| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
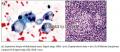
- 一例少见淋巴瘤
印戒细胞淋巴瘤很少遇到。其淋巴瘤细胞由于胞浆含有包涵体或呈空泡状,而细胞核有时偏向胞体的一侧。这很像印戒样细胞,易误诊为印戒细胞癌。因此,需要做IHC标记,或是流式细胞分析,有条件的作电镜检查,免得误诊。
Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2013
Jul;26(3):293-4.
Signet ring lymphoma: a
potential diagnostic mishap.
Source
Section of Hematopathology, Department of Pathology, Baylor
University Medical Center at Dallas.
Abstract
Signet ring lymphomas are
proliferations of malignant lymphoid cells containing cytoplasmic
inclusions or vacuoles that displace the nucleus to the side, imparting a
"signet ring" appearance. These signetring cells,
particularly those with cytoplasmic vacuoles, may be mistaken for an
adenocarcinoma rather than a lymphoma, if sufficient material is not
available to differentiate the case by immunohistochemical stains or flow
cytometry. The pathologist must also be aware of this entity so that
appropriate studies may be untaken.

- 王军臣
细针吸样本诊断印戒细胞淋巴瘤则更为困难,更易误诊为印戒细胞癌。需要IHC等方法用于诊断与鉴别诊断。
Cancer Cytopathol. 2013 Sep;121(9):525-32. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21291.
Epub 2013 Mar 27.
Fine-needle
aspiration diagnosis of lymphomas with signet ring cell features:
Potential pitfalls and solutions.
Wang J, Katz RL, Stewart J, Landon G, Guo M, Gong Y.
Source
Department of Pathology,
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas; Department
of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine, St.
Louis, Missouri.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Lymphoma with signet ring cell features (LSF) is a rare morphologic
variant of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Although it has been well documented in the
surgical pathology literature, to the best of the authors's knowledge, the
features of LSF in fine-needle aspiration (FNA) samples have rarely been
reported. An accurate cytologic diagnosis of LSF is of important therapeutic
significance.
METHODS:
The authors
retrospectively reviewed 7 FNA cases of LSF for cytologic features, ancillary
studies, corresponding histologic findings, and the patients' clinical and
radiologic information to illustrate the diagnostic clues and potential
pitfalls.
RESULTS:
The final diagnoses, based
on a multidisciplinary approach, were follicular lymphoma (5 patients), large B-cell lymphoma of
follicular center cell origin
(1 patient), and low-grade B-celllymphoma with plasmacytoid features (1
patient). FNAs were obtained from both lymph node and extranodal sites. Common
cytologic features included various percentages of signet ring cells in a background of nonvacuolated
lymphomatous cells, lymphoglandular bodies, and cytoplasmic rings.
The majority of signet ring cells contained
a single, large, clear intracytoplasmic vacuole that pushed the nucleus
laterally whereas fewer cells contained ≥ 2
vacuoles that indented the nucleus into a scalloped or stellate configuration.
These cells resemble, to some degree, other
lesions with signetring cell features.
One of the diagnostic clues of LSF was the similarity in nuclear details
betweensignet ring cells and
surrounding nonvacuolated lymphoid cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Familiarity with cytologic
features, correlation with clinical/radiologic information, and ancillary
studies are important for an accurate diagnosis of LSF and for distinguishing
it from other lesions with signet ring cell features
in FNA samples. Cancer (Cancer Cytopathol) 2013;121:525-32.

- 王军臣
印戒细胞淋巴瘤的表型分类可以是大B细胞淋巴瘤。
Int
J Surg Pathol. 2013 Aug;21(4):399-403. doi:
10.1177/1066896912474342. Epub 2013 Jan 30.
Extreme signet ring cell change in a large B-cell lymphoma of follicular origin.
Bogusz AM, Tierno B, Brown D, Pihan G.
Source
Department of Pathology, Beth Israel
Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Abstract
We report a large
B-cell lymphoma of follicular origin with extreme signet ring cell differentiation.
Initially classified as follicular lymphoma on a fine needle core
biopsy, the presence of cohesive sheets of extrafollicular signet ring cells triggered
an excisional biopsy for further characterization. The excised lymph node
revealed focal follicular hyperplasia, follicular lymphoma, and a neoplasm
composed of vague nodules and sheets of large atypical cells, all of which
virtually exhibited large clear intracytoplasmic vacuoles with peripheral
displacement of nuclei. The tumor cells were negative for mucin and
lacked immunoreactivity with pancytokeratin, but were strongly immunoreactive
with CD20, BCL-2, BCL-6, and CD10 antibodies. Electron microscopy studies
revealed electron-lucent vacuoles with no particular internal structure. This
case is unique in that extreme signet ring celldifferentiation
somewhat obscured the true cytological identity of the interfollicular lymphoma and
suggested alternative diagnoses.

