| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
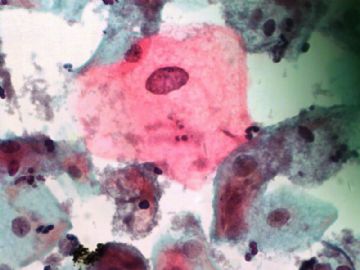
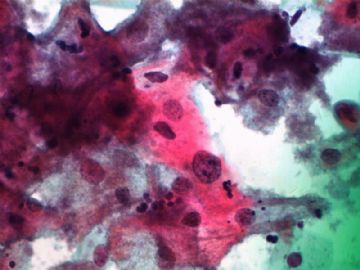
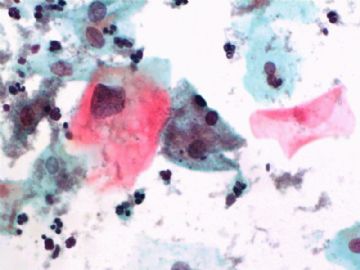
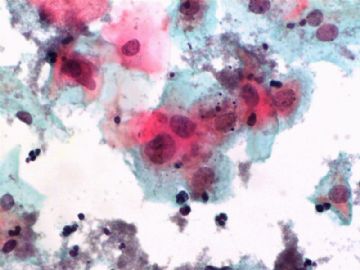
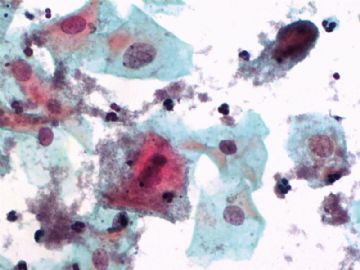
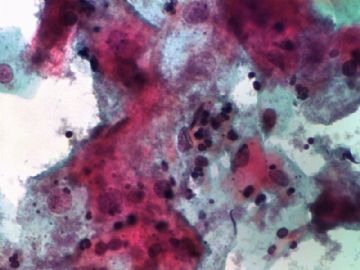
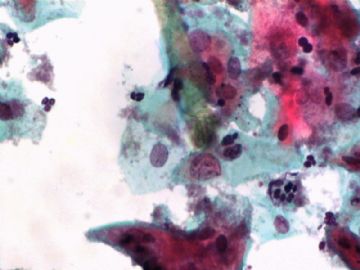
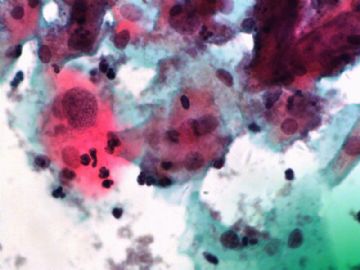
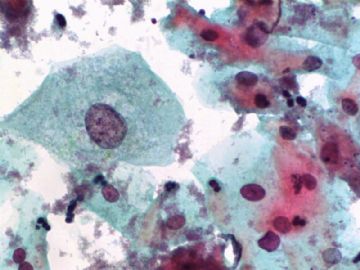
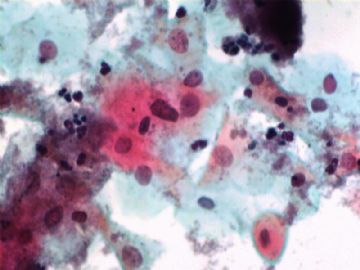
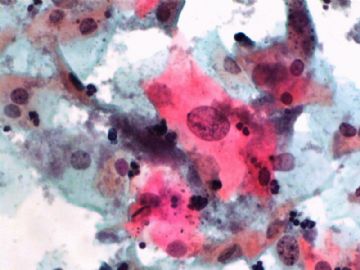
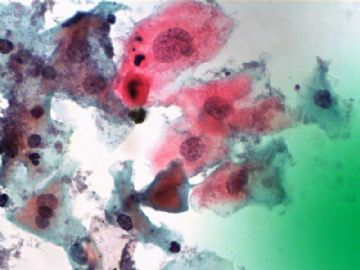
- 一个病例引发的思考......
-
jiangxiaoyu 离线
- 帖子:978
- 粉蓝豆:15
- 经验:1226
- 注册时间:2007-10-31
- 加关注 | 发消息
Agree.
Pap is a screening test. pt with lsil pap can have negative biopsy.
Reasons: 1) not get the lesion by biopsy 2) small lesion regression 3) not a true LSIL in Pap test.
Pathologist is ok even you have over call Pap as LSIL. I think it is reasonable to call LSIL for above case.
The purpose of the biopsy for women with LSIL is to rule out high grade dysplasia or cancer.
Utility of HPV Triage for LSIL Cytology in Women 50 and Older: Efficacy Data From a Large
Amer Heider, R. Marshall Austin, Chengquan Zhao*
* Corresponding author
ABSTRACT
Objective. Recent age-stratified evaluations have supported HPV triage of women with LSIL Paps at age thresholds ranging from over 35 to postmenopausal. We document correlation data on HPV testing and histopathologic follow-up from a large practice serving an older than average population.
