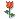| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
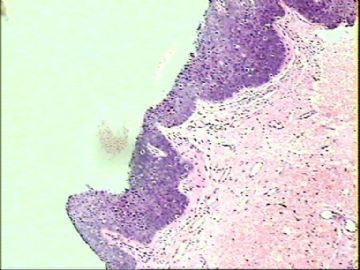
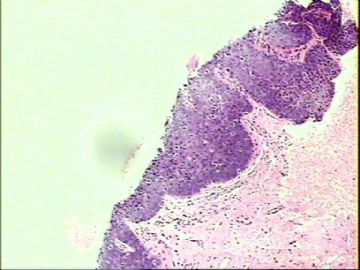
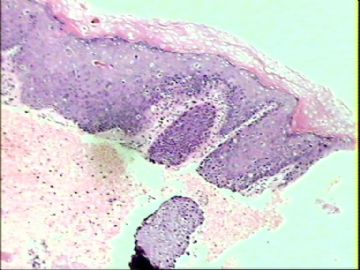
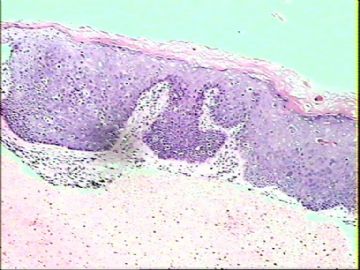
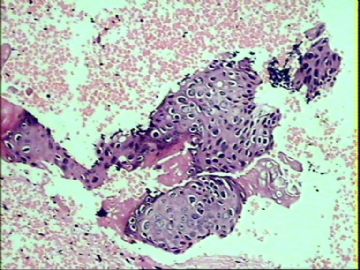
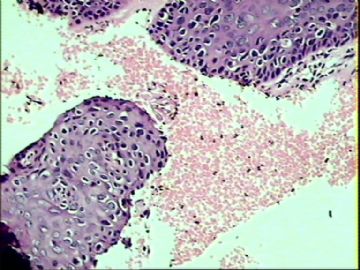
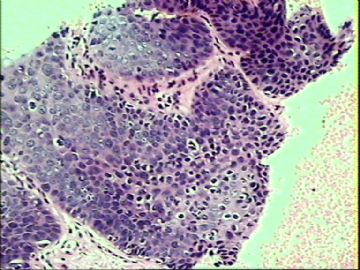
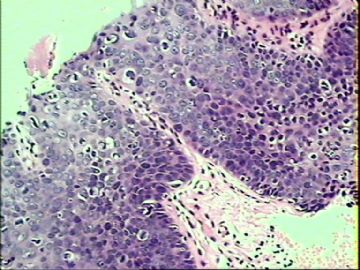
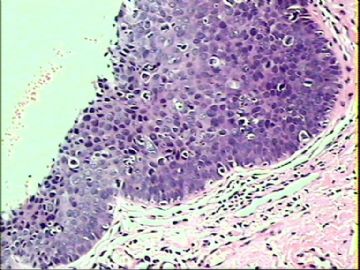
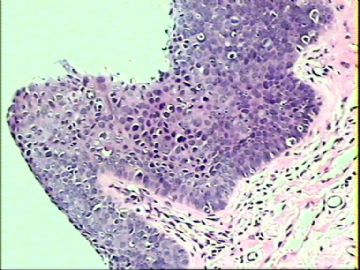
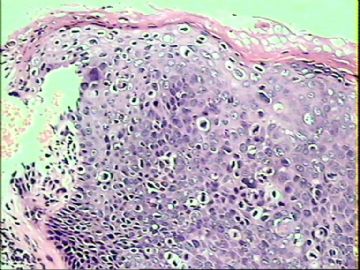
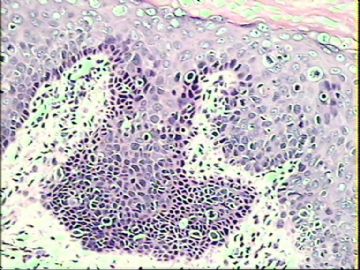
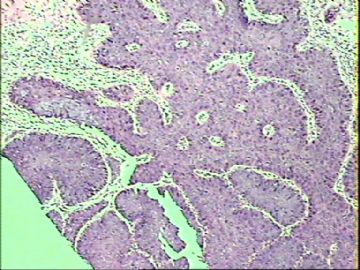
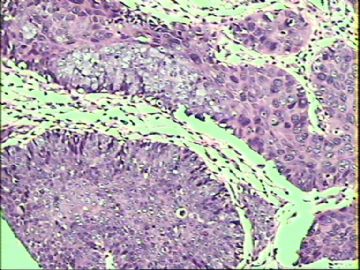
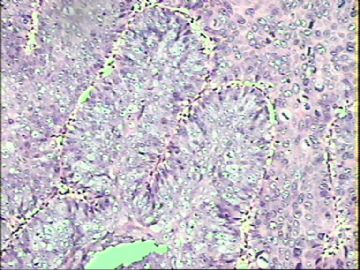
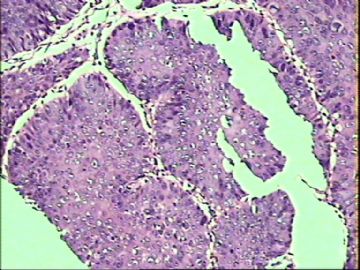
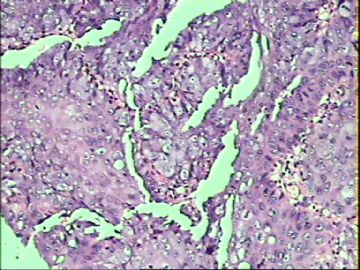
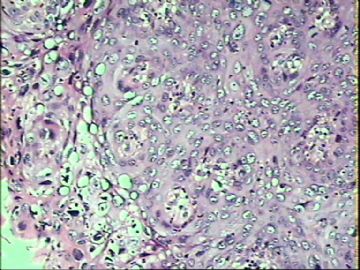
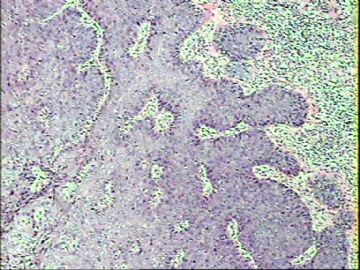
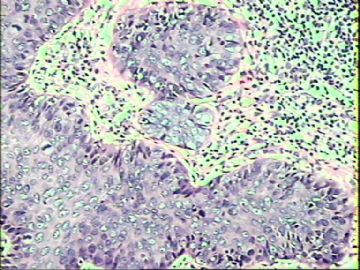
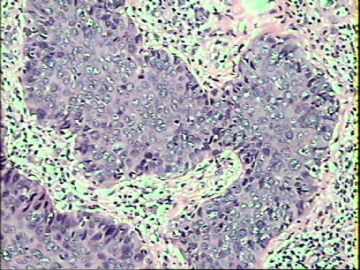
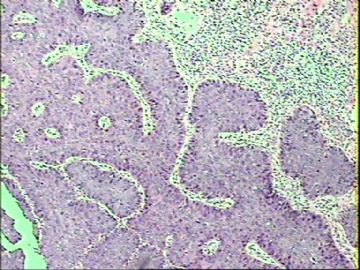
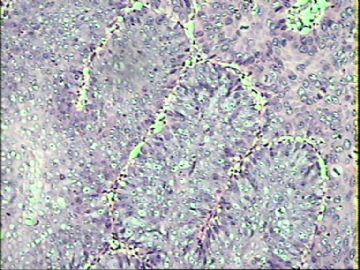
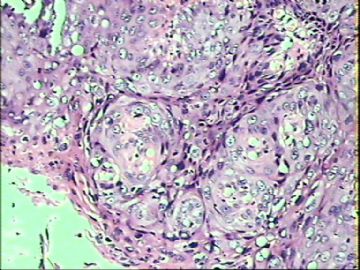
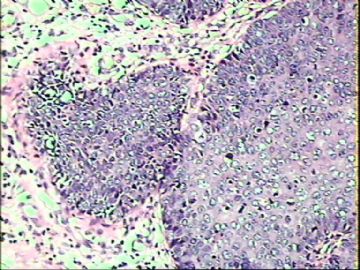
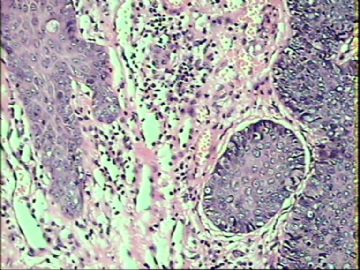