- 王军臣
B细胞性印戒细胞淋巴瘤很易被误诊为印戒细胞癌,
Medicina (B Aires). 2004;64(6):521-4.
[Signet ring cell lymphoma mimicking mucin-producing carcinoma].
[Article in Spanish]
Sáenz de Chirife AM, Rojas Bilbao E, Giménez L, Marino L, Celeste F.
Source
Departamento de Patología, Instituto de
Oncología Angel H. Roffo, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Buenos Aires,
Argentina.
Erratum in
·
Medicina (B Aires). 2005;65(1):92.
Abstract
Signet ring cell lymphoma is
a rare neoplasm characterized by large, vacuolated and clear cellsmimicking
mucin-producing adenocarcinoma. It is localized in nodal and extranodal sites.
A case of a 59 years old male, with a diffuse lymphoma signet ring cell type
localized on oropharyngeal mucosa is reported. The histopathology study showed signet ring cells and
the immunophenotype was: vimentine(+), CD45(+), CD20(+), Ig M(+), Kappa
chain(+) and high index proliferative activity of neoplastic cells (Ki
67:70%). After a review of the literature and previous reports, we could not
find a similar case in this anatomic site. The patient had a unfavourable
clinical course and died two months after the diagnosis without receiving any
treatment.

- 王军臣
皮肤B细胞性淋巴瘤可呈印戒细胞形态。
Am
J Dermatopathol. 2001 Jun;23(3):181-4.
Moran CA, Suster S, Abbondanzo SL.
Source
Department of Anatomic Pathology, University
of Alabama at Birmingham, Kracks Building KB726, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA.
Abstract
Three cases of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma with prominent signet ring-cell features are presented. The patients were three men between the ages of 37 years and 74 years (average, 55.5 years). Clinically, the three patients presented with multiple skin nodules. In one patient, the nodules had been present for approximately 5 weeks, although in the two other patients, the nodules were of unknown duration. The lesions were located in the upper extremities (forearm) and measured from 2 cm to 3 cm in diameter. No evidence of lymphadenopathy was observed in any of the patients. Surgical excision of the nodules was performed. Histologically, in two cases, the superficial and deep dermis was replaced by a diffuse cellular proliferation, and in one patient, the tumor cell population adopted a nodular pattern of growth involving adnexal structures and infiltrating the subcutaneous fat. In all cases, the tumors were composed of cells showing signet ring-cell features, with striking indentation of the nuclei toward the periphery of the cell. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies for B-cell and T-cell markers (L-26 and UCHL) as well as antibodies for leukocyte common antigen, keratin, and kappa and lambda light chains were performed in all cases. The tumor cellsshowed a positive reaction for leukocyte common antigen, L-26, and lambda light chain restriction. Follow-up information was only available in one patient, who has remained alive and well 2 years after diagnosis without evidence of progression of the disease. The present cases highlight the importance of recognizing this unusual morphologic type of lymphoma so as to arrive at a correct diagnosis.

- 王军臣
小淋巴细胞淋巴瘤表现为印戒细胞淋巴瘤,在结内呈窦性生长特点,很容易被误诊为印戒细胞癌。需要IHC鉴别。
Ann Diagn
Pathol. 1999 Aug;3(4):220-6.
Signet-ring cell variant of small lymphocytic lymphoma with a
prominent sinusoidal pattern.
Ramnani D, Lindberg G, Gokaslan ST, Albores-Saavedra J.
Source
Division of Anatomic Pathology,
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.
Abstract
Signet-ring cell lymphoma is
a rare morphologic variant of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma characterized by
neoplastic lymphoid cells with cytoplasmic vacuoles or eosinophilic
globules that impart a signet-ringcell morphology. Although most
cases are variants of follicular center B-cell lymphomas, this pattern
also can be seen in T-cell lymphomas. An indolent clinical course and
prolonged survival have characterized the majority of published cases. We
document the case of a 62-year-old African-American woman with diffuse small
lymphocytic signet-ring lymphoma having a predominant sinusoidal
growth pattern, which, to our knowledge, has not been previously reported. The
prominent sinusoidal pattern of signet-ring lymphocytes contributes
to its confusion with metastatic signet-ring cell adenocarcinoma. The
correct diagnosis is greatly facilitated by the use of appropriate
immunohistochemical stains for lymphoid markers.

