| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B26017个 化疗后的乳腺癌病例 (cqz-30)
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 年龄: | ||
| 标本名称: | |||||
| 简要病史: | |||||
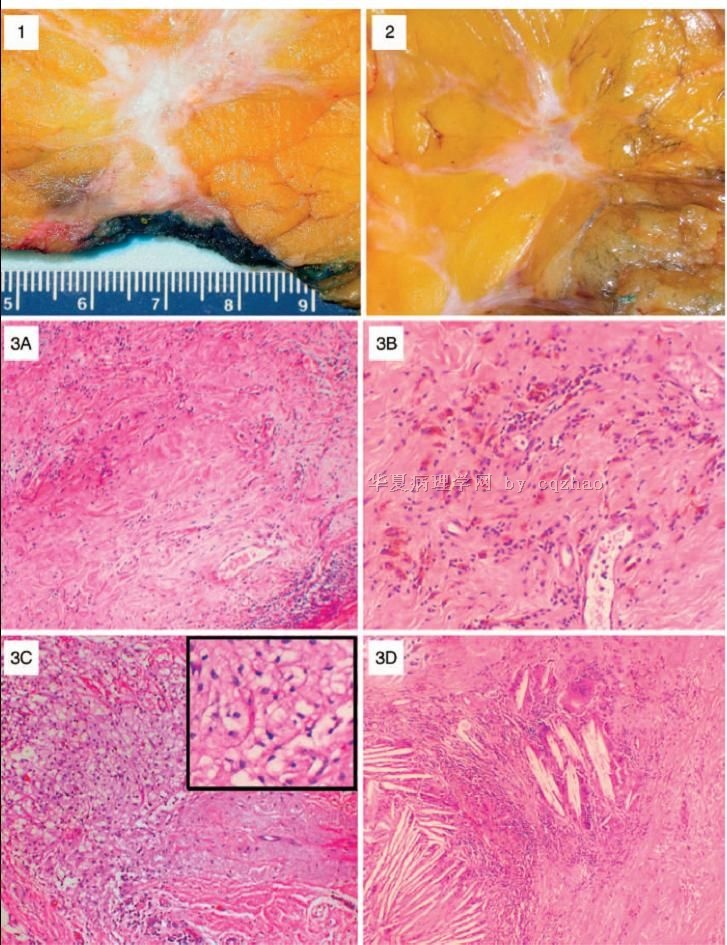
| 肉眼检查: | |||||
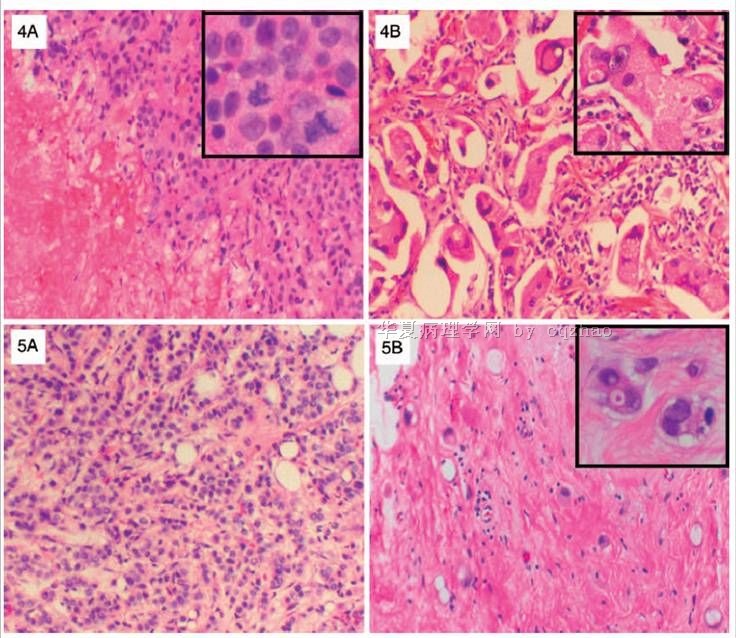
More and more patients accept segmental or total mastectomy after neoadjuvant treatment.
