| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
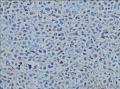
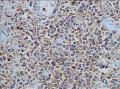
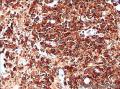
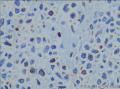
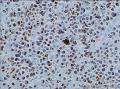
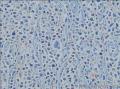
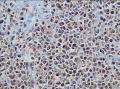
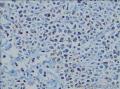
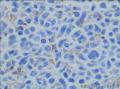
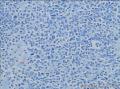
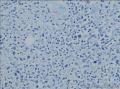
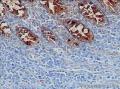
- 回盲部粘膜增厚
- Abstract
- Send to:
- Histopathology. 2015 Jan;66(1):112-36. doi: 10.1111/his.12596.
- Recent advances in intestinal lymphomas.
- Foukas PG1, de Leval L.
- Author information
- Abstract
- A large variety of lymphoma types may develop as primary intestinal neoplasms in the small intestines or, less often, in the colorectum. Among these are a few entities such as enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma or immunoproliferative small intestinal disease that, essentially, do not arise elsewhere than in the gastrointestinal tract. In most instances the primary intestinal lymphomas belong to entities that also occur in lymph nodes or other mucosal sites, and may show some peculiar features. In the case of follicular lymphoma, important differences exist between the classical nodal cases and the intestinal cases, considered as a variant of the disease. It is likely that the local intestinal mucosal microenvironment is a determinant in influencing the pathobiological features of the disease. In this review we will present an update on the clinical, pathological and molecular features of the lymphoid neoplasms that most commonly involve the intestines, incorporating recent developments with respect to their pathobiology and classification. We will emphasize and discuss the major differential diagnostic problems encountered in practice, including the benign reactive or atypical lymphoid hyperplasias, indolent lymphoproliferative disorders of T or natural killer (NK) cells, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-related lymphoproliferations.
- © 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- KEYWORDS:
- diagnosis; indolent lymphoproliferations; intestines; lymphomas; pathology
- PMID: 25639480 [PubMed - in process]
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Google+
Recent advances in intestinal lymphomas.
Abstract
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
KEYWORDS:
diagnosis; indolent lymphoproliferations; intestines; lymphomas; pathology

朱正龙
An unusual enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma with MYC translocation arising in a Japanese patient: a case report.
Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL) is a rare peripheral T-cell lymphoma classified into 2 types, with or without celiac disease, based on histology. Type 2 EATL is less commonly associated with celiac disease, in which cells are characterized by being monomorphic and small- to medium-sized. Cells are characterized by CD8 and CD56 expression and c-MYC oncogene locus gain. We present an atypical case of type 2 EATL in the jejunum, with human T-lymphotropic virus-1 that was CD4- CD8+ CD56- CD30- CD25- TIA-1+ and granzyme B+ on immunohistological staining. It also displayed translocation of chromosome 8p24 (c-MYC), as determined by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Mucosal spreading and intraepithelial invasion by lymphoma with villous atrophy were detected adjacent to the mucosal layer. The lymphoma may be derived from intraepithelial CD8+ T cells, similar to celiac disease.

朱正龙
An unusual presentation of EATL type 1: Emergency surgery due to life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding.
Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL) is a very rare malignancy. Reasons for hospital admission are variable.76 years old man admitted to emergency service with sudden and massive obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. There was no complaints in his history. After initial evaluation, emergency laparatomy had to be done. Bleeding lesion in proximal jejunum was resected. Histopathologically, the muscularis propria had abundant atypical lymphoid infiltrate in diffuse pattern. Atypical lymphoid cells expressed CD3 and CD30. The jejunal mucosa adjacent to the tumor showed effacement of normal villous architecture.EATL is known to cause anemia as a result of chronic bleeding. However in this case, the bleeding was abundant, irreplaceable and requiring emergency surgery. To our knowledge it is not reported previously.A sudden and massive gastrointestinal bleeding can be the first and unique sign of EATL.

朱正龙
Ⅱ型肠病相关性T细胞淋巴瘤的临床病理观察
目的 探讨Ⅱ型肠病相关性T细胞淋巴瘤(Ⅱ型EATL)的临床病理特点、免疫表型、诊断、鉴别诊断以及预后.方法 对南京军区南京总医院病理科收集的14例Ⅱ型EATL患者临床资料、组织学、免疫组织化学进行观察分析并随访,结合文献讨论.结果 14例Ⅱ型EATL患者,男性12例、女性2例,中位年龄49岁,发生部位:空回肠(10例)、结肠(4例).临床主要表现为腹部肿块或腹痛、腹泻等肠道症状,可伴有发热、盗汗、消瘦等消耗性疾病的共同特点,均无麦麸过敏及乳糜泻的临床证据.镜下肿瘤细胞常呈透壁性浸润肠壁全层,瘤细胞核圆形,深染,胞质淡染,间质缺乏炎性背景,伴或不伴坏死;病变及其附近可见肠绒毛萎缩,隐窝增生,上皮内淋巴细胞增多.免疫表型瘤细胞表达CD3、CD43、CD8(14/14),CD56(11/14)、CD30(2/14)部分瘤细胞阳性,CD4、CD20、CD79a、髓过氧化物酶、EB病毒均阴性,Ki-67阳性指数高.EBER原位杂交均阴性.9例获得随访结果(6~36个月),其中7例在14个月内死亡.结论 Ⅱ型EATL患者,以肿瘤细胞累及肠道以至肠穿孔为特点,缺乏乳糜泻等肠病证据.诊断要结合临床表现和相关病史,并依据病理学特征及相关的免疫组织化学标志物综合判断而确诊.

朱正龙
273例肠道原发性非霍奇金淋巴瘤临床病理学研究
目的 探讨肠道原发性非霍奇金淋巴瘤(PINHL)的临床病理学特征及预后因素.方法 收集确诊的273例PINHL患者资料,分析临床病理学特点、诊断情况及预后影响因素.结果 273例患者中男女比例为2.3∶1,中位发病年龄为46(2~85)岁,B细胞淋巴瘤组以腹部包块多见,而T细胞淋巴瘤组以穿孔、下腹疼痛及B症状更为常见.病变部位以回盲部最多见(30.4%).肠镜活检确诊率为90.3%.病理学分型:B细胞淋巴瘤232例(85.0%),以弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤,非特指型(DLBCL,NOS)最为多见(48.4%);T细胞淋巴瘤41例(15.0%),以肠病相关性T细胞淋巴瘤最为多见(36.6%).获得完整随访资料者245例,B细胞淋巴瘤组患者预后明显好于T细胞淋巴瘤组(P<0.05),手术对于患者整体生存率无明显影响,但对于侵袭性淋巴瘤患者可以提高其生存率.结论 国人PINHL以B细胞淋巴瘤多发,T、B细胞淋巴瘤患者具有不同的临床特点.肠镜活检是较好的确诊方法.B细胞淋巴瘤患者预后明显好于T细胞淋巴瘤,侵袭性淋巴瘤患者可能从手术中获益.

朱正龙



















 加入收藏夹
加入收藏夹 


