- 王军臣
印戒细胞窦性组织细胞增生症,更像是印戒细胞癌。
Cancer. 1997
Jul 15;80(2):277-85.
Signet-ring sinus histiocytosis: a reactive disorder that mimics
metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Guerrero-Medrano J, Delgado R, Albores-Saavedra J.
Source
Instituto Nacional de
Cancerología, Distrito Federal, México.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Signet-ring sinus
histiocytosis is a rare and distinctive reactive disorder recently observed in
the axillary lymph nodes of patients with breast carcinoma. This form of sinus
histiocytosis closely resembles and can easily be confused with metastatic
adenocarcinoma.
METHODS:
To determine the incidence
of this reactive process in lymph nodes from different anatomic sites, broaden
its morphologic spectrum, and discuss the differential diagnosis, the authors
examined lymph nodes from 316 radical prostatectomy specimens, 184 modified
radical mastectomy specimens, 108 colectomy specimens, 57 gastrectomy
specimens, and 27 radical hysterectomy specimens. These surgical procedures
were performed to treat carcinoma of the prostate, breast, colon, stomach, and
uterine cervix, respectively. A total of 9741 lymph nodes were histologically
examined. The lymph nodes containing sinus signet-ring cells were stained with mucicarmine, Alcian
blue, and periodic acid-Schiff stains (PAS). Immunostains for epithelial,
lymphoid, and histiocytic markers were also performed. In two cases, tissue was
retrieved from the paraffin block and subsequently processed for electron
microscopic examination.
RESULTS:
Only 4 of 316 radical
prostatectomy specimens (1.2%) and 2 of 184 axillary dissections (1.08%) contained
lymph nodes with signet-ring sinus histiocytosis. Of 9741 lymph
nodes reviewed, 37 (24 pelvic and 13 axillary lymph nodes) had signet-ring sinus
histiocytosis, for an incidence of 0.38%. Microscopically, the signet-ring histiocytes
lacked nuclear atypia and were mucin negative. In two cases, clusters of
histiocytes with rounded, eosinophilic, diastase resistant, PAS positive
cytoplasmic globules were observed. Both types of signet-ring cells showed
reactivity for histiocytic markers and were negative for cytokeratin and
lymphoid markers. By electron microscopy, most histiocytes were shown to have a
large empty vacuole that displaced the nucleus. Granular material was observed
in some of the vacuoles. Some histiocytes exhibited a rounded cytoplasmic body
composed of central electron dense, granular material and a rim of
microfibrils. No lipid droplets were identified.
CONCLUSIONS:
Signet-ring sinus
histiocytosis is a rare and distinctive reactive disorder found incidentally in
the pelvic and axillary lymph nodes of patients with carcinoma of the prostate
and breast, respectively. Although this histiocytic reaction mimics metastatic
adenocarcinoma andsignet-ring cell lymphoma,
it can be identified by careful cytologic analysis together with positive
reactivity for histiocytic markers, negative mucin stains, and lack of
reactivity for epithelial and lymphoid markers. The etiology and pathogenesis
of this unusual form of sinus histiocytosis remains unclear.

- 王军臣
胃发生的MALT也可呈现癌样印戒细胞。
Am
J Surg Pathol. 1996 May;20(5):588-98.
Carcinoma-like signet-ring cells in gastric
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma.
Zamboni G, Franzin G, Scarpa A, Bonetti F, Pea M, Mariuzzi GM, Menestrina F.
Source
Istituto di Anatomia Patologica,
Università di Verona, Italy.
Abstract
We noticed the presence of epithelial signet-ring cells (SRCs) in a proportion of primary gastric B-celllymphomas, and in some endoscopic biopsies we found it difficult to decide whether they represented an associated carcinoma. To evaluate the frequency and nature of this phenomenon, we reviewed 108 stomachs resected for primary lymphoma, including 70 mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) and 38 non-MALT lymphomas. We found SRCs, either isolated or grouped in clusters, in 26 of 70 MALT lymphomas. The SRCs were always localized in the superficial portion of the lamina propria and associated exclusively with lymphomatous areas. Isolated and scarce SRCs were also found in four of 22 cases of polyclonal atypical lymphoid hyperplasia. Our data suggests that SRCs occurring in gastric MALT lymphomas represent a particular type of LEL in which the foveolar cellsdisaggregated by the lymphomatous infiltration acquire a globoid, signet-ring appearance. These "foveolar" LELs are found in 37% of MALT lymphomas and are usually associated with the more classic and constant "neck" LELs, which are localized between the foveolae and mucopeptic glands. An awareness of the existence of the foveolar LEL may help avoid overdiagnosis of SRC carcinoma on gastric endoscopic biopsies.