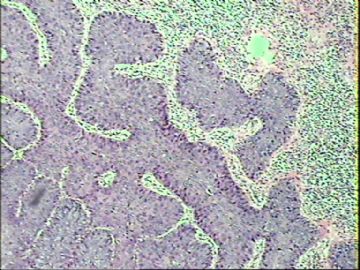
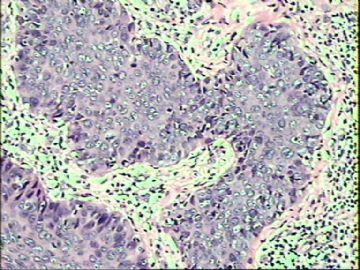
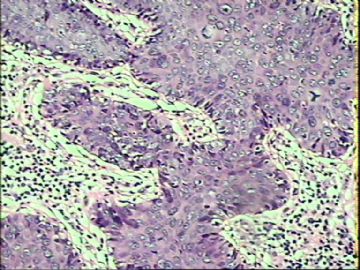
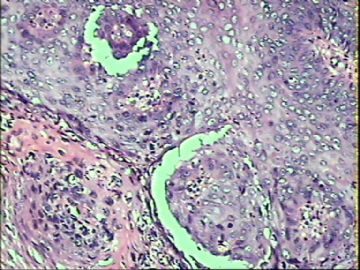
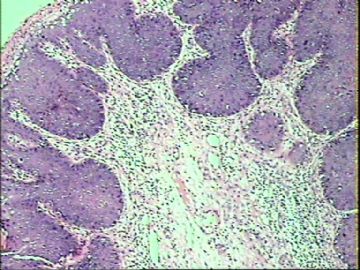
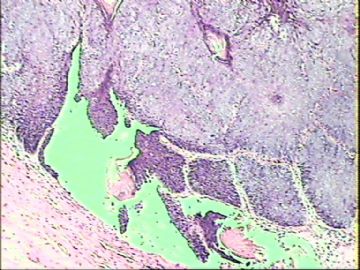
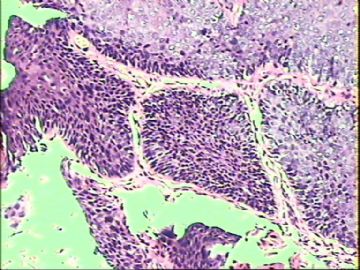
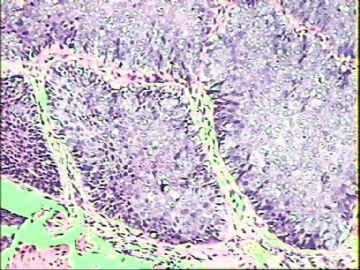
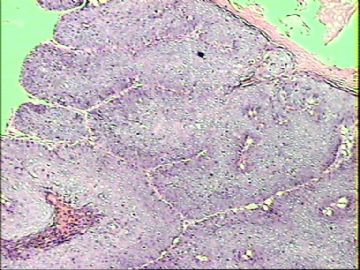
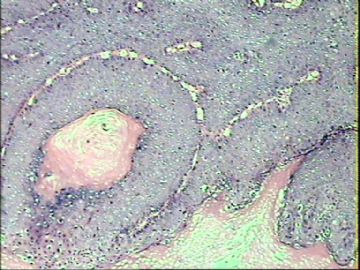
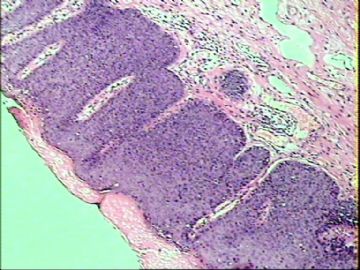
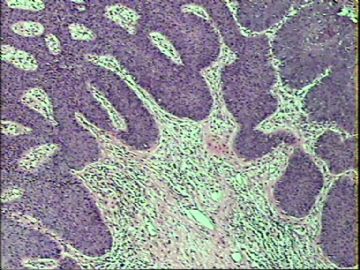
- ‘外阴白斑’活检1例(VINIII第二次手术标本病理会诊报告 2010-09-29)
| 以下是引用mingfuyu在2010-9-23 8:30:00的发言:
Agree with VIN 2-3. You can do mucin stain to exclude extramammary Paget's disease, and do melanoma markers to exclude melanoma in-situ. VIN is a little different from CIN: VIN occurs in skin, could be caused by HPV infection and non-HPV infection (for example p53 mutation), CIN is caused by HPV. Especially in older women, there is a type of high grade VIN (differentiated VIN) is not caused by HPV. |
Great!!


- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-09-23 12:02:00 编辑
| 以下是引用一棵小草在2010-9-20 22:59:00的发言: 是外阴粘膜白斑发展而来的原位癌? |