Methods. LSIL Pap tests with intermediate/high risk HPV DNA testing over a 34 month period between July 1, 2005 and April 30, 2008 were studied along with follow-up histopathological diagnoses. Patients were stratified into age groups, and tissue diagnoses were correlated with HPV test results.
Results. 1,083 (80.2 %) of a total of 1,351 LSIL samples tested HPV positive. HPV prevalence declined in older age groups. 719 women with LSIL Pap and HPV test results had at least one follow-up cervical biopsy result. 89 of 612 patients with HPV positive LSIL (14.5%) had a follow-up histopathological diagnosis of CIN2/3. Only 4 of 107 patients with HPV negative LSIL (3.7%) had CIN 2/3. When stratified into ages <50 and ≥50, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of HPV testing with LSIL Pap results for CIN 2/3 detection were: sensitivity- 95.7% (<50) vs.100.0% (≥50), specificity- 14.9% (<50) vs. 26.1% (≥50), PPV- 15.0% (<50) vs.11.0% (≥50), and NPV- 95.2% (<50) vs.100.0% (≥50).
Conclusions. In the largest study to document histopathological follow-up of older women with LSIL and HPV test results, no histopathological CIN2/3 diagnoses were identified in patients 50 years and older with HPV negative LSIL. These findings support HPV triage testing for women 50 and older with LSIL results.
Table 3
Age Stratified (10 Year Intervals) Histopathological CIN Diagnoses associated with HPV Positive and HPV Negative LSIL Pap Results
|
Age |
Total |
hrHPV Positive |
hrHPV Negative | ||||||
|
F/U No |
CIN 2/3 (%) |
CIN 1 (%) |
F/U No |
CIN 2/3 (%) |
CIN 1 (%) |
F/U No |
CIN 2/3 (%) |
CIN 1 (%) | |
|
10-19 |
44 |
6 (13.6) |
29 (65.9) |
40 |
6 (15.0) |
26 (65.0) |
4 |
0 (0.0) |
3 (75.0) |
|
20-29 |
234 |
24 (10.3) |
141 (60.3) |
211 |
23 (10.9) |
128 (60.7) |
23 |
1 (4.3) |
13 (56.5) |
|
30-39 |
189 |
31 (16.4) |
94 (49.7) |
164 |
30 (18.3) |
84 (51.2) |
25 |
1 (4.0) |
10 (40.0) |
|
40-49 |
156 |
24 (15.4) |
82 52.6) |
124 |
22* (17.7) |
75 (60.5) |
32 |
2 (6.3) |
7 (21.9) |
|
50-59 |
67 |
3 (4.5) |
40 (59.7) |
48 |
3 (6.3) |
31 (64.6) |
19 |
0 (0.0) |
9 (47.4) |
|
≥60 |
29 |
5 (17.2) |
15 (51.7) |
25 |
5 (20.0) |
13 (52.0) |
4 |
0 (0.0) |
2 (50.0) |
|
Total |
719 |
93 (12.9) |
401 (55.8) |
612 |
89 (14.5) |
357 (58.3) |
107 |
4 (3.7) |
44 (41.1) |
*1 case with CIN 3 and AIS
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-06-26 03:59:00 编辑
|
719 |
93 (12.9) |
401 (55.8) |
From my study you will notice that among 719 women with LSIL pap 12.9% had CIN 2/3 and 55.8% had CIN 1 in the histologic follow up. In other words, more than 30% women with lsil pap did not have cin lesion in the follow up biopsy.
Above is my study. Just sent to a journal to require for publication.
To the best of my knowledge it is the largest study on histologic follow up of LSIL pap with HPV testing.
同意LSIL诊断。 Dr. Zhao has provided the best scientific evidence for cytologic-histologic correlation based his first hand experience. I would like to provide couple supplementary points following his comments. The reasons that lower rate CIN1 detection histologically for patients cytologically diagnosed as LSIL include, but not limited to, the followings:
1) Based on most powerful ALTS study conducted by NIH, up to 91% women with HPV-positive and cytologically LSIL/ASC will spontaneously regress back to normal, probablly due to the self-cleaning mechanism immunologically. Therefore, most of ASC/LSIL women have so-called "transient HPV infection". The molecular basis of this "transient infection" is that HPV is biologically in its "episomal stage" which is not integrated into the host genome. Thus, no or minimal amount of viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, produced. Currently CIN1 is considered by most gynecologic doctors and pathologists as a "HPV infected, but non-neoplastic process" in most women. That is why currently the clinical management on LSIL/CIN1 has been loosen up with annual PAP test follow up only in recent ASCCP guideline.
2) Based on our study in China (SPOCCS) and others, we found that about 50% of CIN2+ lesions were missed by colposcopically guided biopsy. We also found that up to 37% of CIN2+ lesions were detected in those areas read as negative after 冰醋酸. These areas are not biopsied in normal clinical settings. In recent review article by Dr. Mark Schiffman with a title of " Colposcopy at the cross road", he stated that about 55% of CIN2 lesions were missed by routine biopsy by clinicians. It is reasonablly to say that colposcopy-guided biopsy based on acetic white changes is the weakest link in cervical cancer prevention and treatment paradigm.

- 不坠青云之志,长怀赤子之心