SRCCs showed a similar staining pattern for antibodies tested except for Hep Par 1 and CDX2 (gastric, 83% Hep Par 1 positivity and heterogeneous, weak, patchy CDX2 nuclear staining; colon, 22% Hep Par 1 positivity and homogeneous, strong, diffuse CDX2 nuclear staining). About half of the cases of gastric SRCC expressed MUC2 and MUC5AC, whereas virtually all cases of colon SRCC expressed them.