现在已不主张用外阴白斑(leukoplakia of vulva)这一术语,代之为外阴营养不良(vulvar dystrophies)或外阴白色病变(white lesions of the vulva)
.它可能是一组原因不明的非感染性炎性疾病或多种原因引起的局部营养代谢障碍疾病。根据病程可分类为1、非特异性外阴炎;2、萎缩性硬化性苔藓;3、神经性皮炎;4、白色角化病。
它们均可继发表皮的非典型性增生,甚至癌变。
VIN3这一类多为高危性HPV(H16、H18等)感染所致。我们在本例上述的组织图像中也可以看到有明显的HPV感染导致的上皮内细胞的改变。



- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。
-
pathologygz 离线
- 帖子:139
- 粉蓝豆:5
- 经验:182
- 注册时间:2009-05-05
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
pathologygz 离线
- 帖子:139
- 粉蓝豆:5
- 经验:182
- 注册时间:2009-05-05
- 加关注 | 发消息
Review for Vulvar Cancer
Types
Squamous cell carcinoma
The vast majority of vulvar cancer (approximately 90%)[2] is caused by squamous cell carcinoma, which originates from the epidermis of the vulva tissue. Carcinoma-in-situ is a precursor stage of squamous cell cancer prior to invading through the basement membrane. Most lesions originate in the labia, primarily the labia majora. Other areas affected are the clitoris, and fourchette, and the local glands. While the lesion is more common with advancing age, younger women who have risk factors (v.i.) may also be affected. In the elderly treatment may be complicated by the interference of other medical conditions.
