| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 请高手指点!
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 男 | 年龄: | 23 |
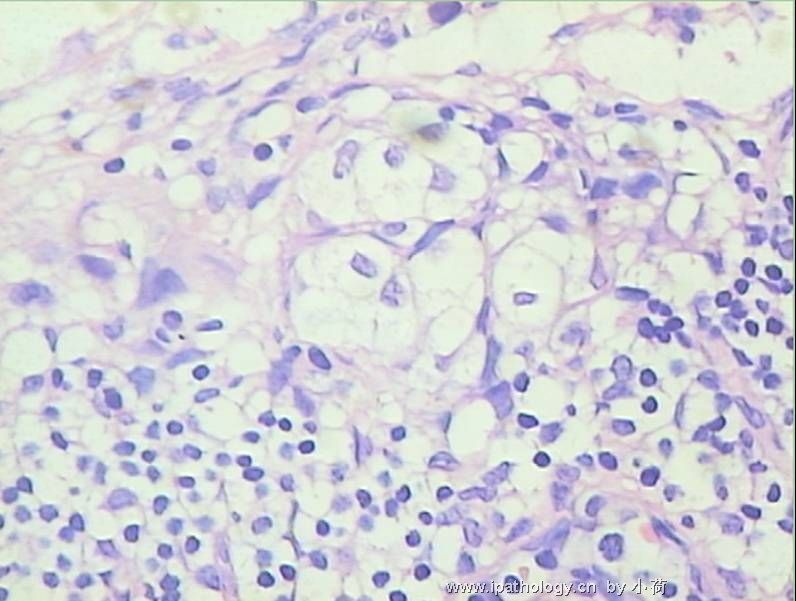
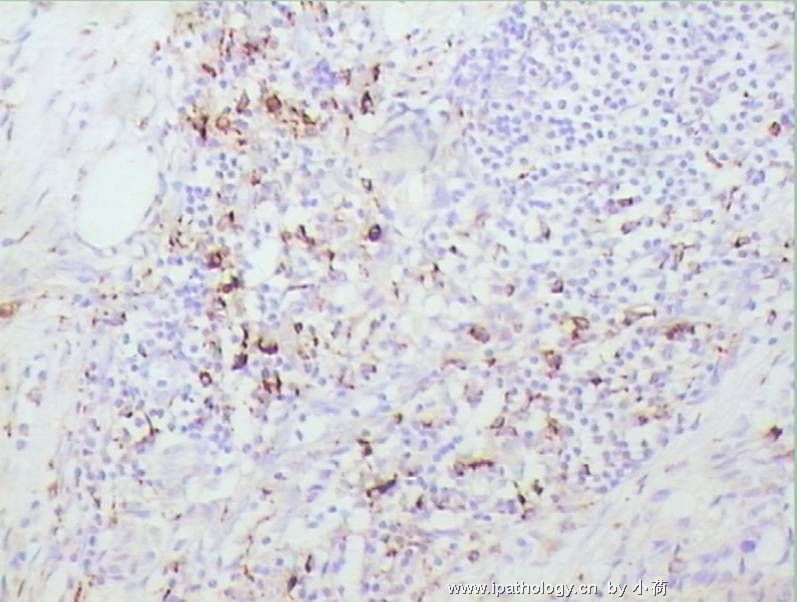
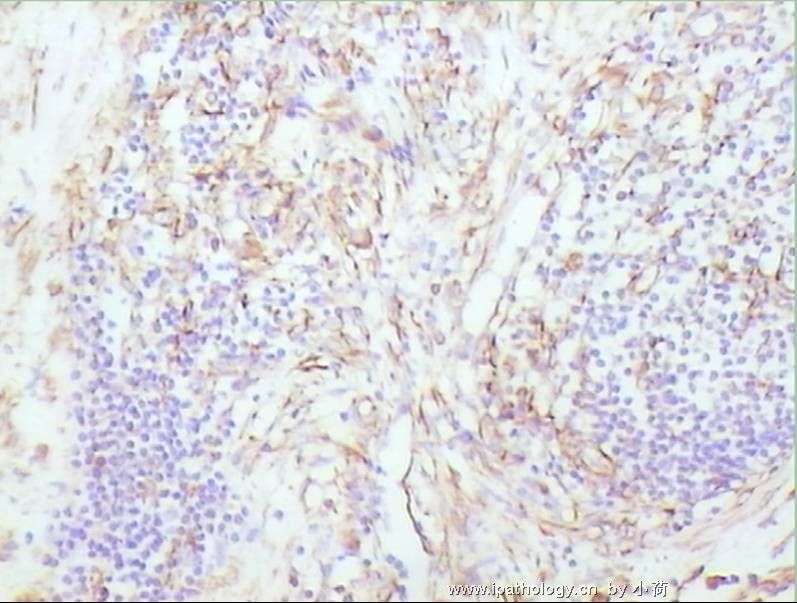
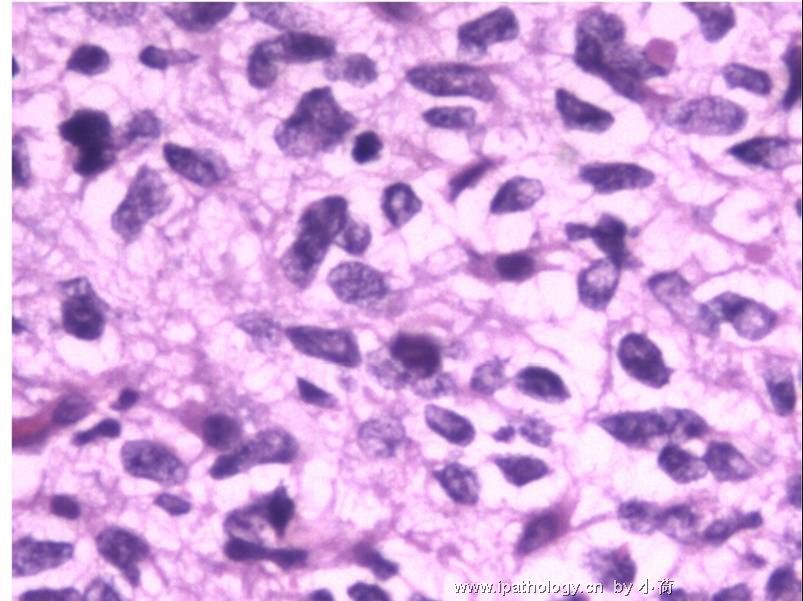
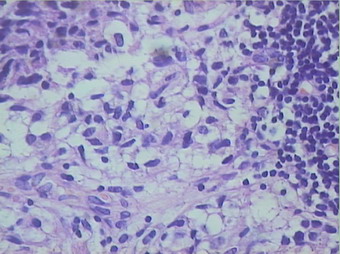
| 标本名称: | 在我院行髋部溶骨性病变和局部淋巴结病灶活检. 免疫组化D68+++,CK(-),EMA(-),S100(-). | ||||
| 简要病史: | 战士,半年前在其它城市脑部手术,术后诊断脑胶质瘤,现多处骨有溶骨性病灶,肺有阴影 | ||||
| 初步诊断意见: | 根据切片和免疫组化我们想诊断非朗格罕组织细胞增生症.缺少经验,请高手指导 | ||||
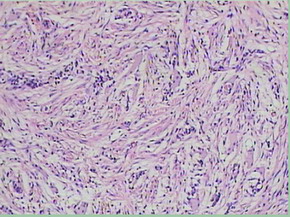
名称:图1
