| 图片: | |
|---|---|
| 名称: | |
| 描述: | |
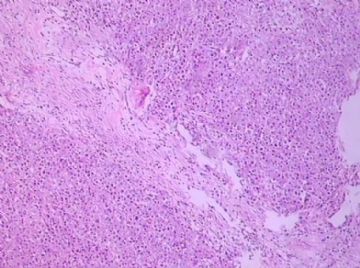
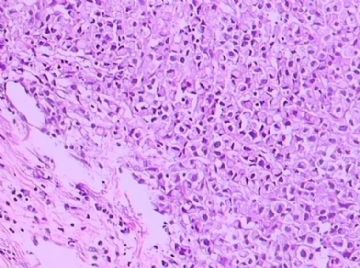
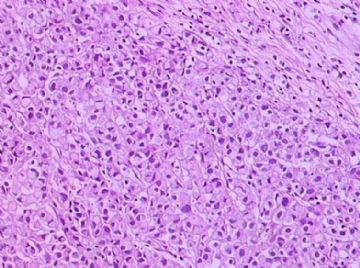
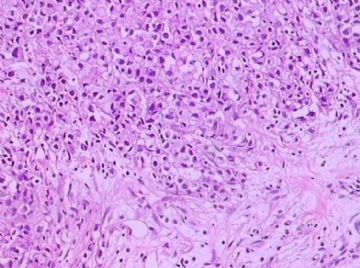
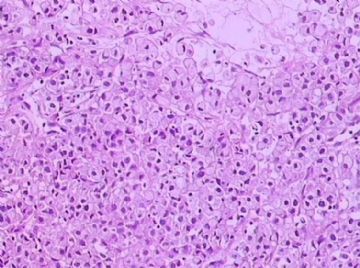
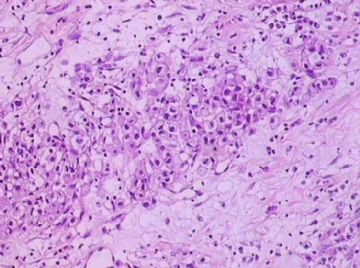
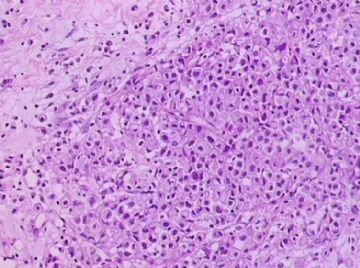
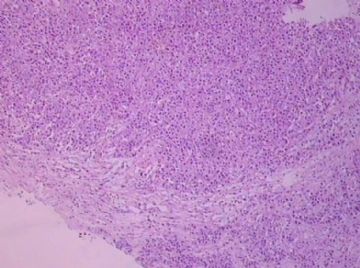
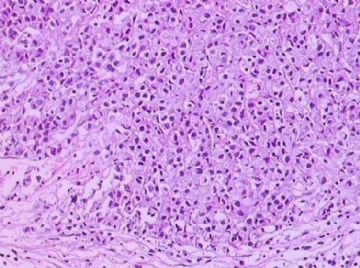
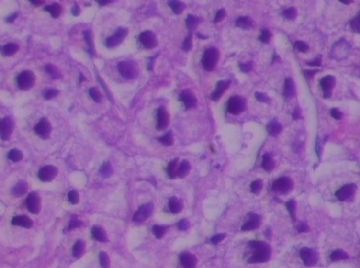
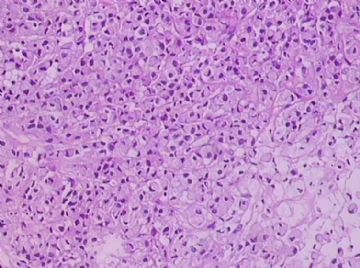
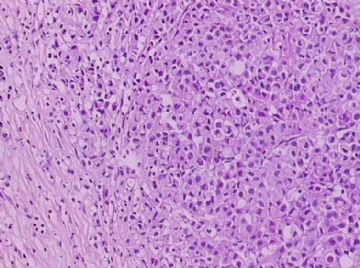
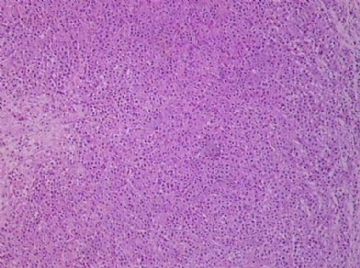
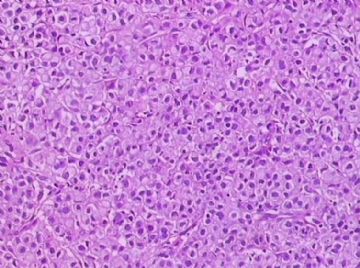
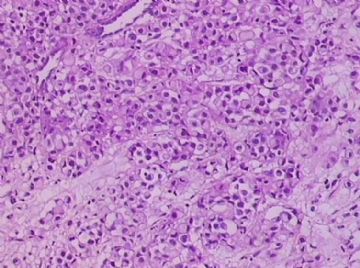
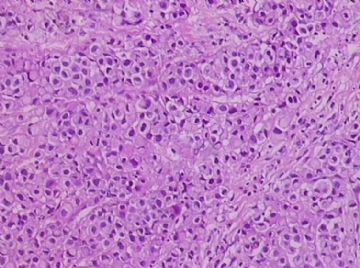
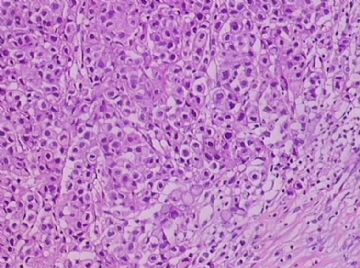
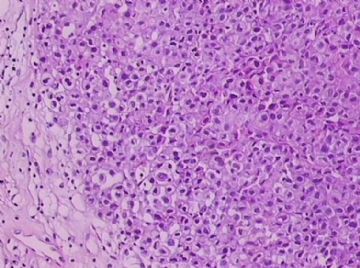
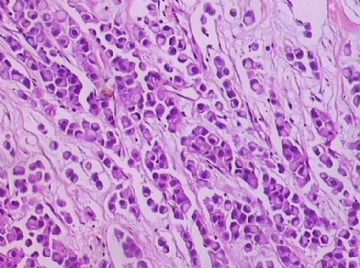
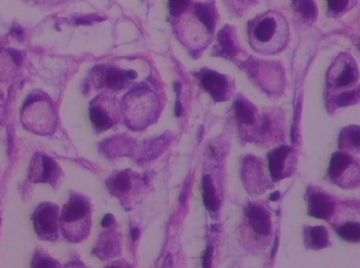
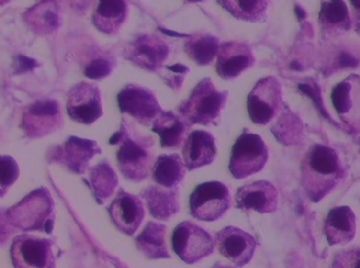
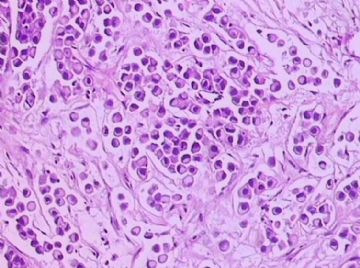
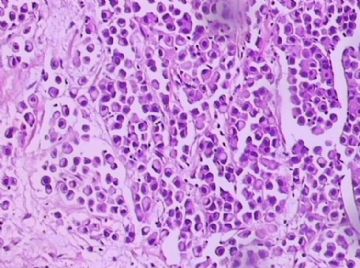
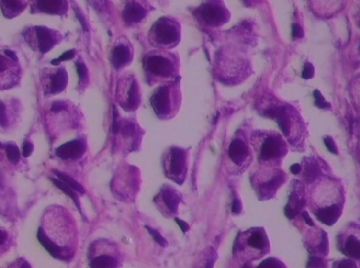
- B1762乳腺印戒细胞癌?
-
zhang197510 离线
- 帖子:409
- 粉蓝豆:2971
- 经验:448
- 注册时间:2009-03-22
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
diandianfei 离线
- 帖子:35
- 粉蓝豆:12
- 经验:40
- 注册时间:2008-10-06
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
zhang197510 离线
- 帖子:409
- 粉蓝豆:2971
- 经验:448
- 注册时间:2009-03-22
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
liziqiang88 离线
- 帖子:957
- 粉蓝豆:262
- 经验:3935
- 注册时间:2007-03-15
- 加关注 | 发消息
-
本帖最后由 于 2009-03-22 21:40:00 编辑
| 以下是引用cqzhao在2009-3-9 20:27:00的发言:
If patients had a breast mass and no any other malignant history we often do not do IHC to rule out GI tumor metast also. We need to consider clinical information for each case. Thank you for your final dx. It is ok for your dx. You also can call "breast lobular carcinoma, signet-ring cell type" if you think it is breast primary. Clinicians often do not know exactly what means signet ring cell carcinoma in breast. |

- 我思故我在! know something about everything,know everything about something.
If patients had a breast mass and no any other malignant history we often do not do IHC to rule out GI tumor metast also. We need to consider clinical information for each case. Thank you for your final dx.
It is ok for your dx. You also can call "breast lobular carcinoma, signet-ring cell type" if you think it is breast primary. Clinicians often do not know exactly what means signet ring cell carcinoma in breast.
