| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 食管癌病理类型?
-
liguoxia71 离线
- 帖子:4174
- 粉蓝豆:3122
- 经验:4677
- 注册时间:2007-04-01
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-05-06 12:12:00 编辑
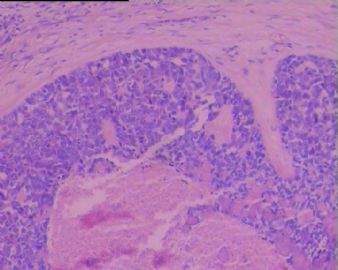
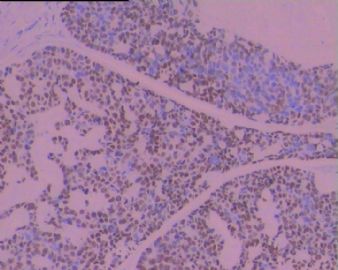
BSCC可呈多向分化,主要成分BSCC,部分可呈双向或多向分化,如含有小细胞癌样、腺癌或经典型鳞癌等。
Histopathology. 2000 Apr;36(4):331-40.
Cho KJ, Jang JJ, Lee SS, Zo JI.
Abstract
AIMS: Basaloid squamous carcinoma (BSC) is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma, with its prevalent sites being the hypopharynx, tongue base and larynx. In the oesophagus, BSC is rarer than in the head and neck region. This study was aimed to document the clinicopathological features of BSCs of the oesophagus, and to present their relative incidence and immunohistochemical findings. METHODS AND RESULTS: Eighteen cases of BSC of the oesophagus, comprising 3.6% of 502 oesophageal carcinomas, were reviewed for their pathological and clinical features, and examined for the immunohistochemical expression of neuroendocrine markers, cytokeratins, p53, pRb and bcl-2. Oesophageal basaloid squamous carcinomas tended to be biphasic or multiphasic carcinomas, most commonly with basaloid and squamous components (eight cases), or with additional adenocarcinoma (three cases) or with small cell carcinoma (two cases). Each component was microscopically clearly distinguishable from the others, and metastasized separately, chiefly the basaloid component. The remaining five cases were apparently pure basaloid carcinomas, being characterized by lobules and nests of monotonous round undifferentiated cells with frequent comedo necrosis. They resembled, but were differentiated from, the small cell carcinoma on the basis of neuroendocrine markers and cytokeratin expression. p53, pRb and bcl-2 oncoprotein, which are known to normally present in the basal/parabasal cells of the oesophageal epithelium, were detected in 40-50% of cases, with a heterogeneous expression pattern. The patients were all male, with the age ranging 47-74 years (median 57) and presented at variable stages. The plotted 3 years survival rate was 51%, and the immunohistochemical expression of p53, pRb and bcl-2 was not related to the survival of the patients. CONCLUSION: Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the oesophagus is a peculiar neoplasm with a capacity of multidirectional differentiation, often with heterogeneous oncogene expression, probably reflecting the pluripotential stem cell origin.

- 王军臣
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-05-06 12:11:00 编辑
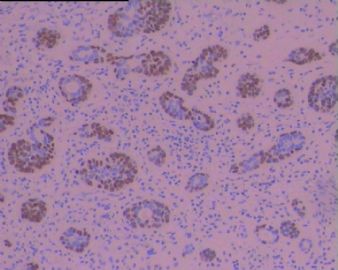
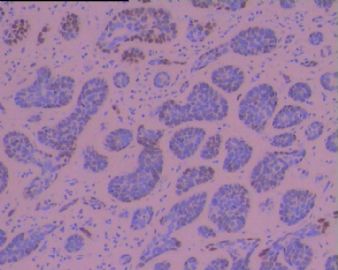
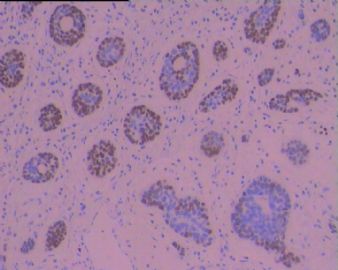
研究上消化道BSCC、ACC和黏液表皮样癌中CK系列的不同表达。BSCC中检测到阳性表达的是:CK14,、CK17 和CK19;.ACC表达CK8、CK14 和 CK17;黏液表皮样癌表达CK8、CK14、CK17 和CK19。
BSCC表达E-cadherin比ACC和黏液表皮样癌表达的少;而P53在BSCC比后两种癌表达率高。
Anticancer Res. 2000 Mar-Apr;20(2B):1205-11.
