| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
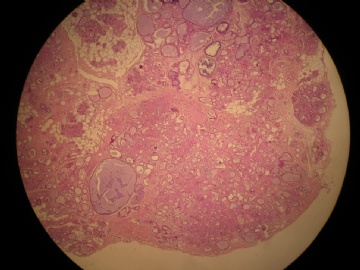
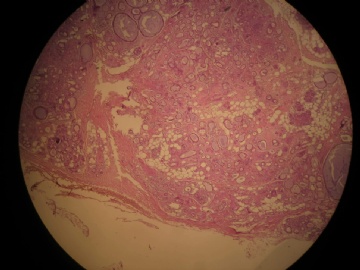
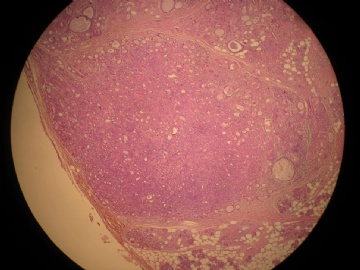
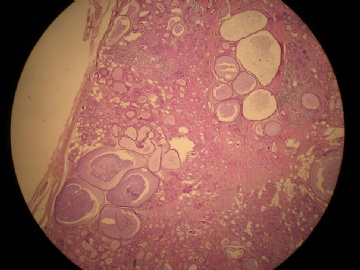
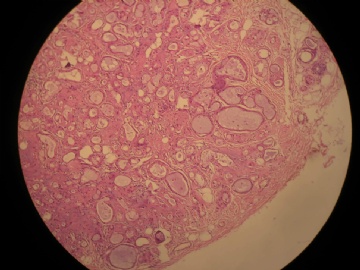
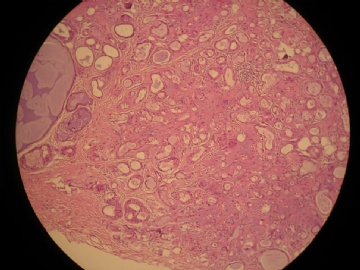
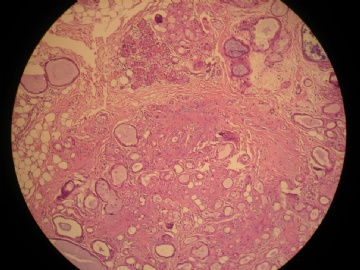
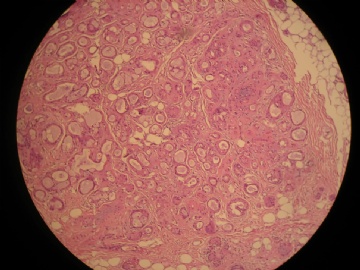
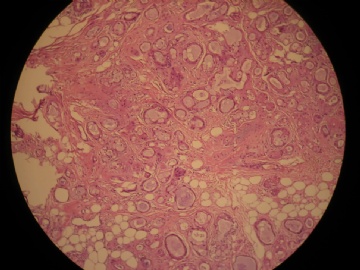
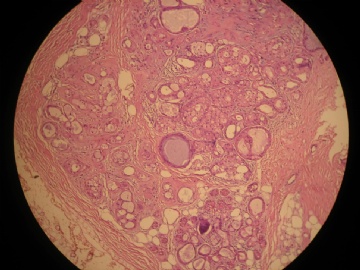
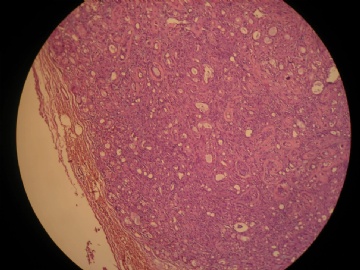
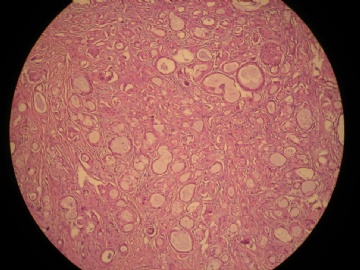
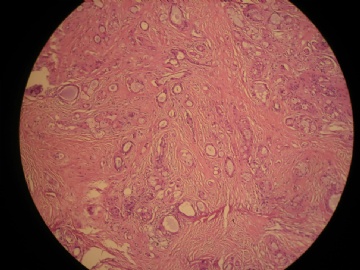
