| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
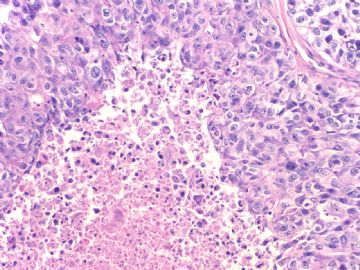
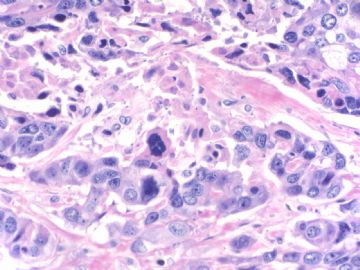
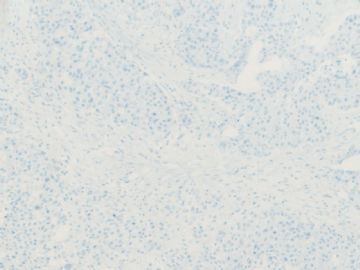
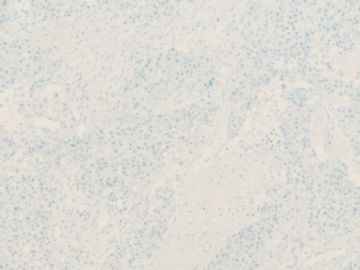
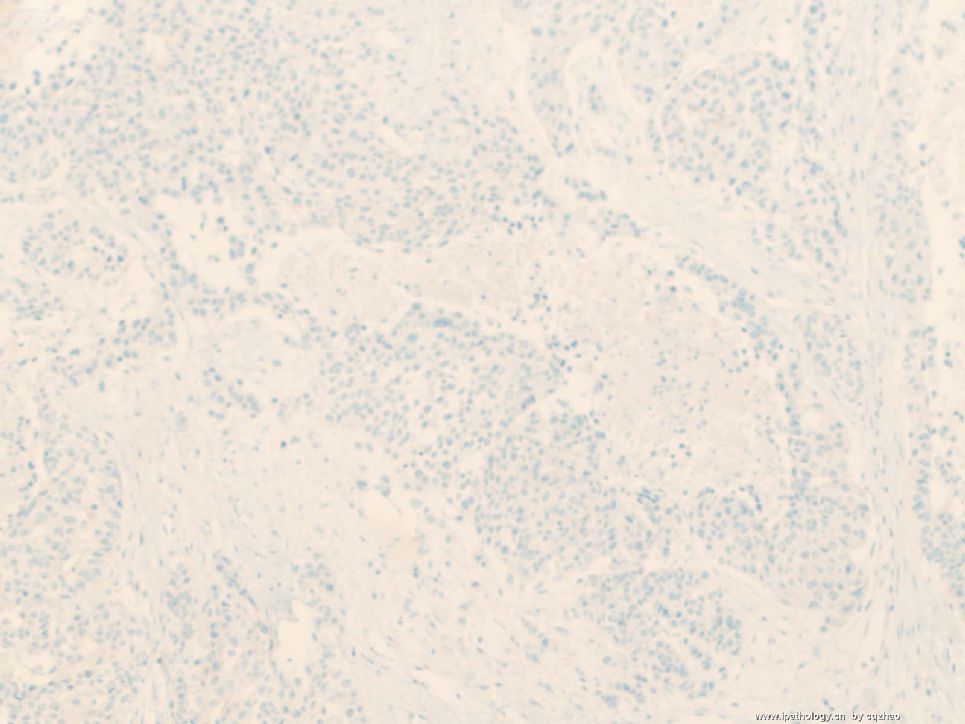
- B20Breast basal-like carcinoma (cqz 6)
Saw you above response. Can you make the final dx based on morphology and IHC results I showed you?
I hope every one can write down your dx and reasons. I am interested in knowing your thinking. Then I know what I should discuss. Internet is good. You can write what you want to and you do not have any responsibility. I do not know any one of you. It is a free stage for every one.
Anyway I will discuss this topic in details later.
-
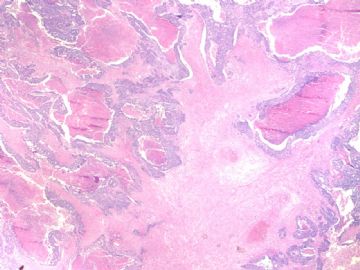
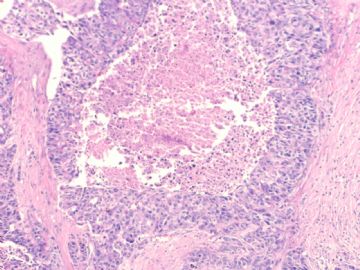
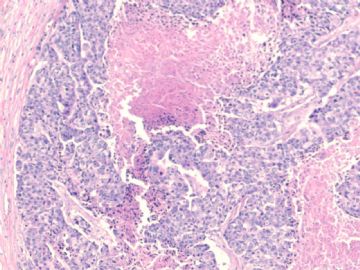
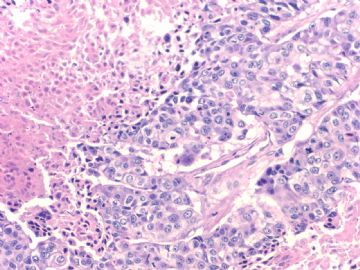
文献记载 乳腺基底细胞样癌形态学特征
• 膨胀性生长方式,推挤性边缘
• 周边多量淋巴细胞浸润
• 肿瘤中央出现无结构的纤维瘢痕,往往还伴有地图样坏死
• 肿瘤细胞多呈合体状,界限不清,胞质不丰富
• 核分裂象多见,常>20个/10HPF
• 肿瘤组织常出现梭形细胞、透明细胞、基底细胞样或鳞状细胞化生
IHC表型
ER、PR和HER2(-)
CK5/6、CK14(+)
EGFR常(+)
但不知道只有免疫表型而无形态学特征者是否可以诊断
期待赵老师讲解


-
本帖最后由 heye 于 2013-03-17 09:04:14 编辑
- PMID:
- 23000897
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
- PMCID:
- PMC3465532
- [Available on 2013/3/23]
http://www.west-info.eu/files/studio-di-nature-cancro-al-seno.pdf
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v490/n7418/full/nature11412.html
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours.
Abstract
We analysed primary breast cancers by genomic DNA copy number arrays, DNA methylation, exome sequencing, messenger RNA arrays, microRNA sequencing and reverse-phase protein arrays. Our ability to integrate information across platforms provided key insights into previously defined gene expression subtypes and demonstrated the existence of four main breast cancer classes when combining data from five platforms, each of which shows significant molecular heterogeneity. Somatic mutations in only three genes (TP53, PIK3CA and GATA3) occurred at >10% incidence across all breast cancers; however, there were numerous subtype-associated and novel gene mutations including the enrichment of specific mutations in GATA3, PIK3CA and MAP3K1 with the luminal A subtype. We identified two novel protein-expression-defined subgroups, possibly produced by stromal/microenvironmental elements, and integrated analyses identified specific signalling pathways dominant in each molecular subtype including a HER2/phosphorylated HER2/EGFR/phosphorylated EGFR signature within the HER2-enriched expression subtype. Comparison of basal-like breast tumours with high-grade serous ovarian tumours showed many molecular commonalities, indicating a related aetiology and similar therapeutic opportunities. The biological finding of the four main breast cancer subtypes caused by different subsets of genetic and epigenetic abnormalities raises the hypothesis that much of the clinically observable plasticity and heterogeneity occurs within, and not across, these major biological subtypes of breast cancer.

- binglihe