本帖最后由 于 2007-02-19 12:32:00 编辑
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms, Including Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
粘液性囊性肿瘤,包括粘液性囊腺癌
Pathologic Features
病理特征
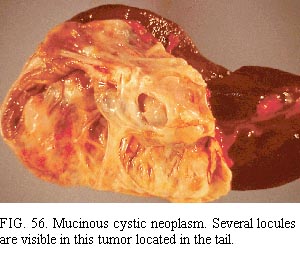
The neoplasms may be irregular in shape, have well-developed capsules with smooth, glistening (sometimes translucent) external surfaces, and are usually multilocular (Fig. 56). They range from 2 to 20 cm in diameter (average 10–11 cm). The tumor can be adherent to adjacent organs and may be surrounded by dense fibrosis (similar to a pseudocyst). Part of the surface may be irregular and dense because of this fibrosis or because malignant epithelium has extended through the capsule. Large blood vessels may extend over the exterior surfaces of the tumor. Sectioning demonstrates the dense collagenous capsule of variable thickness, cavities of different sizes (the largest often several centimeters in diameter), thick mucoid contents, and (if present) papillary excrescences on the interior surfaces. Hemorrhage, degenerative changes, and loss of epithelium occasionally are extensive and therefore suggest a pseudocyst 124. The adjacent pancreatic parenchyma may be somewhat atrophic.
肿瘤外形可不规则,有完整包膜,外观光滑发光(有时半透明),一般多房(图56)。直径2~20cm(平均10~11cm)。肿瘤可与周围器官粘连,四周可能致密纤维化(似假囊肿)。因为纤维化或因恶性上皮穿透包膜,部分表面可能不规则和致密。大血管可能在肿瘤外表面延伸。切面显示致密的胶原化包膜、大小不一的腔隙(最大直径可达数cm)、稠厚的粘液样物以及(如果有的话)内表面乳头状突起。出血、变性以及上皮缺失偶可广泛,因此提示假性囊肿124。相邻胰腺成分可能有些萎缩。
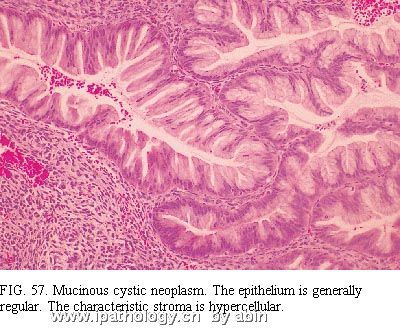
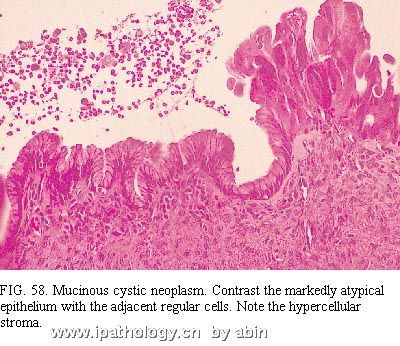
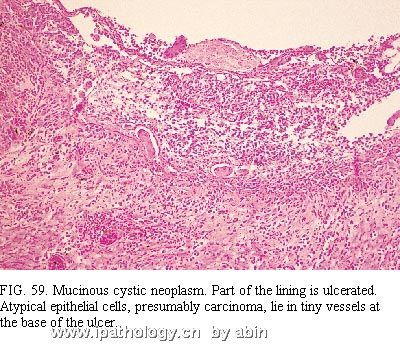
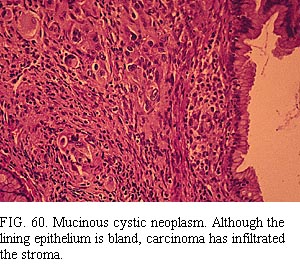
The neoplasms have columnar epithelium similar to that of the large pancreatic ducts and the intestine, especially the colon, and have characteristic stroma composed of plump spindle cells similar to those of ovarian stroma (Fig. 57 and Fig. 58) 126,128. The lining cells include nonciliated mucous columnar cells, goblet cells, absorptive-type cells, cuboidal cells, and (rarely) Paneth cells. Papillary formations are common and range from microscopic in size to large, complex structures visible to the naked eye. Careful search of multiple sections frequently reveals atypical epithelium (Fig. 58), often pseudostratified (with or without the suggestion of invasion into the stroma or the presence of atypical cells in tiny vessels) (Fig. 59). Obvious regions of invasive adenocarcinoma may be apparent (Fig. 60). These findings combine with cases in which clinical carcinoma arose from mucinous “cystadenoma” to suggest that most or all of these neoplasms have malignant potential 124,126. Also, the bland epithelial cells typical of mucinous cystadenoma have been found in lymph node metastases 1. Failure to remove the entire tumor can result in the death of the patient from carcinoma, even if the resected tissue has only the regular epithelium of a mucinous cystadenoma. Conversely, when carcinoma is present within the mass, complete resection can result in cure because the tumor seems to spread less readily than the usual ductal adenocarcinoma. Studies suggest that aneuploidy in the cystadenocarcinomas indicates a bad prognosis 129. Classifying the neoplasms as carcinomas, borderline tumors, and adenomas has been suggested, but we doubt that we can make a reliable benign or borderline diagnosis with confidence for the reasons just mentioned.