- 王军臣
印戒细胞淋巴瘤也可发生在骨髓。
J Clin
Pathol. 1994 Feb;47(2):184-6.
Signet-ring cell lymphoma of bone marrow.
Talbot DC, Davies JH, Maclennan KA, Smith IE.
Source
ICRF Clinical Oncology Unit, Churchill Hospital, Headington,
Oxford.
Abstract
A case
of signet-ring cell lymphoma affecting bone marrow is
reported. The tumour presented as multiple lytic lesions in the lumbosacral
spine. A bone biopsy specimen showed the typical appearances
of signet-ring cell lymphoma, and the cells stained
positively with antiserum to CD20, though neither immunoglobulin light or heavy
chains could be shown within the vacuoles. The patient subsequently responded
to chemotherapy.

- 王军臣
印戒细胞淋巴瘤也可以是T细胞属性。
Acta Derm Venereol. 1993 Aug;73(4):255-8.
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma of signet ring cell type: a
specific clinico-pathologic entity.
Vaillant L, Monégier du Sorbier C, Arbeille B, de Muret A, Lorette G.
Source
Department of Dermatology, University
of Tours, France.
Abstract
We describe a new
case of signet ring cell peripheral T cell lymphoma in
a 45-year-old man. Thislymphoma had a very indolent course, since--without
treatment--the clinical staging has shown no evidence of disease progression 11
years after initial symptoms. Immunophenotype indicated pan T antigens (Leu 4
CD3, Leu 1 CD5) and T suppressor cytotoxic antigen (IOT8 CD8) expression.
Several T antigens (Leu 5b CD2, Leu 9 CD7, Leu 3a CD4) were not expressed. The
proliferation index was less than 5% with Ki 67 monoclonal antibodies. The
ultrastructural study showed characteristic cytoplasmic vacuoles containing
microvesicles. Five cases of signet ring T celllymphoma,
which were very similar to our case, have been previously described. Their
characteristics were primary cutaneous presentation, indolent course, good
response to current therapies and a long survival period. The indolent course
of these signet ring cell lymphomas may indicate that this
type oflymphoma is a low grade malignant lymphoma and not only a
morphological pattern.

- 王军臣
CD30+的T细胞淋巴瘤也可呈印戒细胞形态。
Histopathology. 1997
Jan;30(1):90-2.
CD30+
anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, null
type, with signet-ring appearance.
Falini B, Liso A, Pasqualucci L, Flenghi L, Ascani S, Pileri S, Bucciarelli E.
Source
Institutes of Haematology, University of Perugia, Italy.

- 王军臣
印戒细胞T细胞淋巴瘤的临床病理学报道。
J Clin Pathol. 1989 Mar;42(3):239-45.
Signet ring cell lymphoma of T cell type.
Source
Department of Histopathology, Christie
Hospital, Manchester.
Abstract
A rare variant of
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, signet ring lymphoma of T cell phenotype
(only the fourth to be reported) in a 75 year old man was studied by light
microscopy, immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy and gene rearrangement
studies. Ultrastructurally, a wider spectrum of cell size and nuclear
shape was observed in this case than in the previously recorded cases. The
morphology of the signet ring vacuoles was identical to that
found in the commoner B cell signet ring lymphoma of
clear vacuole type, and it is suggested that the vacuoles derive from
multivesicular bodies. The four cases reported so far have all presented with
skin disease, and the limited evidence available suggests that the prognosis
may be good.

- 王军臣
-
本帖最后由 海上明月 于 2013-09-20 19:35:24 编辑
T细胞性印戒细胞增生发生在皮肤,易误诊为真性组织细胞淋巴瘤。
Am
J Dermatopathol. 1987 Apr;9(2):120-8.
T-cell signet-ring cell proliferation
in the skin simulating true histiocytic lymphoma.
van der Putte SC, Toonstra J, Bruns HM, van Wichen DF, van Unnik JA, van Vloten WA.
Source
Institute of Pathology, University of
Utrecht, The Netherlands.
Abstract
We report the case of a solitary ulcerating lesion on the elbow of a 32-year-old man. Routine histopathological examination strongly suggested a histiocytic malignancy. However, electron-microscopical, enzyme-cytochemical, and immunological studies revealed that the "tumor" cells were T lymphocytes with an unusual (Leu 1+, Leu 3a+, Leu 4+, Leu 5b+, OKT4+, HLA-DR+, Ki-1+, Leu MI+) immunological phenotype and an even more uncommon morphology characterized by the development of giant multivesicular bodies giving some cells a signet-ring cell appearance, and autophagocytosis. The lesion healed spontaneously, notwithstanding its malignant histology.

- 王军臣