| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
- 31y 宫颈活检1例(P10001)
-
hr_20040218 离线
- 帖子:22
- 粉蓝豆:27
- 经验:27
- 注册时间:2008-08-07
- 加关注 | 发消息
对这个病例简单的说几点个人观点,不对之处请见谅:
1、细胞学或组织学报HSIL基本没有异议;但是现有的活检结果组织学是广泛的CIN2+的病变伴累腺,对这种病人我们重点是要提示临床处理做下锥切或LEEP术下来之后的12点取材(范围要广,一定要看外切缘是否阳性)来排除是否合并微浸润是重点和核心内容。
2、不管是组织学还是细胞学HSIL或LSIL我们都可以不用提示HPV感染(HSIL病变95%左右检测HPV阳性,LSIL超过80%检测HPV阳性——这是单一的HC2检测结果;如果经过多重HPV检测叠加或其他的一些高危HPV目前的水平还没有办法检测算在内,这个数据会更高);因为HPV感染是病因而不是形态学诊断的术语。即使我们看到挖空细胞,其实病变程度在LSIL的时候挖空细胞是最明显的,进展到HSIL或癌的时候反而不明显了。另外低危的HPV感染导致的湿疣性病变的挖空细胞是最明显的,反而高危的HPV感染的挖空细胞不明显。
3、对于形态学的诊断术语(我的老师告诉我的原则):先恶后良和先重后轻。既然我都诊断CIN2+了,对于 HPV感染和慢性宫颈炎其实都可以不用提示了;其实我个人对慢性宫颈炎这个术语很是反感(如果女性做宫颈活检,估计这个诊断会100%存在,我不知道这个诊断的临床意义何在;不知道为什么教科书还有这个诊断呢?也不知道这个诊断给那些“黑医生”赚了多少“黑心钱”?)
以上完全是个人的“胡言乱语”行为,跟不代表宫颈细胞学论坛更不代表华夏病理网。请大家批评指责。

- 掌心0164
| 以下是引用掌心0164在2010-1-11 15:53:00的发言:
对这个病例简单的说几点个人观点,不对之处请见谅: 1、细胞学或组织学报HSIL基本没有异议;但是现有的活检结果组织学是广泛的CIN2+的病变伴累腺,对这种病人我们重点是要提示临床处理做下锥切或LEEP术下来之后的12点取材(范围要广,一定要看外切缘是否阳性)来排除是否合并微浸润是重点和核心内容。 2、不管是组织学还是细胞学HSIL或LSIL我们都可以不用提示HPV感染(HSIL病变95%左右检测HPV阳性,LSIL超过80%检测HPV阳性——这是单一的HC2检测结果;如果经过多重HPV检测叠加或其他的一些高危HPV目前的水平还没有办法检测算在内,这个数据会更高);因为HPV感染是病因而不是形态学诊断的术语。即使我们看到挖空细胞,其实病变程度在LSIL的时候挖空细胞是最明显的,进展到HSIL或癌的时候反而不明显了。另外低危的HPV感染导致的湿疣性病变的挖空细胞是最明显的,反而高危的HPV感染的挖空细胞不明显。 3、对于形态学的诊断术语(我的老师告诉我的原则):先恶后良和先重后轻。既然我都诊断CIN2+了,对于 HPV感染和慢性宫颈炎其实都可以不用提示了;其实我个人对慢性宫颈炎这个术语很是反感(如果女性做宫颈活检,估计这个诊断会100%存在,我不知道这个诊断的临床意义何在;不知道为什么教科书还有这个诊断呢?也不知道这个诊断给那些“黑医生”赚了多少“黑心钱”?) 以上完全是个人的“胡言乱语”行为,跟不代表宫颈细胞学论坛更不代表华夏病理网。请大家批评指责。 |

- 三人行,必有我师焉,择其善者而从之,择其不善者而改之。
| 以下是引用掌心0164在2010-1-11 15:53:00的发言:
对这个病例简单的说几点个人观点,不对之处请见谅: 1、细胞学或组织学报HSIL基本没有异议;但是现有的活检结果组织学是广泛的CIN2+的病变伴累腺,对这种病人我们重点是要提示临床处理做下锥切或LEEP术下来之后的12点取材(范围要广,一定要看外切缘是否阳性)来排除是否合并微浸润是重点和核心内容。 2、不管是组织学还是细胞学HSIL或LSIL我们都可以不用提示HPV感染(HSIL病变95%左右检测HPV阳性,LSIL超过80%检测HPV阳性——这是单一的HC2检测结果;如果经过多重HPV检测叠加或其他的一些高危HPV目前的水平还没有办法检测算在内,这个数据会更高);因为HPV感染是病因而不是形态学诊断的术语。即使我们看到挖空细胞,其实病变程度在LSIL的时候挖空细胞是最明显的,进展到HSIL或癌的时候反而不明显了。另外低危的HPV感染导致的湿疣性病变的挖空细胞是最明显的,反而高危的HPV感染的挖空细胞不明显。 3、对于形态学的诊断术语(我的老师告诉我的原则):先恶后良和先重后轻。既然我都诊断CIN2+了,对于 HPV感染和慢性宫颈炎其实都可以不用提示了;其实我个人对慢性宫颈炎这个术语很是反感(如果女性做宫颈活检,估计这个诊断会100%存在,我不知道这个诊断的临床意义何在;不知道为什么教科书还有这个诊断呢?也不知道这个诊断给那些“黑医生”赚了多少“黑心钱”?) 以上完全是个人的“胡言乱语”行为,跟不代表宫颈细胞学论坛更不代表华夏病理网。请大家批评指责。 |
有不同的观点或认识这样很好,这才是学术,这不是‘胡言乱语’哈,也供我参考学习,谢谢了!


- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。
-
本帖最后由 于 2010-01-11 22:26:00 编辑
有网友提及到与‘不成熟的鳞化’鉴别诊断的问题,这个思路很好。
我们知道ASC-H术语常常与不成熟鳞化及HSIL相关。
为此今天我也抽空复习了一下关于:
不成熟鳞化(immature metaplasia of cervix)
不典型不成熟鳞化(Atypical immature metaplasia of cervix,AIM)
移行细胞化生(Transitional cell metaplasia)
贴图上来与大家分享如下:(图示顺序)
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9
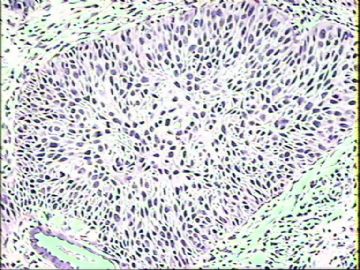
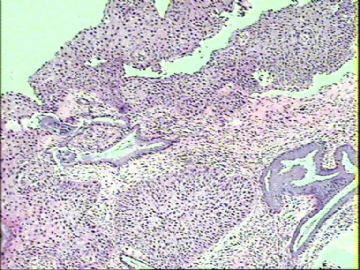
1.
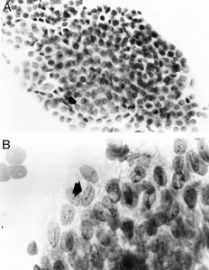
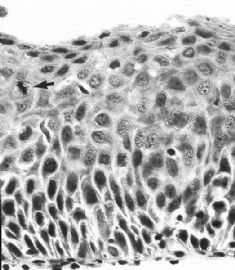
Transitional cell metaplasia. There is a surface layer of umbrellalike cells and a streaming proliferation of elongated nuclei. Note the nuclear grooves (arrow).(Modern Pathology)
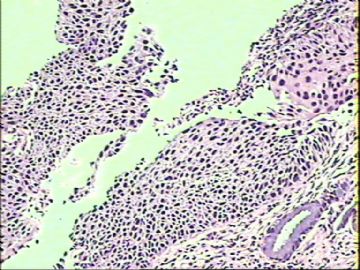
2.
Transitional cell metaplasia. Elongated cells in the basal third of the epithelium showing serotonin immunoreactivity of the cytoplasm.(Modern Pathology)
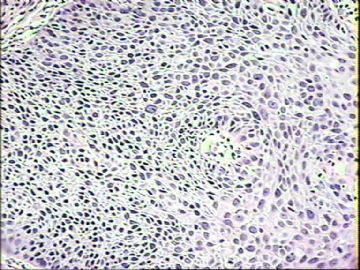
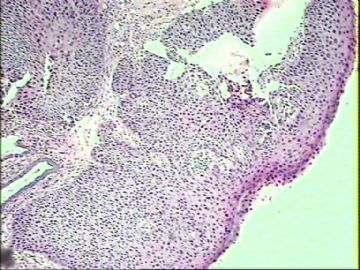
3.