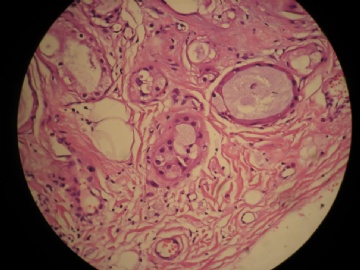
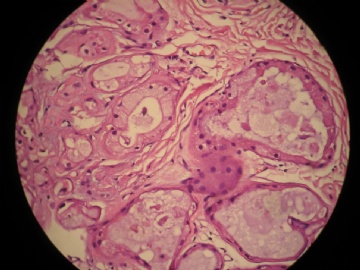
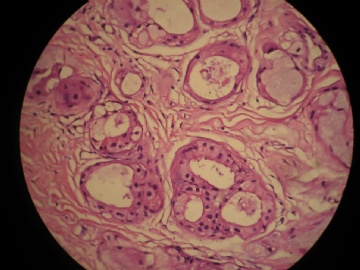
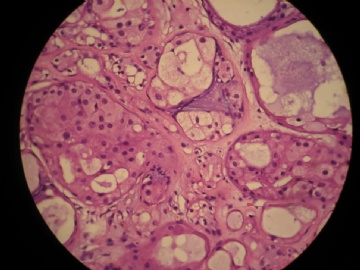
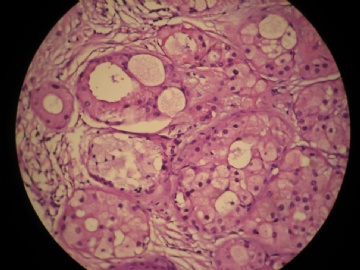
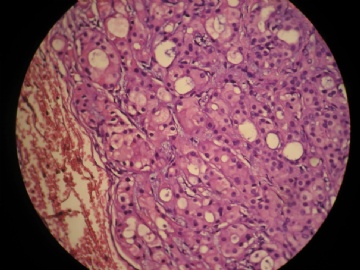
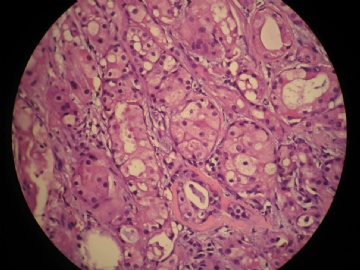
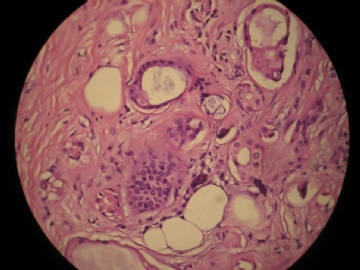
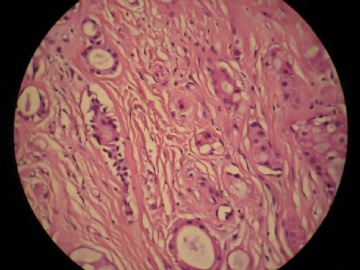
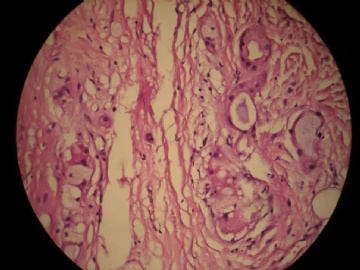
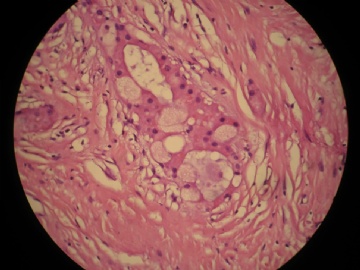
- 女,29岁,发现右耳垂下肿物2年余(PT11-11943)
女,29岁,发现右耳垂下肿物2年余。
行右腮腺切除+右腮腺肿物切除术。
大体:腮腺肿物一枚,5*4*2cm,切面灰白略灰黄,质韧。
我们考虑粘液表皮样癌?低级别腺癌NOS?
请老师们教导,谢谢!