Some patients can obtain complete pathologic response and some do not. The cytomorphology of the tumor cells and benign breast tissue can have some degree of change due to the treatment. Here I show 7 different cases after treatment.
case 1. original invasive lobular carcinoma; now look like ductal ca
case 2. original invasive ductal ca (IDC); now like lobular ca
case 3-5: IDC
case 6. IDC+DCIS
case 7. DCIS
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-03-12 10:55:00 编辑
| 以下是引用笃行者在2010-3-9 22:27:00的发言: 为了验证乳腺癌化疗后肿物缩小的方式,我们做过一些乳腺癌的大切片,为一些肿物较大的乳癌患者新辅助化疗后是否适合做保乳术提供依据。发现化疗只能使肿瘤细胞数目减少,但不能使其范围缩小,除非达到病理CR。 |
I cannot completely agree above.
Often we can see some degree of 乳腺癌化疗后肿物缩小 compared with the size in imaging before the treatment. Of cause some cases do not show the reduced size.
Thank for your sharing your experience.
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-08-03 20:59:00 编辑
Pathol Res Pract. 1997;193(3):187-96.
Morphologic effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer.
Department of Pathology, State University of New York at Stony Brook, USA.
The use of chemotherapy as primary treatment in early and locally advanced breast cancer is rising. As a result, many resected tumors were exposed to cytotoxic drugs in vivo. To study resulting histopathologic changes, we examined 61 patients with locally advanced stage III breast cancer who had been treated with a standardized neoadjuvant polychemotherapy regimen before undergoing surgical resection 3 months later. Matched pairs of pre- and posttherapy breast tissue were evaluated for morphologic changes in the residual malignant and benign breast tissue compartment. A potential correlation between changes and the original p53 immunophenotype was examined as well. In 11 cases (18%), complete pathologic remission with no residual tumor in the mastectomy specimen was achieved. This response was not correlated to the original p53 status. The remaining 50 cases showed residual tumor. The most prominent histologic change was an increase in nuclear atypia of tumor cells (51% of the cases). This effect was independent of the presence or absence of nuclear p53 accumulation in the pre-treatment specimens. Nuclear atypia was frequently accompanied by tumor cell enlargement (in 49% of the cases). Most commonly, a tumor with relatively small cells presented with large epithelioid apocrine features after treatment. In 6 cases (13%), the mitotic rate decreased significantly, while in 12 cases (26%) the mitotic rate increased after chemotherapy. Elston histogrades remained unchanged in 70% of the cases but increased in 17% and decreased in 13%, mainly due to changes in mitotic rates. Extensive tumor cell vacuolization, a common change seen after radiotherapy, was a minor finding but was seen focally. Within the non-malignant compartment, lobular atrophy with hyalinization and minimal epithelial atypia of lobules and ducts were common. We conclude that changes in residual tumor and normal breast are common following systemic cytotoxic therapy. As neoadjuvant chemotherapy becomes mainstream management for locally advanced breast cancer, pathologists are required to recognize treatment induced changes. For correct histopathologic assessment, therapy induced morphologic alterations need to be distinguished from tumor-intrinsic morphologic features
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-08-03 21:00:00 编辑
You can find the chinese article to read
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2009 Nov;31(11):858-62.
[Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on histologic grade and expression of biological markers in breast cancer.]
[Article in Chinese]
Yin HF, Wang YH, Qin XQ, Zhang H, Li T, Ye JM, Liu YH.
Department of Pathology, First Teaching Hospital, Peking University, Beijing 100034, China. Email: yinhf@hotmail.com.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study is to investigate the changes of expression of estrogen receptors (ER), progesterone receptors (PR), Her-2, Ki-67 and histological grade after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. METHODS: Sixty-seven patients with histopathalogically confirmed breast cancer by core needle biopsy received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy was assessed according to the criteria of the Japanese Breast Cancer Society: non-effective (G1), mildly effective (G2), moderately effective (G3), markedly effective (G4) and completely effective (G5). All pathological slides were retrospectively reviewed. Immunohistochemical staining (EnVision method) was used to detect the expression of ER and PR, Her-2 and Ki-67. The pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy status of tumor histological grade, ER and PR, Her-2 and Ki-67 expression in the 49 cases were compared. RESULTS: The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy was assessed in 67 patients. There were 5 cases (7.5%) in G1, 19 in G2 (28.4%), 20 in G3 (29.9%), 17 in G4 (25.4%) and 6 in G5 (9.0%), respectively. PR positive rate was 71.4% after chemotherapy versus 91.8% before chemotherapy, with a statistically significant reduction (P = 0.021). However, the ER and Her-2 expression before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy was stable. Of the patients with invasive ductal carcinoma, 28.6% had histological grade change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and 85.7% of patients decreased one grade. The proportion of histological grade change in the G1, G2, G3, G4 were 0, 5.9%, 41.2% and 54.5%, respectively (P = 0.013). The average rate of Ki-67 expression decreased from 28.3% pre-chemotherapy to 11.0% post-chemotherapy (P = 0.011). After the neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the Ki-67 expression rate decreased by > 10%, > 20%, > 30%, > 40% and > 50% in 3 groups (G1 and G2, group G3, group G4 and G5) showed a tendency to be increased, with a significant difference (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: PR expression in breast cancer decreases after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, while ER and Her-2 expressions remain stable. After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the histological grade and proliferation index are decreased and correlated with the response to chemotherapy. Therefore, histological grade and proliferation index may be effective complementary factors in assessment of the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-08-03 20:59:00 编辑
Best review paper to read. cz
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009 Apr;133(4):633-42.