描述:图1
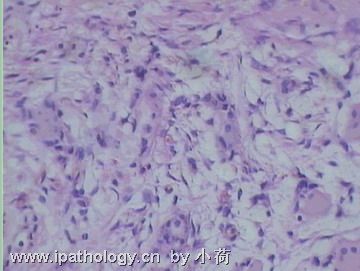
名称:图2
描述:图2
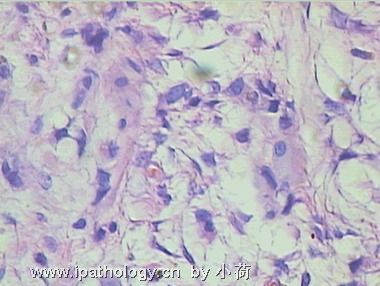
名称:图3
描述:图3
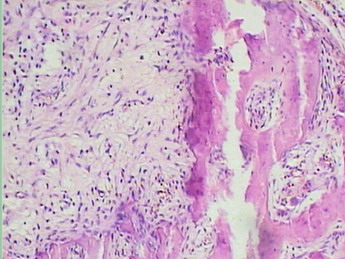
名称:图4
描述:图4
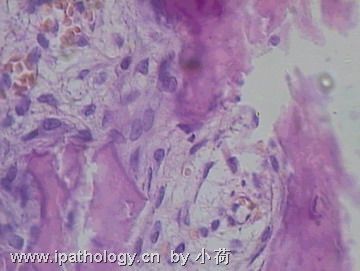
名称:图5
描述:图5
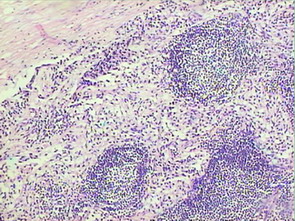
名称:图6
描述:图6
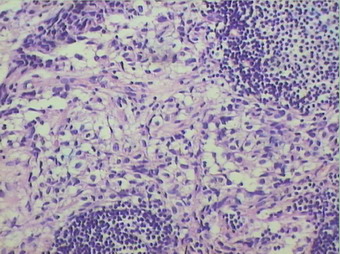
名称:图7
描述:图7
名称:图8
描述:图8
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-03-15 07:58:00 编辑

- 没有完美的个人,只有完美的团队
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-03-03 20:57:00 编辑
Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD) is a rare non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis first described by Jakob Erdheim and William Chester in 1930. They described two patients who had a distinctive lipidosis with associated bone changes. In 1972, Jaffe reported a third patient and coined the term "Erdheim-Chester disease". Jaffe described the disease as a rare histiocytic disorder of adults characterized by an infiltrate of lipid-laden macrophages, multinucleated giant cells, inflammatory infiltrate of lymphocytes and histiocytes in the bone marrow and a generalized sclerosis of the long bones sparing the epiphysis. Approximately 80 cases have been reported in the literature. (ECD是一种罕见的非朗格罕组织细胞增生症,1930由Jakob Erdheim和William Chester首先描述。他们描述的2例,患者有特殊的与骨病变有关的脂质沉积病。1972年,Jaffe报道了第三例,并创造了一个新的诊断名词“Erdheim-Chester disease”。 Jaffe将此病描述为一种罕见的发生于成人的组织细胞病变,特征是充满脂质的巨噬细胞、多核巨细胞、淋巴细胞和组织细胞浸润骨髓,以及全身长骨骨皮质硬化。文献已报道约80例。abin译)
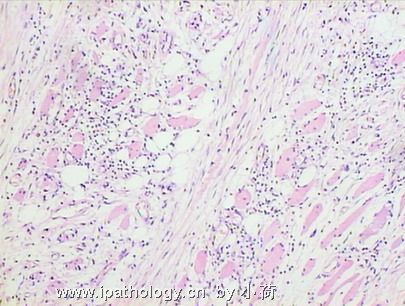
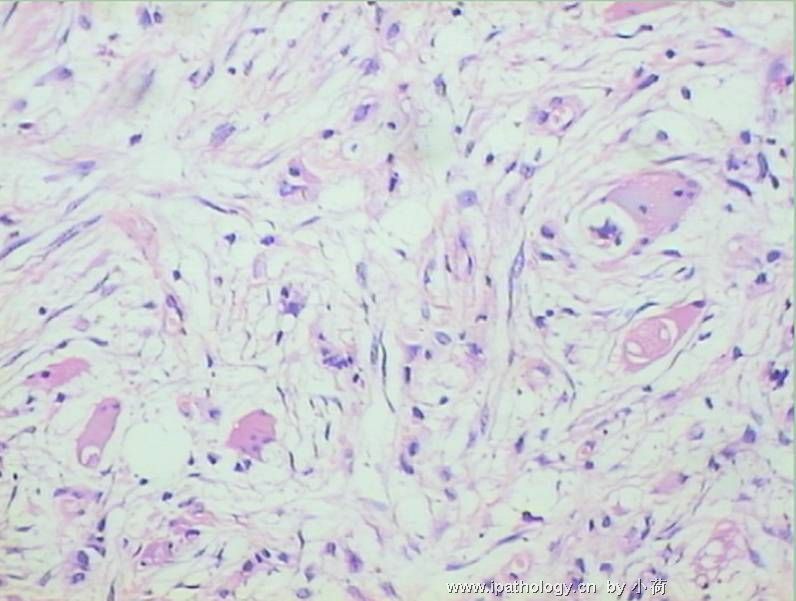
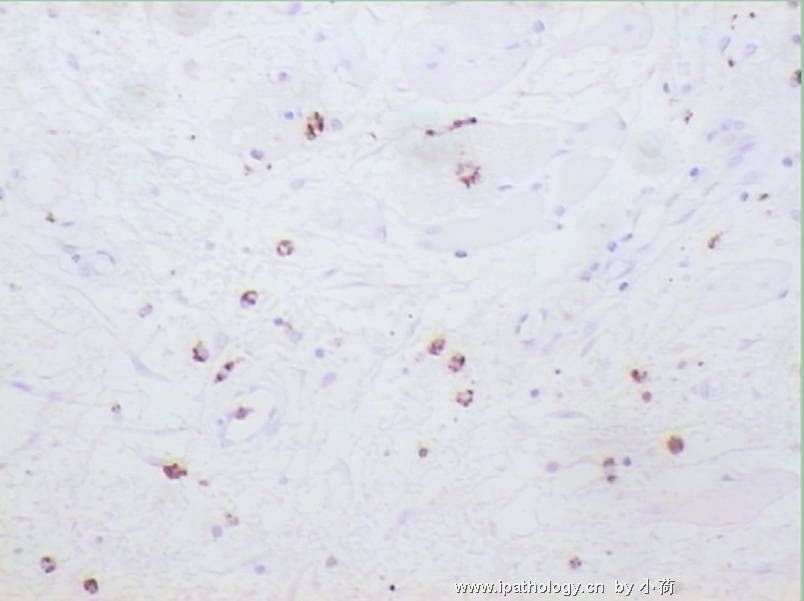
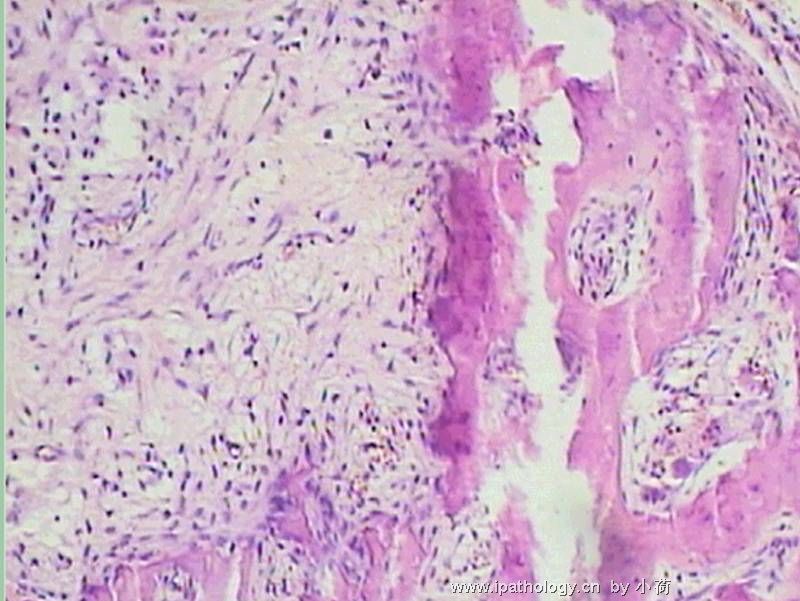
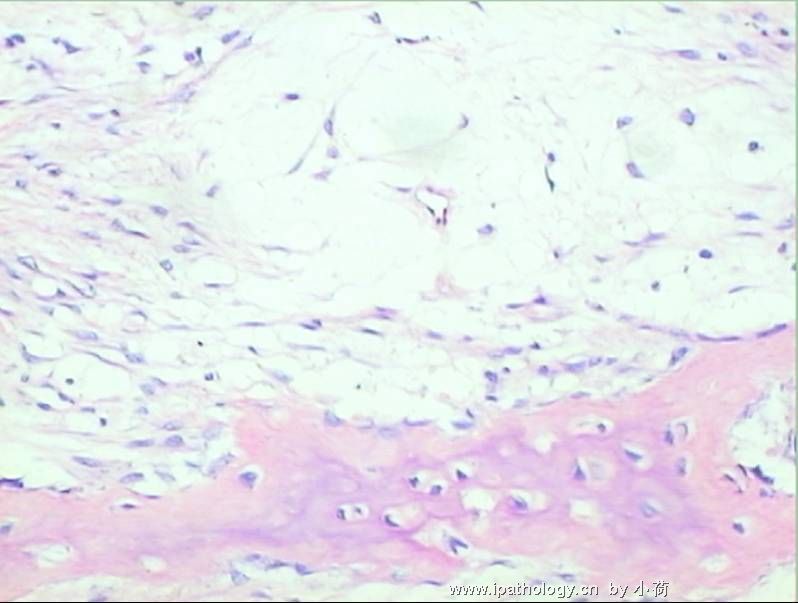
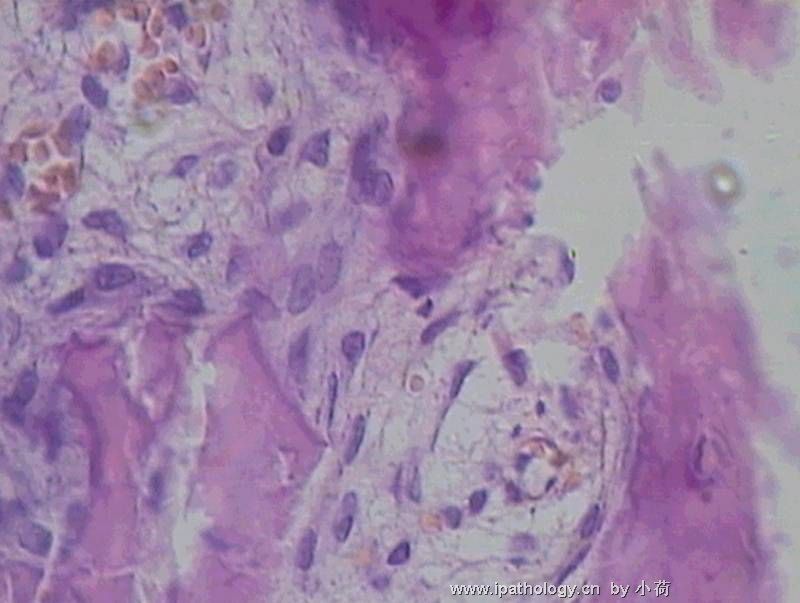
