| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- B2265请会诊
| 姓 名: | ××× | 性别: | 女 | 年龄: | 41 |
| 标本名称: | 宫颈组织 | ||||
| 简要病史: | 宫颈炎 复查 | ||||
| 肉眼检查: | 小块组织全取 | ||||
相关帖子
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-09-03 22:42:00 编辑
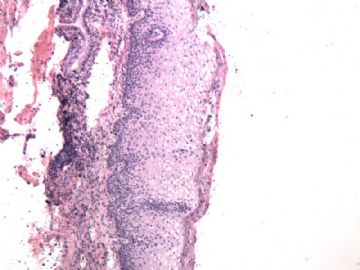
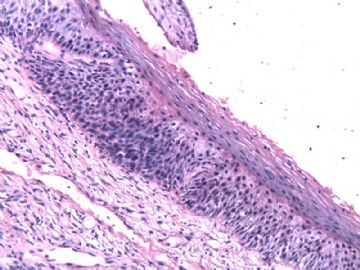
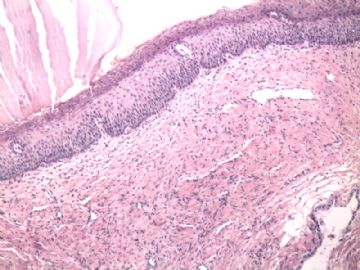
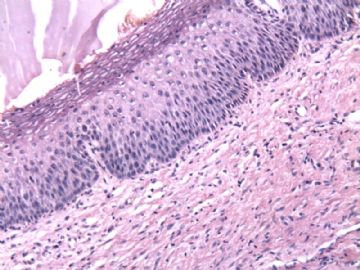
| 以下是引用cqzhao在2010-1-24 21:11:00的发言: For above case, I do not think it is dysplasia or CIN1. it is pseudokoilocytosis in photo 1, parakeratosis and parabasal cell proliferation----reactive change. |
以上本病例,我不认为是异型增生或CIN1。图1是假中空细胞,伴有角化不全和副基底细胞增生——反应性改变。
| 以下是引用cqzhao在2010-1-24 21:03:00的发言:
1.The diagnosis of CIN1 is confusing. 2. Most people consider cervical condylomas a from of CIN1. Most cndylomas are flat, but some can be papillary or exophytic type. 3. The way to make dx of cin1: (forget the trasitional way) Typically, it requires the presenc of superficial nuclear atpia, in other words, it requireds the presence of HPV related koilocytotic atypia. In additional to usual superficial koilocytotic atypia, some CIN1 show cells with dysplastic features similar to those described for high grade dysplasia, but in contract to the latter, such cells are within the lower third of the epithelium. 4. CIN1 is poor reproducibility of diagnosis. A study indicates that less than 50% of CIN1 are classified as CIN1 by a panel. Diagnostic agreement of LSIL in Pap cytology is better than CIN1 in histology. Distinguishing CIN1 from non-specific cellular changes can be problematic. Generally people over diagose CIN1. 5. How to make dx: Step: a). Low power epithelial alterations including epithelial thickness, conspicuous hyperchromasia and halo cinformation contour in upper layers b) High power for major histologic criteria: evaluate density, size and staining of the intermediate and superficial cells. c). Minor criteria: binucleation is present in 90% of CIN1, irregularly shaped cytoplasmic halos. 6. Singnificance: CIN1 is a morphological sign of recent acquired HPV infection. Most cases of CIN1 are caused by high risk HPV, some by low risk HPV. You are wrong if you think that low grade dysplasia is caused by low risk HPV. 7. Without treatment, 1-3% CIN1 can progress to CIN3 or above. 8. Ki67 and p16 or ProEX stains are usful for asissting the dx of CIN2/3, but not CIN1. just for your reference |
1、 CIN1的诊断是令人困惑的;
2、 很多人认为宫颈湿疣是CIN1类型之一。多数湿疣是扁平,但也有部分是乳头状或外生性;
3、 CIN1的诊断方法(忘掉传统方式):
典型表现是出现表层胞核非典型性,换句话说,就是出现HPV相关的中空细胞非典型性;
另外,不同于表层中空细胞非典型性,部分CIN1表现为细胞具有类似于高级别发育不良所见的异型特征,只不过相比于后者,这种异型增生局限于上皮层的下三分之一;
4、 CIN1诊断的可重复性差。一项研究表明,只有不到50%的CIN1被合理分类到CIN1组别中。巴氏细胞中LSIL诊断的一致性高于组织学中CIN1的诊断。
CIN1与非特异性细胞改变的鉴别存在一些问题,通常会过诊CIN1;
5、如何诊断CIN1?步骤如下:
1)低倍镜下看上皮改变,包括上皮厚度、显著深染及表层中空细胞轮廓;
2)高倍镜看主要组织学标准:评估细胞密度、中表层细胞大小和染色情况;
3)次要标准:90%的CIN1会出现双核化,胞质空晕的外形不规则。
6、重要提示:CIN1是新近感染HPV的形态学符号。多数CIN1由高危型HPV感染引起,少数由低危型HPV导致。认为低级别发育不良由低危型HPV感染引起的观点是错误的。
7、不用治疗,只有1-3% 的CIN1能够进展为CIN3或以上病变;
8、Ki67和p16 或ProEX染色对CIN2/3的诊断有帮助,而不是CIN1。
仅供参考。
1.The diagnosis of CIN1 is confusing.
2. Most people consider cervical condylomas a from of CIN1. Most cndylomas are flat, but some can be papillary or exophytic type.
3. The way to make dx of cin1: (forget the trasitional way)
Typically, it requires the presenc of superficial nuclear atpia, in other words, it requireds the presence of HPV related koilocytotic atypia.
In additional to usual superficial koilocytotic atypia, some CIN1 show cells with dysplastic features similar to those described for high grade dysplasia, but in contract to the latter, such cells are within the lower third of the epithelium.
4. CIN1 is poor reproducibility of diagnosis. A study indicates that less than 50% of CIN1 are classified as CIN1 by a panel. Diagnostic agreement of LSIL in Pap cytology is better than CIN1 in histology.
Distinguishing CIN1 from non-specific cellular changes can be problematic.
Generally people over diagose CIN1. 5. How to make dx: Step:
a). Low power epithelial alterations including epithelial thickness, conspicuous hyperchromasia and halo cinformation contour in upper layers
b) High power for major histologic criteria: evaluate density, size and staining of the intermediate and superficial cells.
c). Minor criteria: binucleation is present in 90% of CIN1, irregularly shaped cytoplasmic halos.
6. Singnificance: CIN1 is a morphological sign of recent acquired HPV infection. Most cases of CIN1 are caused by high risk HPV, some by low risk HPV. You are wrong if you think that low grade dysplasia is caused by low risk HPV.
7. Without treatment, 1-3% CIN1 can progress to CIN3 or above.
8. Ki67 and p16 or ProEX stains are usful for asissting the dx of CIN2/3, but not CIN1.
just for your reference