Tsubochi H, Suzuki T, Suzuki S, Ohashi Y, Ishibashi S, Moriya T, Fujimura S, Sasano H.
Department of Pathology, Tohoku University School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan. tsubochi@patholo2.med.tohoku.ac.jp
Abstract
Non-squamous cell carcinoma is a rare but distinct neoplasm of the upper aerodigestive tract. Among these carcinomas, basaloid-squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) has frequently been confused with adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) and mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. In this study, we examined immunohistochemically the expression of differentiation-related substances, including cytokeratin (CK) subtypes, p53 and p27, and cell adhesion-related molecules E-cadherin and alpha-catenin to clarify the biological features of these neoplasms. We studied seven cases of BSCC of the oesophagus, five cases of ACC and seven cases of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus and trachea were also studied for comparison. Among the cytokeratin subtypes examined, CK14, CK17 and CK19 immunoreactivity was detected in BSCC. ACC and mucoepidermoid carcinoma were immunopositive for CK8, CK14 and CK17 and for CK8, CK14, CK17 and CK19, respectively. These findings suggest that CK subtypes, especially CK8, CK14 and CK17, are useful in differentiating these malignancies. BSCC was more frequently associated with decreased E-cadherin and alpha-catenin immunoreactivity than ACC and mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Nuclear p53 immunoreactivity was detected more frequently in BSCC (5 out of 7) than in ACC (2 out of 5) and mucoepidermoid carcinoma (4 out of 7). There were no significant differences in p27 immunoreactivity among these carcinomas. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) immunoreactivity was detected in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (2 out of 7), SCC (8 out of 11) and adenocarcinoma (9 out of 9), but it was not detected in BSCC (7) or ACC (5). Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) immunoreactivity was detected only in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (4 out of 7) and adenocarcinoma, but not in BSCC, ACC, or SCC. These findings indicate that BSCC, ACC and mucoepidermoid carcinoma are distinct neoplasms arising in the upper aerodigestive tract. In addition, decreased expression of E-cadherin and alpha-catenin proteins and increased p53 expression in BSCC may be correlated with aggressive behaviour.

- 王军臣
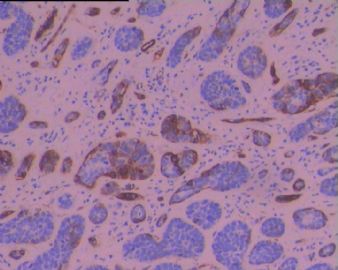
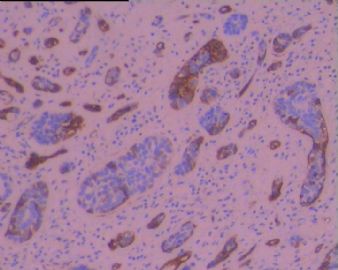
个例报道食管BSCC在组织学上显示伴有ACC样和小细胞癌样分化,应与之鉴别。IHC标记显示肿瘤细胞AE1/AE3+和CAM 5.2+,在癌巢周边的细胞显示 laminin+.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001 May;16(5):586-90.
Basaloid-squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: diagnosis based on immunohistochemical analysis.
Nishimura W, Naomoto Y, Hamaya K, Toda S, Miyagi K, Tanaka N.
Department of Surgery, Akaiwa-Gun Ishikai Hospital, Okayama, Japan. wakuwaku@dd.iij4u.or.jp
Abstract
Basaloid-squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (BSCC) is an extremely rare tumor. Histologically, this tumor should be differentiated from adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) and small cell undifferentiated carcinoma (SCUC). Biologically, this tumor is very aggressive, with a propensity for distant metastasis. We report a 64-year-old male with esophageal BSCC. The patient complained of dysphagia and was found to have a torous lesion in the esophagus on radiological examination. Upper gastrointestinal fiberscopy showed a localized ulcerative type tumor, which was diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on biopsy. Surgery resulted in curative resection. A histological examination of the resected tumor showed features of BSCC. Immunohistochemical examination demonstrated AE3/1- and CAM 5.2-positive tumor cells, and laminin-positive cells in the periphery of the nests. These data were useful in differentiating this tumor from ACC and SCUC. Six months after surgery, the patient developed hepatic metastases, which were successfully treated by regional chemotherapy via the hepatic artery by using fluorouracil. The patient is currently being followed up at the outpatient clinic and shows no signs of any recurrence.

