| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- CP (1)
-
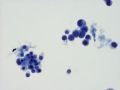
Figure 1 - Left lower corner shows a cluster of mesothelia with perfectly round nuclei, smooth nuclear membrane, and intermediate nucleocytoplasmic ratio. Right upper corner shows one, two- or five-cell clusters. These cells have large nucleoli and atypical features when compared with reactive mesothelia - much larger nuclei and irregular nuclear membranes. In addition, the five-cell cluster does not ball up like reactive mesothelia would.
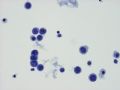
Figures 2 - Isolated or small clusters of atypical cells with large nuclei and irregular (clefted) nuclear membranes. Again, four cohesive cells form a slightly angulated but linear profile, something not commonly found in reactive mesothelia.
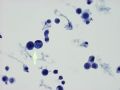
Figure 3 - Rare atypical cells (arrow) have cytoplasmic vacuoles that may or may not contain dot-like inspissated secretion.
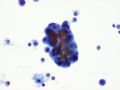
Figure 4 - A larger cluster of atypical cells with large and often eccentric nuclei.
This is a case of proven metastatic, low grade infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast. Malignant pleural effusion resulting from metastatic well differentiated adenocarcinoma of mammary or pulmonary origin may not be easy to detect by casual low power evaluation. Reactive mesothelia and inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils) are always present. Only with careful high power examination would one detect subtle cytologic atypia. One very helpful hint is the odd shapes of malignant cell clueters - often linear or angulated and not rounded like balled aggregates.

聞道有先後,術業有專攻