Squamous lesions tend to be unifocal, growing with local extension, and spreading via the local lymph system. The lymphatic drainage of the labia proceeds to the upper vulva and mons, then to the inguinal and femoral nodes with both superficial and deep lymph nodes. The last deep femoral node is called the Cloquet’s node; spread beyond this node affects the lymph nodes of the pelvis. The tumor may also invade adjacent organs such as the vagina, urethra, and rectum and spread via their lymphatics.
A verrucous carcinoma of the vulva is a subtype of the squamous cell cancer and tend to appear as a slowly growing wart.
Melanoma
About 5% of vulvar malignancy is caused by melanoma of the vulva. Such melanoma behaves like melanoma in other locations and may affect a much younger population. Contrary to squamous carcinoma, melanoma has a high risk of metastasis.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma affects about 1-2% of vulvar cancer is a slowly growing lesion and affects the elderly. Its behavior is similar to basal cell carcinoma in other locations that is it tends to grow locally with a low potential of deep invasion or metastasis.
Other lesions
Vulvar cancer can be caused by other lesions such as adenocarcinoma or sarcoma.

- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。
| 以下是引用pathologygz在2010-9-28 9:16:00的发言: VIN就是高级别,没有VIN1了 |
Good point.
Basaed on the new calssification, we sign out VIN lesion as below.
Guide for signing out VIN cases according to new ISSVD Classification:
|
Histology |
Final Diagnosis |
Comment |
|
VIN-1 |
SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH ATYPIA, CONSISTENT WITH HPV-RELATED CHANGES |
The above lesion is equivalent to vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia 1(VIN-1) lesion according to the old classification scheme. The new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification no longer includes “VIN-1” as a type of VIN. This is due to lack of evidence that “VIN-1” is a cancer precursor lesion. References: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. J Reprod Med. 2005;50:807-10. |
|
VIN-2 or VIN-3 |
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL WARTY TYPE.
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL BASALOID TYPE.
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), USUAL MIXED (WARTY/BASALOID) TYPE. |
The above diagnosis is based on the new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification of vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia (VIN). The above lesion is equivalent to VIN-2 (or VIN-3) according to the old classification scheme. Reference: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. |
|
VIN-differentiated type |
VULVAR INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA (VIN), DIFFERENTIATED TYPE. |
The above diagnosis is based on the new International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) classification of vulvar intra-epithelial neoplasia (VIN). The risk of progression to invasion seems greater in differentiated VIN than in usual VIN. References: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:46-47. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2001;20:16-30. |
J Reprod Med. 2005 Nov;50(11):807-10.
Squamous vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: 2004 modified terminology, ISSVD Vulvar Oncology Subcommittee.
Sideri M, Jones RW, Wilkinson EJ, Preti M, Heller DS, Scurry J, Haefner H, Neill S.
European Institute of Oncology, Milan, Italy.
Abstract
In the current classification, squamous vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is categorized as VIN 1, 2 and 3 according to the degree of abnormality. There is neither evidence that the VIN 1-3 morphologic spectrum reflects a biologic continuum nor that VIN 1 is a cancer precursor. The VIN 2 and 3 category includes 2 types of lesion, which differ in morphology, biology and clinical features. VIN, usual type (warty, basaloid and mixed), is HPV related in most cases. Invasive squamous carcinomas of warty or basaloid type is associated with VIN, usual type. VIN, differentiated type, is seen particularly in older women with lichen sclerosus and/or squamous cell hyperplasia in some cases. Neither VIN, differentiated type, nor associated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma is HPV related. The term VIN should apply only to histologically high grade squamous lesions (former terms, VIN 2 and VIN 3 and differentiated VIN 3). The term VIN 1 will no longer be used. Two categories should describe squamous VIN: VIN, usual type (encompassing former VIN 2 and 3 of warty, basaloid and mixed types) and VIN, differentiated type (VIN 3, differentiated type).
| 以下是引用cqzhao在2010-9-29 1:52:00的发言:
|

 谢谢赵老师经典话语。
谢谢赵老师经典话语。

- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。