-
本帖最后由 城北 于 2011-08-04 13:30:26 编辑
-
yumaoqiu715 离线
- 帖子:227
- 粉蓝豆:26
- 经验:356
- 注册时间:2008-06-05
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
lantian0508 离线
- 帖子:1250
- 粉蓝豆:42
- 经验:1495
- 注册时间:2007-08-01
- 加关注 | 发消息
|
谢谢Dr.PTAH提供这个好的病例! 谢谢Dr.TK1905的诊断提示和提供一系列相关资料信息! 唾腺的硬化性多囊性腺病(Sclerosing polycystic adenosis,SPA)的确有可能被误诊为腺癌(如腺样囊性癌、粘液表皮样癌和腺泡细胞癌)。 学习Dr.TK1905提供的文献资料,受益如下: 1)SPA可发生在大唾腺和小唾腺。生长较缓慢;巨检:肿块境界清晰,可呈多结节状,但不形成完整的包膜; 2)主要由扩张的导管结构和纤维性间质构成,致密纤维组织常围绕唾腺小叶和导管结构,保留有小叶的构筑; 3)囊状扩张导管间有筛状腺泡,胶原性间质在其间顺势分布; 4)导管上皮具有不同的细胞形态表型:(1)大汗腺样;(2)腺泡状(细胞浆内含有嗜酸性颗粒,具有明显的核仁);(3)空泡状;(3)皮脂腺样。甚至有黏液样表观,胞浆偏碱性,等等;局灶可有鳞状化生;囊状扩张导管可现实囊内乳头状增生、细胞桥。有的显示显示筛状结构;腺体致密区和实性巢可显示细胞异型增生; 5)免疫组化肌上皮标记显示SMA、MSA、Calponin阳性,肌上皮层完整环绕导管的小叶腺泡;标记ER和PR阳性; 6)不同程度的慢性炎细胞浸润,可见黄色瘤样组织细胞浸润局灶; 7)文献报道有的病例其中有导管原位癌,有的有浸润癌; 8)肿块手术切净后随访显示,30%病例完全治愈,但有部分病例复发,提示本病可能具有肿瘤的潜能,甚至可进展转化为癌; 9)克隆性分析显示,本病具有雄激素受体(AR)多态性,提示本病为肿瘤性质,而不是反应性增生。 10)病因和发病机制目前尚不清楚,ER、PR阳性提示其发病可能与激素刺激有关;有报道EBV病毒检测阳性,是否与病毒感染相关。其发病机制和肿瘤属性有待于进一步研究。 |

- 王军臣
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the salivary gland: a report of 16 cases.
Source
Brown University School of Medicine, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI 02903, USA. DGnepp@Lifespan.org
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis is a recently described, extremely rare, reactive, sclerosing, inflammatory process somewhat similar to fibrocystic changes and adenosis tumor of the breast. To date, there have been 22 cases described in the literature. Because of the infrequency of this lesion, we describe our combined experience with 16 cases, 1 of which has been previously reported. Thirteen tumors arose in the parotid gland, two involved the submandibular gland, and one arose in the buccal mucosa. There were 9 men and 7 women. Patients ranged in age from 9 to 75 years. Fourteen patients presented with a primary mass. Two were incidental findings in patients with a mixed tumor and an oncocytoma. Tumors ranged in size from 0.3 to 6 cm in greatest dimension. They are typically well circumscribed and are composed of densely sclerotic lobules with prominent cystic change. Hyperplasia of ductal and acinar elements and areas of apocrine-like metaplasia are frequent. Foci with mild ductal epithelial atypia were frequent with >50% of cases demonstrating at least focal areas of duct epithelial hyperplasia with atypia. Follow-up ranged from 1.5 to 40 years. One tumor recurred twice; no patient has developed metastases or died of disease.
Clonal nature of sclerosing polycystic adenosis of salivary glands demonstrated by using the polymorphism of the human androgen receptor (HUMARA) locus as a marker.
