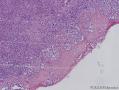
| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
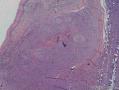
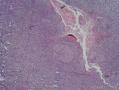
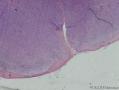
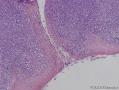
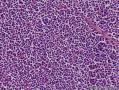
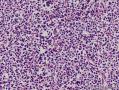
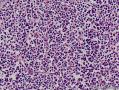
- 扁桃体肿物
Waldeyer's ring marginal zone B cell lymphoma: are the clinical and prognostic features nodal or extranodal? A study by the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL).
Oh SY, Kim WS, Kim JS, et al. Int J Haematol, 2012,96(5): 631-637
There has been controversy surrounding Waldeyer's ring (WR), especially focused on the question of whether it should be regarded as a nodal or an extranodal site. We conducted retrospective analyses of marginal zone B cell lymphomas involving WR (WR-MZLs) to observe their clinical features and prognosis, with specific regard to the nodal-or-extranodal question. A total of 52 patients with histological diagnosis of WR-MZL were retrospectively analyzed. The most common involvement site was the tonsil (40.4 %). Ann Arbor stage III/VI disease was present in 48.1 % (25 of 52). The response rate of the 27 stage I/II patients was 88.9 %, with 21 complete remissions and three partial remissions. The median time to progression (TTP) was 3.7 years (95 % CI 2.5-4.9 years). The estimated 5-year TTP and overall survival rates were 39.4 and 90.5 %, respectively. In a comparison with the historical data regarding extra-WR MALT lymphoma and nodal MZL (N-MZL), MALT lymphoma showed better TTP results than did WR-MZL and N-MZL (P < 0.001).
Tonsillar lesions of infectious mononucleosis resembling MALT type lymphoma. A report of two cases.
Kojima M, Kitamoto Y, Shimizu K, et al. Pathol Oncol Res. 2008,14(4):489-492.
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is an acute lymphoproliferative disorder that typically occurs in young patients and is usually caused by Epstein-Barr virus. We report here, two cases of tonsillar lesion of IM resembling marginal zone B-cell lymphoma mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) type. The patients consisted of an 18-year-old Japanese woman and a 36-year-old Japanese man. Both patients presented with tonsillar mass. Histologically, in one case, the tonsil showed diffuse proliferation of medium-sized lymphocytes. The medium-sized lymphocytes had round or slightly indented nuclei with a small solitary nucleoli and abundant clear cytoplasm and somewhat resembled monocytoid B-cells. In the remaining one case, the lymphoid follicles had hyperplastic germinal centers with ill-defined borders surrounded by a sheet-like proliferation of polymorphous infiltration showing a marginal zone distribution pattern. On high-power field, the interfollicular area was diffusely infiltrated by a polymorphous infiltrate of medium-sized lymphocytes with angulated nuclei somewhat resembling centrocyte-like cells, immunoblasts, plasma cells, plasmacytoid cells and histiocytes with or without epithelioid cell feature. However, there were no CD43+ B-cells in either lesion. Moreover, the polytypic nature of the B-cells was demonstrated by immunohistochemistry or polymerase chain reaction. Although MALT type lymphoma rarely affected young adults, notably, a number of cases have been reported in the tonsil. The present two cases indicated that acute IM should be added to the differential diagnosis for MALT type lymphoma in young adults.