肿瘤有柱状上皮,相似于胰腺大导管和肠上皮(尤其似结肠上皮),并有特征性胖梭形细胞间质,似卵巢间质(图57、58)126,128。衬覆细胞包括:无纤毛的粘液柱状细胞、杯状细胞、吸收细胞、立方细胞和罕见的潘氏细胞。乳头状结构常见,大小从仅镜下可见到肉眼可见的很大复杂结构。多切片仔细寻找,通常能发现不典型性(atypical)上皮(图58),多呈假复层,伴/不伴间质浸润或小血管内存在不典型细胞(图59)。也可能出现明显的腺癌区域(图60)。这些表现,结合临床上发现的起源于粘液性“囊腺瘤”的癌的病例,提示这些肿瘤绝大多数或全部具有恶性潜能124,126。而且,典型粘液性囊腺瘤的良性上皮细胞可见于淋巴结转移1。如果不能将整个肿瘤完全切除,即使切取组织中仅为粘液性囊腺瘤的规则上皮,也可能导致患者因癌死亡。相反,肿瘤内有癌时,完全切除可治愈,因为肿瘤似乎不比普通导管腺癌容易扩散。研究提示,囊腺癌出现非整倍性是预后差的标记129。曾经提出将这些肿瘤(neoplasms)分类为癌、交界性肿瘤和腺瘤,但是由于上述原因,我们怀疑是否能够作出可靠的良性或交界性的诊断。
资料来自Stephen S. Sternberg主编,Disgnostic Surgical Pathology, 3ed.
References
1. Cubilla AL, Fitzgerald PJ. Tumors of the exocrine pancreas. In: Hartmann WH, Sobin LH, eds. Atlas of tumor pathology, vol 19, 1st ed. Washington, DC: AFIP, 1984.
124. Binford CH, Connor DH, eds. Pathology of tropical and extraordinary diseases. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1976.
126.Lerner CW, Tapper ML. Opportunistic infection complicating acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical features of 25 cases. Medicine 1984;63:155–164.
128.Srigley JR, Vellend H, Palmer N, et al. Q-fever. The liver and bone marrow pathology. Am J Surg Pathol 1985;9:752–758.
129.Vanderstigel M, Zafrani ES, Lejonc JL, Schaeffer A, Portos JL. Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome as a cause of hepatic fibrin-ring granulomas. Gastroenterology 1986;90:188–190.
ABSTRACT
124 Within a 12-year period we treated 67 patients (49 women, 18 men; mean age, 61 years) with cystic neoplasms of the pancreas, including 18 serous cystic adenomas, 15 benign mucinous cystic neoplasms, 27 mucinous cystadenocarcinomas, 3 papillary cystic tumors, 2 cystic islet cell tumors, and 2 cases of mucinous ductal ectasia. Mean tumor size was 6 cm (2 to 16 cm). In 39% the patients had no symptoms, and in 37% the lesions had been misdiagnosed as a pseudocyst. Computed tomography was useful for detection, for distinguishing the microcystic subgroup of serous cystadenoma, and for showing rim calcification (all 7 cases were malignant) but was not reliable for distinguishing neoplasm from pseudocyst, serous from mucinous tumors, or benign from malignant. Arteriography showed hypervascularity in 4 of 10 serous adenomas, 3 of 11 mucinous carcinomas, and 1 of 1 papillary cystic tumors. Endoscopic pancreatography showed no communication with the cyst cavity in 37 of 37 cases of cystic neoplasms but opacified the ectatic ducts in 2 of 2 cases of mucinous ductal ectasia. Stenosis or obstruction of the pancreatic duct indicated cancer. The tumor was resected by distal pancreatectomy in 25 patients, by proximal resection in 29, and by total pancreatectomy in one, with no operative deaths. Forty-four per cent of the tumors were malignant. In 10 cases the tumor was unresectable because of local extension or distant metastases, and those patients died at a mean of 4 months. Seventy-five per cent of those resected for cure are alive without evident recurrence. Because the epithelial lining of the tumor was partially (5% to 98%) absent in 40% to 72% of cases of the major tumor types, and the mucinous component comprised only about 65% of mucinous cystadenoma lining, misdiagnoses on frozen and even permanent sections were made. Mitoses and histologic solid growth correlated with malignancy. Neuroendocrine elements were seen in 87% of benign and 47% of malignant mucinous tumors. It is recommended that the terms macrocystic and microcystic be abandoned in favor of the histologic designations serous and mucinous. Incomplete examination of the cyst wall can be misleading, however. It is suggested that mucinous ductal ectasia be recognized separately from cystic tumors and that all of these lesions be resected, with the possible exception of asymptomatic confirmed serous cystadenomas.