Suggestion to our pathology friends.
If you are interested to some subjects and want to know in details, it is better to review some important original articles. The text books often are not enough.
I did a lot of studies in immunostaing. My impression is that IHC can help you, but no any IHC is 100% pos or negative.
-
Mod Pathol. 1993 Sep;6(5):516-20.
-
Signet ring variant of lobular carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study.
Department of Pathology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan.
Signet ring carcinoma of the breast often metastasizes to gastrointestinal tract and female genital tract. We report clinicopathologic features of 10 breast carcinomas with signet ring features, five of which had unusual metastatic patterns. The primary breast tumor in all these cases was lobular carcinoma. Although signet ring cells were prominent in metastatic sites, the primary tumor lacked signet ring cells in two cases. A linitis plastica-like presentation and presence of signet ring cells in gastric metastases raised a strong possibility of primary gastric carcinoma in three cases. The monoclonal antibody to gross cystic disease fluid protein (GCDFP-15) was positive in signet ring cell-rich areas in the primary breast tumor (8/10) and/or in the metastases in all cases. For comparison we studied GCDFP-15 immunoreactivity in 10 infiltrating lobular and 10 infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas with no obvious signet ring cells, and in 14 signet ring carcinomas from other sites (10 gastric, 2 prostatic, 2 colonic). The gastric, colonic, and one prostatic signet ring carcinoma were nonreactive. One prostatic signet ring carcinoma exhibited focal but unequivocal positivity with GCDFP-15. The cases of this report reinforce the concept that signet ring carcinoma of the breast is usually a variant of lobular carcinoma and not a distinct entity. Signet ring cell predominance in metastases, even in the absence of signet ring cells in the primary tumor, attest to the morpho-functional heterogeneity of lobular carcinoma. GCDFP-15 is a sensitive marker for signet ring breast carcinoma and a very useful adjunct tool in the diagnosis of metastatic signet ring carcinoma of mammary origin