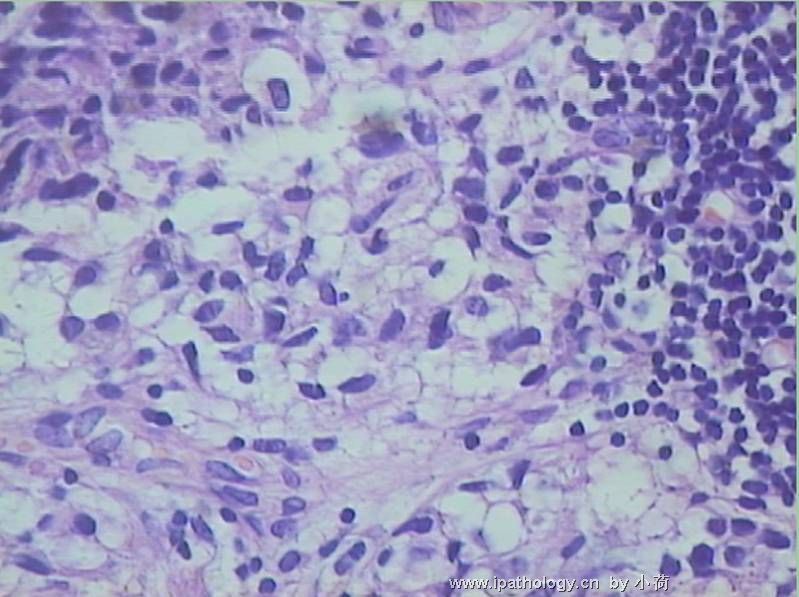
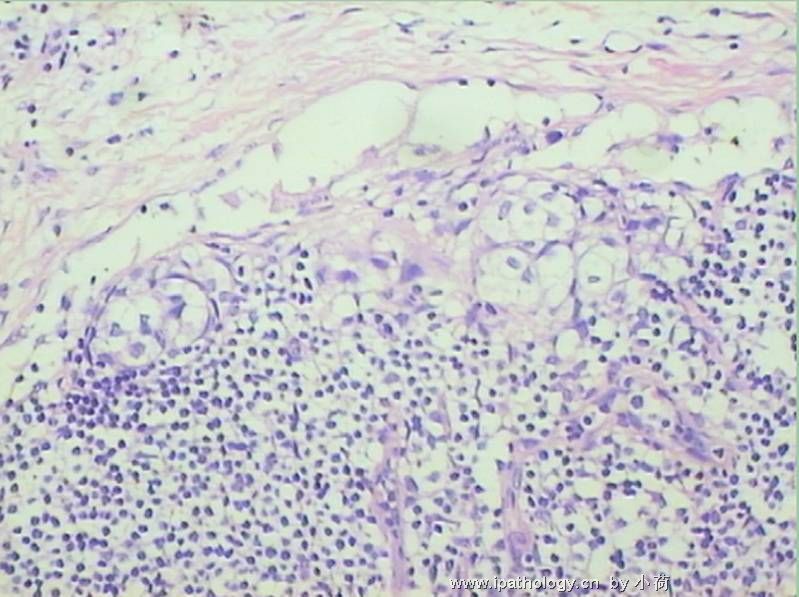
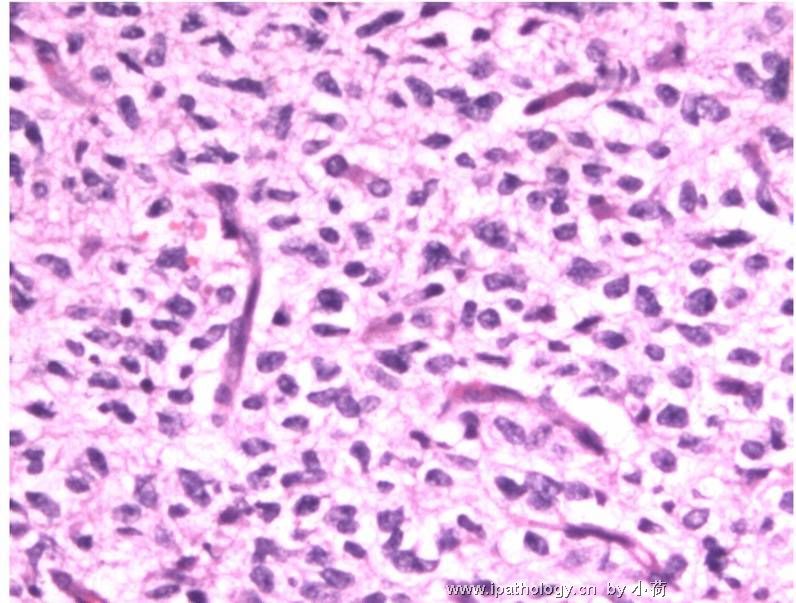
患者半年前在某医院脑瘤手术,术后诊断为脑胶质瘤,现全身多处骨溶骨性病灶,股骨颈病理性骨折,我们取的活检就在该部位.肺部有阴影,但是该战士现全身状况比较好,患者因骨折取活检,镜下见明显的噬脂性的组织细胞浸蚀横纹肌(前3张图),浸润淋巴结的窦(后三张),第4第5张为浸蚀髋骨.做免疫组化瘤细胞表达CD68+++,CK(-),EMA(-),S100(-).我们怀疑本例为Erdheim-Chester disease非朗格罕细胞组织细胞增生症.因没有见过,想请高手指点.
请高手指点,谢谢小荷传图.
-
从免疫组化结果来看,淋巴结内富于脂质的组织细胞不是朗格罕组织细胞,诊断非朗格罕组织细胞增生症感觉没有问题。Erdheim-Chester disease 也属于非朗格罕组织细胞增生症的一种,多有下肢干骺端的对称性硬化性骨病变,也可有溶骨性病变,并且常常有骨外多部位的累及,组织学上表现为富于脂质的组织细胞浸润。本科曾诊断过一例,此病预后不好。综合考虑,感觉诊断ECD还是成立的。图片比较小,意见不成熟,供岳主任参考。