- 王军臣
| 以下是引用海上明月在2010-5-6 0:07:00的发言:
BSCC可呈多向分化,主要成分BSCC,部分可呈双向或多向分化,如含有小细胞癌样、腺癌或经典型鳞癌等。 Histopathology. 2000 Apr;36(4):331-40. Cho KJ, Jang JJ, Lee SS, Zo JI. Abstract AIMS: Basaloid squamous carcinoma (BSC) is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma, with its prevalent sites being the hypopharynx, tongue base and larynx. In the oesophagus, BSC is rarer than in the head and neck region. This study was aimed to document the clinicopathological features of BSCs of the oesophagus, and to present their relative incidence and immunohistochemical findings. METHODS AND RESULTS: Eighteen cases of BSC of the oesophagus, comprising 3.6% of 502 oesophageal carcinomas, were reviewed for their pathological and clinical features, and examined for the immunohistochemical expression of neuroendocrine markers, cytokeratins, p53, pRb and bcl-2. Oesophageal basaloid squamous carcinomas tended to be biphasic or multiphasic carcinomas, most commonly with basaloid and squamous components (eight cases), or with additional adenocarcinoma (three cases) or with small cell carcinoma (two cases). Each component was microscopically clearly distinguishable from the others, and metastasized separately, chiefly the basaloid component. The remaining five cases were apparently pure basaloid carcinomas, being characterized by lobules and nests of monotonous round undifferentiated cells with frequent comedo necrosis. They resembled, but were differentiated from, the small cell carcinoma on the basis of neuroendocrine markers and cytokeratin expression. p53, pRb and bcl-2 oncoprotein, which are known to normally present in the basal/parabasal cells of the oesophageal epithelium, were detected in 40-50% of cases, with a heterogeneous expression pattern. The patients were all male, with the age ranging 47-74 years (median 57) and presented at variable stages. The plotted 3 years survival rate was 51%, and the immunohistochemical expression of p53, pRb and bcl-2 was not related to the survival of the patients. CONCLUSION: Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the oesophagus is a peculiar neoplasm with a capacity of multidirectional differentiation, often with heterogeneous oncogene expression, probably reflecting the pluripotential stem cell origin. |
This is a very good reference article. Thank you.
| 以下是引用笃行者在2010-5-5 21:31:00的发言:
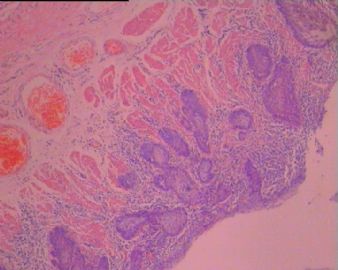
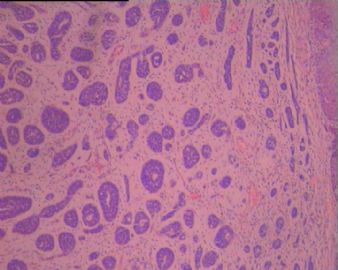
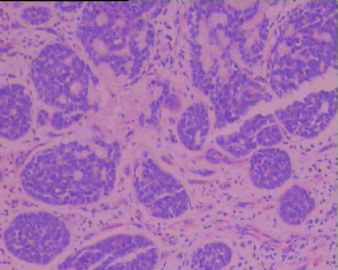
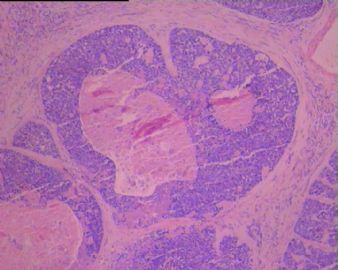
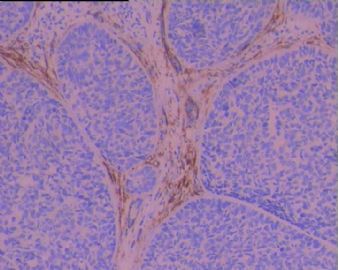
BSCC的形态特征是以基底样细胞构成的小叶状、巢状、筛孔状、条索或小梁状结构,通常在这些细胞巢内可见鳞状分化灶,周边部的基底样细胞核呈栅栏状排列。坏死较常见,表现为单个细胞坏死或较大癌巢中央的粉刺状坏死。也可伴有表面黏膜的鳞状上皮原位癌,在一些病例可见BSCC与表面上皮原位癌直接相移行。有些癌巢内还可见小的假腺腔与腺样囊性癌相似,肿瘤常伴有透明嗜伊红或黏液样间质。 |
Excellent!
BSCC would be very hetergeneous, even focally with neuroendocrine features.
