| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
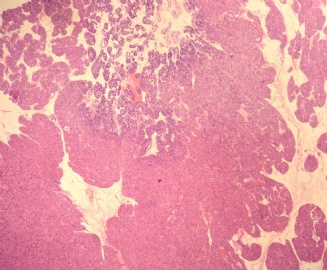
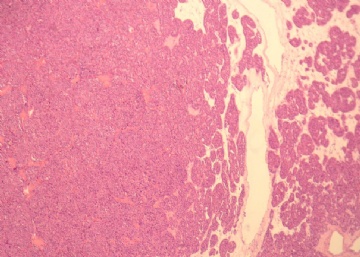
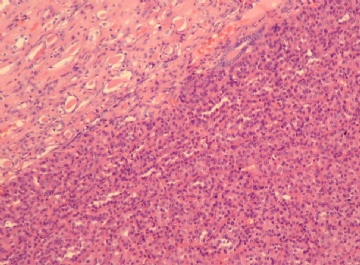
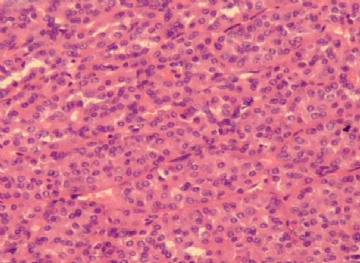
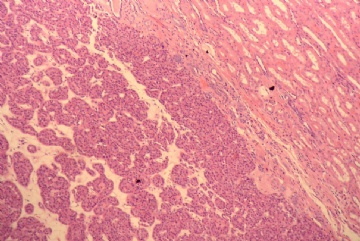
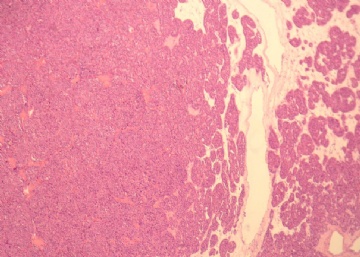
- 右肾下级肿块(6)
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-03-14 20:37:00 编辑
| 以下是引用xljin8在2010-3-14 8:29:00的发言: Rekha PR,
Rajendiran S, Rao S, Shroff S, Joseph LD, Prathiba D. Histological
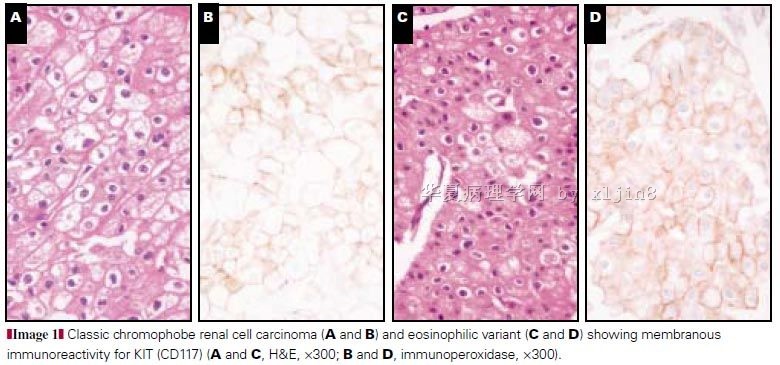
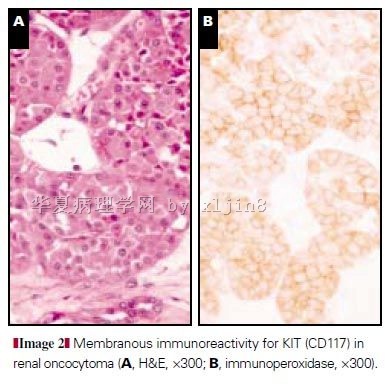
reclassification, histochemical characterization and c-kit 胶体铁染色:嫌色细胞癌和嗜酸性腺瘤均为阳性;CD117 仅嗜酸性腺瘤阳性。 |

- xljin8