Source
Department of Pathology, Medical Faculty Hospital, Charles University, Plzen, Czech Republic. skalova@fnplzen.cz
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis (SPA) is a recently described, rare lesion of the salivary glands that bears a resemblance to epithelial proliferative lesions of the breast. The true nature of the lesion is unknown, but up to now it has been generally believed to represent a pseudoneoplastic sclerosing and inflammatory process. However, local recurrence developed in about one-third of the cases. Superimposed dysplastic changes ranging from low-grade dysplasia to carcinoma in situ were described in SPA. Although no metastases-related and/or disease-related patient deaths were documented, these clinical and histopathologic features raise the possibility that SPA might represent a neoplastic lesion. Polymorphism of the human androgen receptor locus is most frequently used to assess whether the pattern of X-chromosome inactivation is random or nonrandom, the latter strongly indicating clonality. In this study, the assay was applied to tissue from 12 examples of SPA. Three cases (males) were noninformative and 3 cases (females) could not be analyzed owing to poor quality of DNA, but all the remaining 6 lesions satisfied the criteria for monoclonality. We therefore conclude that the findings in the present study are further supporting evidence that SPA is a neoplasm, and not just a reactive process.
Adv Anat Pathol. 2003 Jul;10(4):218-22.
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the salivary gland: a lesion that may be associated with dysplasia and carcinoma in situ.
Source
Dept. of Pathology, 593 Eddy St., Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, Rhode Island 02905, USA.
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis is a recently described, extremely rare, reactive sclerosing inflammatory process somewhat similar to adenosis tumor of the breast. To date, 31 cases have been described in the literature. Twenty-seven tumors involved the parotid gland, two involved the submandibular gland, and two arose within the oral cavity in minor salivary gland sites. Patients ranged in age from 9 to 80 years, with an approximate 2.5:1 female-to-male incidence. Primary tumors range in size from 1 to 7 cm in greatest dimension, are typically unencapsulated, and are composed of densely sclerotic lobules with prominent cystic change. Hyperplasia of ductal and acinar elements and areas of apocrine-like metaplasia are typical. Foci with dysplasia of ductal epithelium ranging from mild dysplasia to occasional cases with carcinoma in situ are moderately frequent. Invasive carcinoma has not been reported in these patients. Tumors in 5 (29%) of the 16 patients with follow-up have recurred. To date, no patients have developed metastases or have died from disease.
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of minor salivary glands: report of three cases and review of the literature.
Source
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Boston University School of Dental Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis (SPCA) of the salivary gland is a rarely encountered lesion of uncertain pathogenesis that shares histologic features with sclerosing adenosis and fibrocystic disease of the mammary gland. To date, fewer than 40 cases of SPCA have been reported in the literature; all but one have arisen in the major salivary glands. We report 3 cases of SPCA involving minor salivary glands and discuss the characteristic histopathologic features of SPCA , which include a combination of fibrosis, tubuloacinar proliferation, and cystic change with retention of a somewhat lobular architecture. We also provide a review of contemporary relevant literature. Given that SPCA has been mistaken for malignant salivary gland neoplasia, a familiarity with the entity is critical. Three new cases of SPCA involving minor glands are added to 1 existing case in the literature to raise awareness of the lesion and to reduce the likelihood of misdiagnosis.
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the buccal mucosa.
Source
Division of Oral Pathology, School of Oral Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Private Bag 3, Johannesburg, WITS 2050, South Africa. shabnum.meer@nhls.ac.za
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis (SPA) is a rare lesion of salivary glands with a striking resemblance to fibrocystic disease of the breast. Most of the 47 reported cases have occurred within the parotid gland, with only a single case being described within the buccal mucosa. We report an additional case of SPA of the buccal mucosa. The exact nature of this entity is unknown, but has up until recently believed to be a pseudoneoplastic reactive and inflammatory sclerosing process. Even though SPA has satisfied the criteria for monoclonality, the debate as to whether SPA represents a true neoplasm or a pseudoneoplastic inflammatory sclerosing process, with low-grade neoplastic potential continues. Awareness of the occurrence of this lesion in both major and minor salivary glands is important to promote its differentiation from other more sinister salivary gland pathology. Cure is effected by localized surgical excision and all reported cases of SPA show an excellent prognosis with no true recurrence or metastasis.
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the parotid gland: report of one case diagnosed by fine-needle cytology with in situ malignant transformation.
