| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
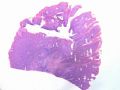
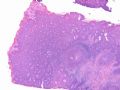
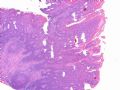
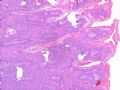
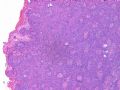
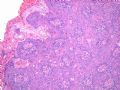
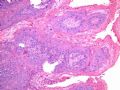
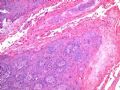
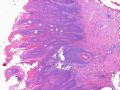
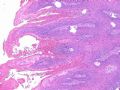
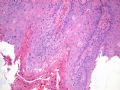
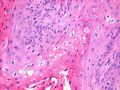
- B516外阴赘生物
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | 82 | |
| 标本名称: | 外阴 | ||||
| 简要病史: | 发现 赘生物3个月 | ||||
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
-
本帖最后由 于 2007-08-17 15:54:00 编辑
相关帖子
- • GYN Case 3 from USCAP 2007
- • 外阴肿物
- • 外阴疣状物
- • 外阴肿块
- • 外阴肿块
- • 欣赏-外阴病变
- • 外阴结节
- • 搞笑病例2__妇科专家不知道外阴派杰病?
- • 外阴粘液性肿物
- • 外阴大肿块
-
Sorry for missing Professor Zhou's teaching on this case and I have no idea what the final diagnosis of Dr. Zhou provides. My two penny personal opinion is a "Warty type of squamous carcinoma" in this 82 year old lady. I do not think this is a verrucous carcinoma due to less impressive "bulky and pushing base" which is vanishingly rare. Also it is way beyond of condyloma cytologically. You have to think three times before to make a diagnosis of condyloma in a 82 year old lady socioeconomically. I am humblely listening to Professor Zhou's comment and critiques here. Thanks you.

- 不坠青云之志,长怀赤子之心
Guide for signing out VIN cases according to new ISSVD Classification:
|
Histology |
Final Diagnosis |
Comment |
|
VIN-1 |
SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH ATYPIA, CONSISTENT WITH HPV-RELATED CHANGES |
The above lesion is equivalent to vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia 1(VIN-1) lesion according to the old classification scheme. The new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification no longer includes “VIN-1” as a type of VIN. This is due to lack of evidence that “VIN-1” is a cancer precursor lesion. References: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. J Reprod Med. 2005;50:807-10. |
|
VIN-2 or VIN-3 |
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL WARTY TYPE.
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL BASALOID TYPE.
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL MIXED (WARTY/BASALOID) TYPE. |
The above diagnosis is based on the new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification of vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia (VIN). The above lesion is equivalent to VIN-2 (or VIN-3) according to the old classification scheme. Reference: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. |
|
VIN-differentiated type |
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), DIFFERENTIATED TYPE. |
The above diagnosis is based on the new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification of vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia (VIN). The risk of progression to invasion seems greater in differentiated VIN than in usual VIN. References: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2001;20:16-30. |