Transitional cell metaplasia. A.a sheet of overlapping cells with round uniform nuclei includes rows of umbrellalike cells (arrow). B.note the nuclear grooves (arrow).(Modern Pathology)
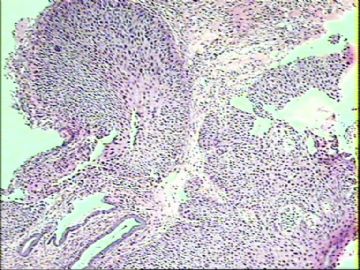
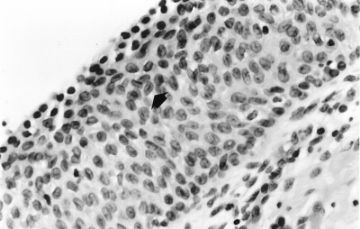
4.
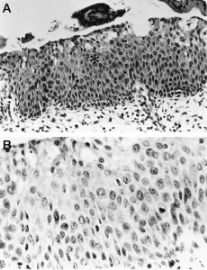
A.atypical immature metaplasia. The squamous metaplastic epithelium showing nuclear atypia, occasional perinuclear halos (asterisk), and a surface layer of mucinous epithelium. B.the hyperplastic epithelium showing a mitotic figure in the basal one third of the epithelium.(Modern Pathology)
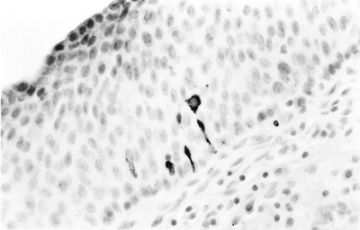
5.
Atypical immature metaplasia. The squamous atypia can mimic a squamous intraepithelial lesion and show koilocytosis.(Modern Pathology)
6.
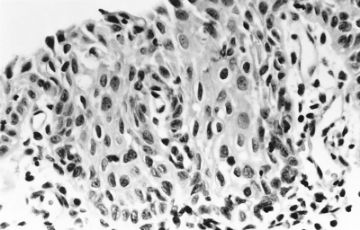
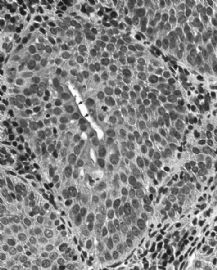
Immature squamous metaplasia (H&E x 400): Proliferation of reserve cells results in a 3-5 cell layer of nonglycogenated metaplastic cells. The remnant columnar cells are at the surface.(ASCCP)
7.
IMMATURE SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA WITH ATYPIA
This figure shows immature squamous metaplasia with nuclear enlargement and mild atypia. So-called atypical immature metaplasia filling endocervical glands may simulate high-grade CIN. In contrast to CIN, the cells are not crowded or disorganized; the nuclei are uniform, round, and many have prominent nucleoli. The presence of
mucinous epithelium overlying the metaplastic epithelium (arrows) is also helpful in distinguishing metaplasia from CIN. Mucinous epithelium rarely overlies CIN. (AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology)
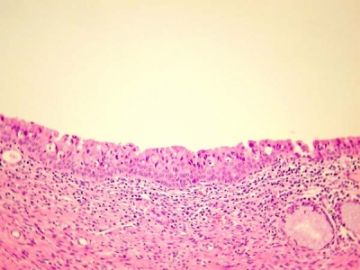
8.IMMATURE SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA
There is increased cellularity in the deep levels and increased mitotic activity (arrow) in this illustration of immature squamous metaplasia. There is retention of polarity, and the cells mature normally as they approach the surface. Chromatin is prominent, but nuclei are uniform. (AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology)
9.
Immature squamous metaplasia (JCP)

- 三十功名尘与土,八千里路云与月。
Agree with the diagnosis and analysis of 26 floor.
Biosy: CIN II with endocervical gland involvement. I don't mention HPV infection because our current understanding is that almost all the cervical dyaplasia is caused by HPV infection. Cervicitis is not an important diagnosis in this case anymore, it doesn't matter you mention it or not. I do mention it when the cervical biopsy doesn't have anything else (no dysplasia).
Pap smear: ASC-H.
The biopsy and pap smear correlate.