128 Twenty mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas, most of which occurred in the tail of the pancreas in middle-aged women, were examined histologically and by immunohistochemical stains. Thirteen tumors displayed a marked histological heterogeneity and expressed intestinal differentiation as shown by the colonic appearance of the glands both at the light- and electron-microscopic levels. Other intestinal features included varying numbers of goblet cells, argyrophil and argentaffin cells, and even Paneth cells. By immunohistochemistry, endocrine cells were present in 13 of the 20 tumors (65%) and were more numerous in the poorly differentiated than in the well-differentiated epithelial component of the tumors. Serotonin-containing cells were the most common endocrine cells, followed by somatostatin-containing cells and cells that showed immunoreactivity for pancreatic polypeptide and gastrin. However, none of the patients had clinical manifestations of carcinoid, somatostatinoma, or the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The findings support the hypothesis that mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas arise from an "endodermal stem cell" that differentiates into cells with intestinal phenotypes.
129 BACKGROUND. Benign and malignant pancreatic mucinous tumors differ in proliferative activity, production of tumor markers, and expression of growth factors. DNA ploidy is a useful index of aggressiveness and poor survival in ductal adenocarcinoma, but has not been studied in pancreatic cystic tumors. METHODS. The DNA ploidy status of Fuelgen- stained tissue sections of pancreatic mucinous cystic tumors was evaluated by image cytometry and related to clinical outcome obtained by case record review. RESULTS. Ploidy status correlated with malignancy and poor clinical outcome. All benign mucinous cystadenomas (n = 13) were diploid and cured by resection. Patients with diploid cystadenocarcinomas (n = 6) had an 83% survival rate following resection, while patients with aneuploid cystadenocarcinomas (n = 5) all died (four of disease and the fifth of another cause). The difference in survival between the diploid and aneuploid carcinomas was significant (P = 0.04). CONCLUSIONS. DNA ploidy status of pancreatic mucinous tumors by image analysis provides quantifiable information that may be predictive of clinical outcome. DNA aneuploidy appears to be a significant differential factor in pancreatic mucinous tumors and is associated with shortened survival in mucinous cystadenocarcinomas.
文献摘要就不用翻译了吧?对文献感兴趣的老师肯定英语很好了。
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms, Including Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
粘液性囊性肿瘤,包括粘液性囊腺癌
Pathologic Features
病理特征
The neoplasms may be irregular in shape, have well-developed capsules with smooth, glistening (sometimes translucent) external surfaces, and are usually multilocular (Fig. 56). They range from 2 to 20 cm in diameter (average 10–11 cm). The tumor can be adherent to adjacent organs and may be surrounded by dense fibrosis (similar to a pseudocyst). Part of the surface may be irregular and dense because of this fibrosis or because malignant epithelium has extended through the capsule. Large blood vessels may extend over the exterior surfaces of the tumor. Sectioning demonstrates the dense collagenous capsule of variable thickness, cavities of different sizes (the largest often several centimeters in diameter), thick mucoid contents, and (if present) papillary excrescences on the interior surfaces. Hemorrhage, degenerative changes, and loss of epithelium occasionally are extensive and therefore suggest a pseudocyst 124. The adjacent pancreatic parenchyma may be somewhat atrophic.