- the more we discuss, the more we learn from each other !!
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-02-20 12:24:00 编辑
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-02-20 12:40:00 编辑
Neurologic presentation of Erdheim-Chester disease.
Brodkin CL, Wszolek ZK.
Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic, 4500 San Pablo Road, Jacksonville, FL 32224, USA.
Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2006 Sep-Oct;40(5):397-403
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-02-20 12:47:00 编辑

聞道有先後,術業有專攻
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-02-20 01:00:00 编辑

聞道有先後,術業有專攻
脑部病变为胶质瘤没有问题,肌肉和骨头细胞比较稀疏,的确如马教授所说,未见典型的泡沫状组织细胞,不过对于一些硬化性骨病变来说,细胞有疏有密,在活检标本上也不一定都能找到泡沫状组织细胞,有些组织细胞可以胞浆嗜酸。不过从第二次传的肌肉照片来看,免疫组化显示的CD68阳性细胞好像也不是很多。
ECD属于非朗罕组织细胞增生症,由于缺少认识,可能多数被诊断为黄色肉芽肿或仅仅做描述性诊断。此例有支持的地方,如多处骨病变,肺、肌肉、淋巴结累及,淋巴结内明显的CD68阳性组织细胞增生等;但也有不太像的地方,如无典型的对称性长骨干骺端硬化、骨及肌肉内细胞稀疏、组织细胞少以及缺乏典型的泡沫状组织细胞、Tuton巨细胞等。因此,从后面所传图片来看,此例可能做描述性诊断比较合适。

- the more we discuss, the more we learn from each other !!
| 以下是引用梅兰 在2007-3-4 0:25:00的发言:
|

华夏病理/粉蓝医疗
为基层医院病理科提供全面解决方案,
努力让人人享有便捷准确可靠的病理诊断服务。