Source
S.S.D. di Citopatologia, A.F. di Anatomia Patologica e Citopatologia, 80131 Naples, Italy. franco.fulciniti@gmail.com
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis (SPA) is a rare pathological condition affecting the salivary glands, first described by Smith etal. in 1996. Even though this lesion is being increasingly diagnosed, less than 50 cases have been published in the world literature to date. In line with numerous other pathological analogies between breast and salivary gland lesions, SPA shares with fibrocystic disease of the breast many histopathological features, i.e., fibrosis, oncocytic (apocrine) changes, hyperplasia of ductal and acinar epithelium, cystic dilation of ducts, and, often, atypical epithelial changes. Most of the described cases have followed a benign clinical course, despite the frequent possibility of atypical hyperplasia in more than 50% of the cases and of the more than occasional in situ malignant transformation. In this article, we introduce a new case occurring in the parotid gland of a 57-year-old male showing atypical epithelial hyperplasia and low-grade in situ mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Fine-needle cytology (FNC) was performed on the lesion and, when a diagnosis of SPA was prospected, the variegated cytological features of the obtained sample posed several differential diagnostic problems. The spectrum of pathological lesions entering differential diagnosis comprised sebaceous adenoma, Warthin's tumors with presence of sebaceous remnants, and low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Histopathological examination disclosed SCA with intraductal neoplastic transformation resembling noninvasive low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma. The cytological diagnosis of SPA should be entertained whenever a polymorphous picture is found on FNC samples comprising oncocytic/apocrine changes, sebaceous cells, cystic background, and epithelial hyperplasia with low-grade cytological atypias.
The pathogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in sclerosing polycystic adenosis.
Source
Division of Oral Pathology, Department of Biomedical Dental Sciences, College of Dentistry, Dammam University, Dammam 1982-31441, Saudi Arabia. wmswelam@gmail.com <wmswelam@gmail.com>
Abstract
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis (SPA) is a pathology of the salivary gland which occurs infrequently and has a controversial etiology. In this study, we investigated the possible roles of HPV and EBV in the pathogenesis of SPA. Archived cases of salivary gland lesions were retrieved, and their diagnoses were re-evaluated; cases that fit the diagnosis of SPA were selected and subjected to Alcian Blue-Periodic Acid Schiff's histochemical staining and immunohistochemical staining for HPV-1, EBV, S-100, and Bcl-2 proteins in addition to the proliferative marker Ki-67. In addition, RNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues was subjected to RT-PCR to confirm any positive immunohistochemical results. Co-localization of EBV and Bcl-2 in lesional cells was the most striking finding; Ki-67 was expressed in basal cells, while no expression was seen in the adjacent salivary gland cells. Our EBV (+) ve immunostaining results were confirmed by RT-PCR using RNA extracted from paraffin sections. Our results suggest a significant pathogenic role of EBV in SPA. Moreover, they provide new evidence on the neoplastic nature of SPA.
Sclerosing Polycystic Adenosis of the Parotid Gland: Report of a Bifocal, Paucicystic Variant with Ductal Carcinoma in situ and Pronounced Stromal Distortion Mimicking Invasive Carcinoma.
Source
Department of Pathology, National University Health System, 5 Lower Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, 119074, Singapore, fredrikpetersson@live.se.
Abstract
We present a case (female patient, age 45 years) with a bifocal, paucicystic variant of sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the parotid gland with cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and pronounced stromal distortion affecting the in situ component to such an extent that it gave a distinct impression of intralesional invasive adenocarcinoma. P63-and calponin-positive myoepithelial cells were present in the periphery of the acini and ducts in the benign component, somewhat discontinuously in the DCIS-component, and even in the periphery of the small irregular atypical cell nests that appeared infiltrative on the haematoxylin and eosin stained sections. Strong cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for GCDFP-15 was detected in the benign component with a variable, patchy and mostly weak positivity in the DCIS. More than 90% of the cells in the DCIS component displayed strong nuclear immunoreactivity for androgen receptors and 10% of the benign ducts showed positivity. Weak to moderate nuclear immunoreactivity for estrogen receptors was seen in 30% of cells in the benign ductal component whereas the DCIS was negative. Occasional cells in the adenosis-component were weakly positive for PR. The proliferative activity (Mib-1/Ki-67) was low (1-2%) in the benign component whereas increased proliferation was seen in the DCIS and in the areas with pseudoinfiltration which also featured atypical mitoses.