肿瘤外形可不规则,有完整包膜,外观光滑发光(有时半透明),一般多房(图56)。直径2~20cm(平均10~11cm)。肿瘤可与周围器官粘连,四周可能致密纤维化(似假囊肿)。因为纤维化或因恶性上皮穿透包膜,部分表面可能不规则和致密。大血管可能在肿瘤外表面延伸。切面显示致密的胶原化包膜、大小不一的腔隙(最大直径可达数cm)、稠厚的粘液样物以及(如果有的话)内表面乳头状突起。出血、变性以及上皮缺失偶可广泛,因此提示假性囊肿124。相邻胰腺成分可能有些萎缩。
The neoplasms have columnar epithelium similar to that of the large pancreatic ducts and the intestine, especially the colon, and have characteristic stroma composed of plump spindle cells similar to those of ovarian stroma (Fig. 57 and Fig. 58) 126,128. The lining cells include nonciliated mucous columnar cells, goblet cells, absorptive-type cells, cuboidal cells, and (rarely) Paneth cells. Papillary formations are common and range from microscopic in size to large, complex structures visible to the naked eye. Careful search of multiple sections frequently reveals atypical epithelium (Fig. 58), often pseudostratified (with or without the suggestion of invasion into the stroma or the presence of atypical cells in tiny vessels) (Fig. 59). Obvious regions of invasive adenocarcinoma may be apparent (Fig. 60). These findings combine with cases in which clinical carcinoma arose from mucinous “cystadenoma” to suggest that most or all of these neoplasms have malignant potential 124,126. Also, the bland epithelial cells typical of mucinous cystadenoma have been found in lymph node metastases 1. Failure to remove the entire tumor can result in the death of the patient from carcinoma, even if the resected tissue has only the regular epithelium of a mucinous cystadenoma. Conversely, when carcinoma is present within the mass, complete resection can result in cure because the tumor seems to spread less readily than the usual ductal adenocarcinoma. Studies suggest that aneuploidy in the cystadenocarcinomas indicates a bad prognosis 129. Classifying the neoplasms as carcinomas, borderline tumors, and adenomas has been suggested, but we doubt that we can make a reliable benign or borderline diagnosis with confidence for the reasons just mentioned.
肿瘤有柱状上皮,相似于胰腺大导管和肠上皮(尤其似结肠上皮),并有特征性胖梭形细胞间质,似卵巢间质(图57、58)126,128。衬覆细胞包括:无纤毛的粘液柱状细胞、杯状细胞、吸收细胞、立方细胞和罕见的潘氏细胞。乳头状结构常见,大小从仅镜下可见到肉眼可见的很大复杂结构。多切片仔细寻找,通常能发现不典型性(atypical)上皮(图58),多呈假复层,伴/不伴间质浸润或小血管内存在不典型细胞(图59)。也可能出现明显的腺癌区域(图60)。这些表现,结合临床上发现的起源于粘液性“囊腺瘤”的癌的病例,提示这些肿瘤绝大多数或全部具有恶性潜能124,126。而且,典型粘液性囊腺瘤的良性上皮细胞可见于淋巴结转移1。如果不能将整个肿瘤完全切除,即使切取组织中仅为粘液性囊腺瘤的规则上皮,也可能导致患者因癌死亡。相反,肿瘤内有癌时,完全切除可治愈,因为肿瘤似乎不比普通导管腺癌容易扩散。研究提示,囊腺癌出现非整倍性是预后差的标记129。曾经提出将这些肿瘤(neoplasms)分类为癌、交界性肿瘤和腺瘤,但是由于上述原因,我们怀疑是否能够作出可靠的良性或交界性的诊断。
资料来自Stephen S. Sternberg主编,Disgnostic Surgical Pathology, 3ed.
References
1. Cubilla AL, Fitzgerald PJ. Tumors of the exocrine pancreas. In: Hartmann WH, Sobin LH, eds. Atlas of tumor pathology, vol 19, 1st ed. Washington, DC: AFIP, 1984.
124. Binford CH, Connor DH, eds. Pathology of tropical and extraordinary diseases. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1976.
126.Lerner CW, Tapper ML. Opportunistic infection complicating acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical features of 25 cases. Medicine 1984;63:155–164.
128.Srigley JR, Vellend H, Palmer N, et al. Q-fever. The liver and bone marrow pathology. Am J Surg Pathol 1985;9:752–758.
129.Vanderstigel M, Zafrani ES, Lejonc JL, Schaeffer A, Portos JL. Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome as a cause of hepatic fibrin-ring granulomas. Gastroenterology 1986;90:188–190.
