| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 系统学病理及英语病理学之一
1a Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by patchy fibrous replacement of whole lobules or parts of lobules, focal fat necrosis in different stages, and chronic inflammation. Grossly, depending on the etiology and degree of injury, the gland may be slightly firm but have a normal outline, lobular pattern, and color. Severe cases may be smaller than normal, bosselated, rock-hard, and display foci of fat necrosis, calcification, or fully developed calculi.
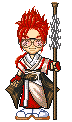
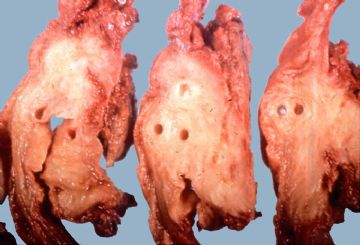
Gross: This chronically inflamed pancreas is small and scarred. The dilated pancreatic duct contains a stone (arrow). Chronic Pancreatitis with stone
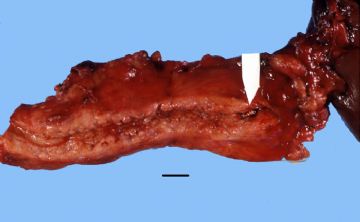
onmouseover="showMenu(this.id, 0, 1)"> X-ray: This is an example of chronic pancreatitis with marked calcification of the pancreatic parenchyma. This calcification could be demonstrated by an x-ray of the abdomen.
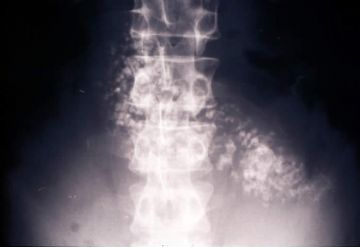
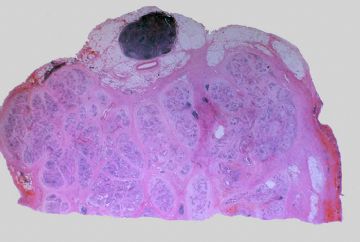
onmouseover="showMenu(this.id, 0, 1)"> Gross: These are cross sections taken through the head of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis. The sections of pancreas which you have in your class sets were taken in a similar fashion. Notice that the dense white fibrous scarring has almost totally obliterated the lobular architecture of the pancreas.
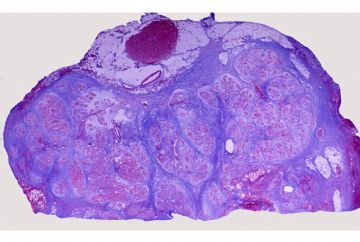
onmouseover="showMenu(this.id, 0, 1)"> This is a low magnification picture of the H&E slide of chronic pancreatitis in your class set. This particular patient had an obstructive type of pancreatitis due to carcinoma of the head of the pancreas. The lobular architecture of the pancreas is accentuated by broad bands of interstitial fibrosis.
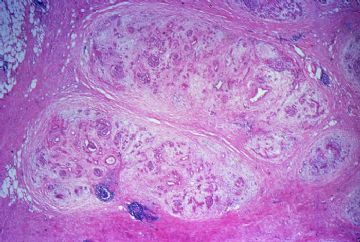
onmouseover="showMenu(this.id, 0, 1)"> The fibrous scarring of the pancreas is highlighted with the Trichrome stain. The fibrous septa appear as blue bands surrounding the residual pancreatic lobules, which stain red.
The fibrous scarring of the pancreas is highlighted with the Trichrome stain. The fibrous septa appear as blue bands surrounding the residual pancreatic lobules, which stain red. Shows the dense interstitial fibrosis surrounding two pancreatic lobules. Note there is also an increase in intralobular fibrous tissue and there is chronic inflammation.
Shows the dense interstitial fibrosis surrounding two pancreatic lobules. Note there is also an increase in intralobular fibrous tissue and there is chronic inflammation.
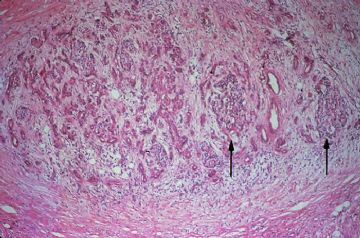
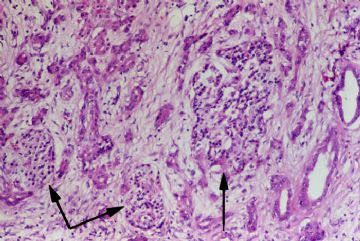
onmouseover="showMenu(this.id, 0, 1)"> The exocrine portion of the gland is most severely affected. There is almost total atrophy and fibrous replacement of pancreatic acini with relative preservation of the pancreatic ducts and islets of Langerhans (arrows). The intralobular pancreatic ductules are irregularly shaped and are embedded in chronically inflamed fibrous tissue. Several preserved islets are marked with arrows
The exocrine portion of the gland is most severely affected. There is almost total atrophy and fibrous replacement of pancreatic acini with relative preservation of the pancreatic ducts and islets of Langerhans (arrows). The intralobular pancreatic ductules are irregularly shaped and are embedded in chronically inflamed fibrous tissue. Several preserved islets are marked with arrows
Higher magnification shows preservation of the islets of Langerhans to better advantage (arrows).

- 赚点散碎银子养家,乐呵呵的穿衣吃饭