Three histological landmarks are very helpful for daily practice. Classically, it is very BLUE due to high N/C ratio and basaloid featrues, with a central-located COMEDO-LIKE NECROSIS and often a PSEDUO-CLEFT (a narrow empty artifact space) around the peripheral rims of the tumor nests.
个例报道食管基底样鳞癌伴有明显的肌上皮分化,该例中70%的肿瘤成分是典型的基地样型,而另30%为腺样或闰管样成分(上皮与肌上皮分化),镜下有一小部分筛状结构呈典型的ACC形态观,IHC标记内层细胞CK14阳性,外层细胞a-SMA阳性,显示肌上皮分化。
2..Pathol Int. 2002 Apr;52(4):313-7.
Esophageal basaloid carcinoma with marked myoepithelial differentiation.
Hishida T, Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Kato H, Yamaguchi H, Iinuma G.
Clinical Laboratory Division, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Department of Surgery, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
Abstract
A case of esophageal basaloid carcinoma with marked myoepithelial differentiation in a 60-year-old man is reported. The tumor arose as an exophytic mass, measuring 65 x 60 mm, in the middle thoracic esophagus. Approximately two-thirds of the tumor surface was covered with non-cancerous esophageal epithelium. The depth of tumor invasion was limited to the submucosal layer. Histologically, about 70% of the tumor contained a typical basaloid carcinoma component and about 30% contained glandular and intercalated duct-like components with distinct epithelial and myoepithelial differentiation. The tumor presented no component of distinct squamous cell carcinoma, but a small portion of cribriform-like structure, which is typical of adenoid cystic carcinoma, was visible. The inner epithelium composing the intercalated duct-like structure showed immunohistochemical positivity for cytokeratin 14, and the outer epithelium lining adjacent to the stroma showed positivity for alpha-smooth muscle actin. These findings supported epithelial/myoepithelial differentiation. To our knowledge, our case is the first patient with an esophageal basaloid carcinoma showing marked myoepithelial differentiation.

- 王军臣
基底样鳞癌(Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma, BSCC)可伴有或不伴有腺样囊性癌(Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, ACC)的形态。LI等研究239例食管癌中有12例为BSCC。这12例BSCC中,有7例显示有ACC的局部区域,而其他5例才是纯BSCC。免疫组化标记显示,无论是否局部有ACC样的机构均表达一致的CK分子,很少表达(或不表达)S-100和SMA。伴有或不伴有ACC样结构的BSCC在组织学、IHC和超微结构均属高级别鳞癌特征。BSCC尽管内含有 相关的ACC样结构,但BSCC是一种少见的差分化鳞癌,其侵袭性远比ACC大。所以本例局灶出现的腺样结构不应与ACC混淆。
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004 Oct;128(10):1124-30.
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus with or without adenoid cystic features.
Li TJ, Zhang YX, Wen J, Cowan DF, Hart J, Xiao SY.
Abstract CONTEXT: Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) of the esophagus is a rare malignant tumor that morphologically could bear some resemblance to adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) originating from salivary glands. OBJECTIVE:The purpose of this study is to describe the histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural findings of BSCCs of the esophagus, with an emphasis on comparing tumors with or without adenoid cystic features. DESIGN: We reviewed 239 cases of primary esophageal carcinoma and detected 12 cases (5%) of BSCC. The light and electron microscopic findings and immunocytochemical localization of various antigens, including cytokeratins (AE1, AE3), carcinoembryonic antigen, epithelial membrane antigen, S100, smooth muscle actin, and p53, were examined in these BSCC cases. RESULTS: Histologically, all BSCCs were composed of solid lobules or nests of basaloid cells with well-demarcated outlines surrounded by a fibrous stroma. Seven of 12 tumors showed areas of ACC-like features, that is, cribriform-like pseudoglandular lumina formation and hyaline material surrounding the tumor nests, whereas the remaining 5 tumors were apparently pure basaloid carcinomas. These 2 groups of tumors were histologically and immunohistochemically identical in many aspects, namely, high-grade nuclei of the tumor cells with frequent mitoses, abundant comedo-type necrosis, focal areas of concomitant squamous differentiation, consistent immunoreactivity for cytokeratins, and poor or absent staining for S100 and smooth muscle actin. Ultrastructurally, the basaloid tumor cells exhibited relatively undifferentiated cellular characteristics and undeveloped cell organelles. CONCLUSION: Basaloid squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus frequently have an intimate association with ACC-like patterns, but their histologic, immunocytochemical, and ultrastructural features correspond more to poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma than to salivary gland ACC. This distinction is important because genuine ACC is much less aggressive than BSCC.

- 王军臣