ABSTRACT
124 Within a 12-year period we treated 67 patients (49 women, 18 men; mean age, 61 years) with cystic neoplasms of the pancreas, including 18 serous cystic adenomas, 15 benign mucinous cystic neoplasms, 27 mucinous cystadenocarcinomas, 3 papillary cystic tumors, 2 cystic islet cell tumors, and 2 cases of mucinous ductal ectasia. Mean tumor size was 6 cm (2 to 16 cm). In 39% the patients had no symptoms, and in 37% the lesions had been misdiagnosed as a pseudocyst. Computed tomography was useful for detection, for distinguishing the microcystic subgroup of serous cystadenoma, and for showing rim calcification (all 7 cases were malignant) but was not reliable for distinguishing neoplasm from pseudocyst, serous from mucinous tumors, or benign from malignant. Arteriography showed hypervascularity in 4 of 10 serous adenomas, 3 of 11 mucinous carcinomas, and 1 of 1 papillary cystic tumors. Endoscopic pancreatography showed no communication with the cyst cavity in 37 of 37 cases of cystic neoplasms but opacified the ectatic ducts in 2 of 2 cases of mucinous ductal ectasia. Stenosis or obstruction of the pancreatic duct indicated cancer. The tumor was resected by distal pancreatectomy in 25 patients, by proximal resection in 29, and by total pancreatectomy in one, with no operative deaths. Forty-four per cent of the tumors were malignant. In 10 cases the tumor was unresectable because of local extension or distant metastases, and those patients died at a mean of 4 months. Seventy-five per cent of those resected for cure are alive without evident recurrence. Because the epithelial lining of the tumor was partially (5% to 98%) absent in 40% to 72% of cases of the major tumor types, and the mucinous component comprised only about 65% of mucinous cystadenoma lining, misdiagnoses on frozen and even permanent sections were made. Mitoses and histologic solid growth correlated with malignancy. Neuroendocrine elements were seen in 87% of benign and 47% of malignant mucinous tumors. It is recommended that the terms macrocystic and microcystic be abandoned in favor of the histologic designations serous and mucinous. Incomplete examination of the cyst wall can be misleading, however. It is suggested that mucinous ductal ectasia be recognized separately from cystic tumors and that all of these lesions be resected, with the possible exception of asymptomatic confirmed serous cystadenomas.
128 Twenty mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas, most of which occurred in the tail of the pancreas in middle-aged women, were examined histologically and by immunohistochemical stains. Thirteen tumors displayed a marked histological heterogeneity and expressed intestinal differentiation as shown by the colonic appearance of the glands both at the light- and electron-microscopic levels. Other intestinal features included varying numbers of goblet cells, argyrophil and argentaffin cells, and even Paneth cells. By immunohistochemistry, endocrine cells were present in 13 of the 20 tumors (65%) and were more numerous in the poorly differentiated than in the well-differentiated epithelial component of the tumors. Serotonin-containing cells were the most common endocrine cells, followed by somatostatin-containing cells and cells that showed immunoreactivity for pancreatic polypeptide and gastrin. However, none of the patients had clinical manifestations of carcinoid, somatostatinoma, or the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The findings support the hypothesis that mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas arise from an "endodermal stem cell" that differentiates into cells with intestinal phenotypes.
129 BACKGROUND. Benign and malignant pancreatic mucinous tumors differ in proliferative activity, production of tumor markers, and expression of growth factors. DNA ploidy is a useful index of aggressiveness and poor survival in ductal adenocarcinoma, but has not been studied in pancreatic cystic tumors. METHODS. The DNA ploidy status of Fuelgen- stained tissue sections of pancreatic mucinous cystic tumors was evaluated by image cytometry and related to clinical outcome obtained by case record review. RESULTS. Ploidy status correlated with malignancy and poor clinical outcome. All benign mucinous cystadenomas (n = 13) were diploid and cured by resection. Patients with diploid cystadenocarcinomas (n = 6) had an 83% survival rate following resection, while patients with aneuploid cystadenocarcinomas (n = 5) all died (four of disease and the fifth of another cause). The difference in survival between the diploid and aneuploid carcinomas was significant (P = 0.04). CONCLUSIONS. DNA ploidy status of pancreatic mucinous tumors by image analysis provides quantifiable information that may be predictive of clinical outcome. DNA aneuploidy appears to be a significant differential factor in pancreatic mucinous tumors and is associated with shortened survival in mucinous cystadenocarcinomas.
文献摘要就不用翻译了吧?对文献感兴趣的老师肯定英语很好了。