Pathology of breast carcinomas after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: an overview with recommendations on specimen processing and reporting.
Department of Pathology, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY 40202, USA. sunati.sahoo@louisville.edu
CONTEXT: Currently, more women are being treated with chemotherapy or hormonal agents before surgery (neoadjuvant chemoendocrine therapy) for earlier-stage operable breast carcinoma. The pathologic examination of these specimens can be quite challenging. OBJECTIVE: To give an overview of (1) pathologic changes that occur during treatment, (2) systems for evaluating response to treatment, and (3) recommendations for pathologic examination and reporting of such cases. DATA SOURCES: The recommendations are based on the review of selected literature on breast carcinoma after neoadjuvant therapy and the authors' personal experience with the clinical and pathologic characteristics of cases from each of the authors' own institutions. CONCLUSIONS: Pathologists play a key role in the evaluation of pathologic response, which is extremely important as a prognostic factor for individual patients, as a short-term endpoint for clinical trials, and as an adjunct for research studies. Therefore, surgical pathologists must be familiar with the gross examination, sampling, and reporting of breast carcinomas after neoadjuvant therapy.
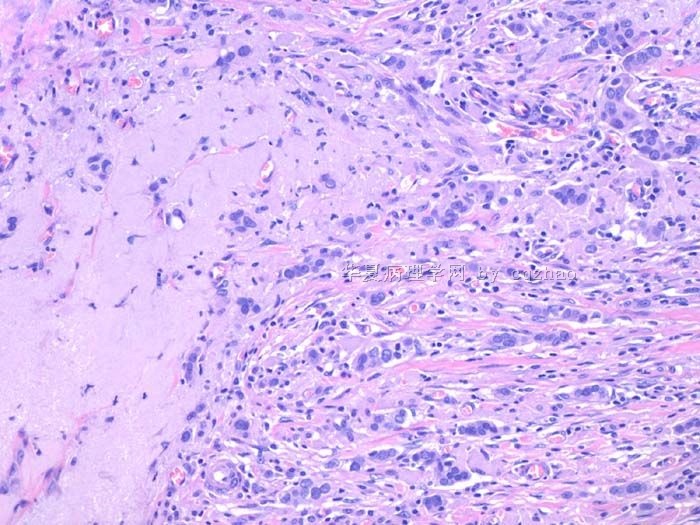
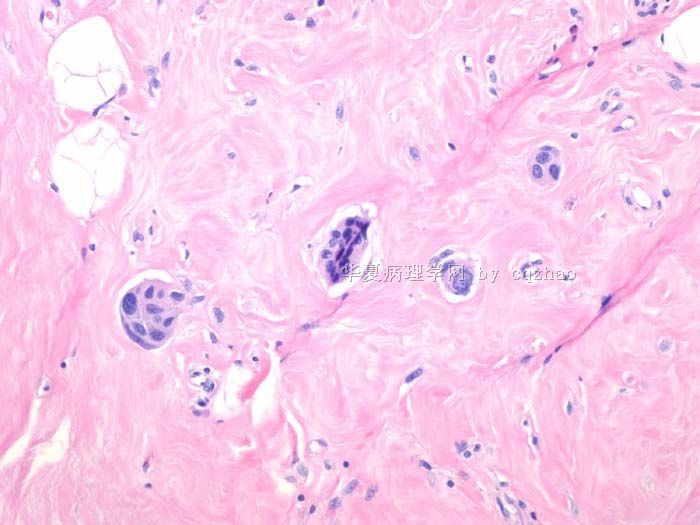
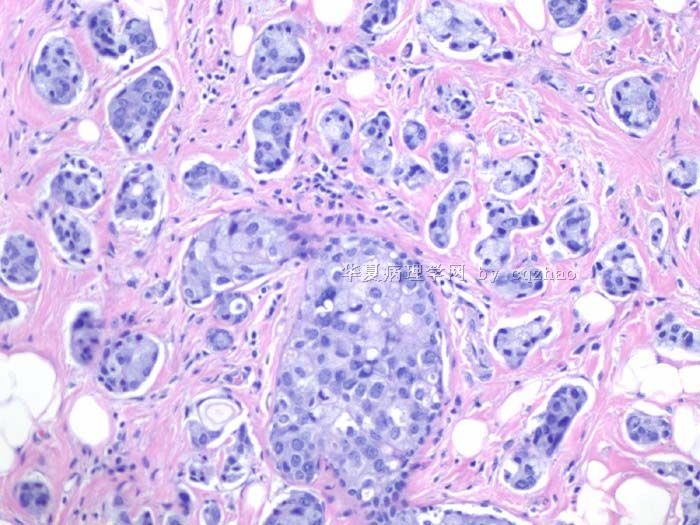
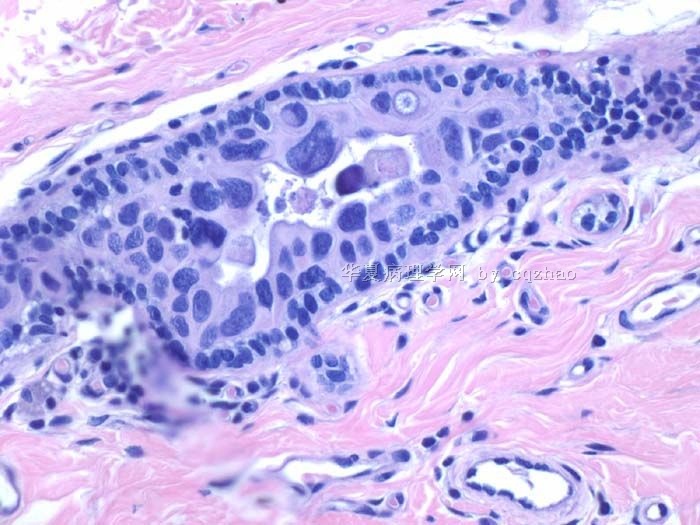
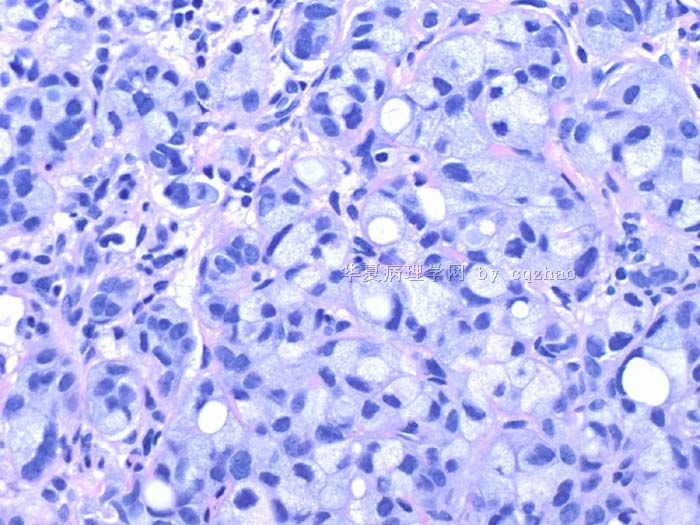

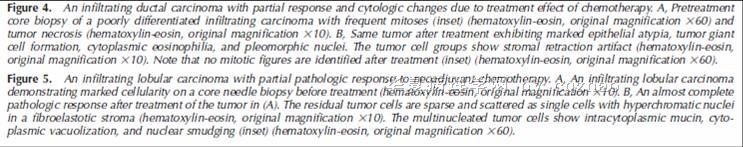
 赵老师的帖子大概就是这个意思。
赵老师的帖子大概就是这个意思。